Status code 401
Status code 401
Что делать с ошибкой 401 Unauthorized Error – методы исправления
Ошибка 401 Unauthorized Error – это код состояния HTTP, который означает, что страница, к которой вы пытались получить доступ, не может быть загружена, пока вы не войдете в систему с действительным идентификатором пользователя и паролем.
Если вы только что вошли в систему и получили 401 ошибку авторизации, это означает, что введенные вами учетные данные по какой-то причине недействительны.
Сообщения об ошибках 401 часто настраиваются на каждом веб-сайте индивидуально, особенно если это крупный портал, поэтому имейте в виду, что эта ошибка может проявляться многими способами, из которых самые распространенные:
401 ошибка авторизации отображается внутри окна веб-браузера, как обычная веб-страница. Как и большинство подобных ошибок, вы можете найти их во всех браузерах, работающих в любой операционной системе.
Как исправить ошибку 401
Проверьте на наличие ошибок в URL. Возможно, ошибка 401 Unauthorized возникла, потому что URL-адрес был введен неправильно, или выбранная ссылка указывает на неправильный URL-адрес, предназначенный только для авторизованных пользователей.
Если вы уверены, что URL-адрес действителен, посетите главную страницу веб-сайта и найдите ссылку с надписью «Логин» или «Безопасный доступ». Введите здесь свои учетные данные, а затем повторите попытку.
Если у вас нет учетных данных или вы забыли свои, следуйте инструкциям на веб-сайте для настройки учетной записи или изменения пароля.
Если вам трудно вспоминать свои, храните их в диспетчере паролей, чтобы приходилось помнить только один пароль.
Перезагрузите страницу. Как бы просто это не показалось, закрытия страницы и её повторное открытие может помочь исправить ошибку 401, но только если она вызвана ошибочно загруженной страницей.
Удалите кеш вашего браузера. Возможно, в вашем браузере хранится неверная информация для входа в систему, что нарушает процесс входа и выдает ошибку 401. Очистка кеша устранит все проблемы в этих файлах и даст странице возможность загружать свежие файлы прямо с сервера.
Другие варианты ошибки 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительную информацию об ошибке 401 Unauthorized, например:
| Коды ошибок Microsoft IIS 401 | |
|---|---|
| Ошибка | Объяснение |
| 401,1 | Войти не удалось. |
| 401,2 | Ошибка входа в систему из-за конфигурации сервера. |
| 401,3 | Несанкционированный доступ из-за ACL на ресурс. |
| 401,4 | Авторизация не пройдена фильтром. |
| 401,5 | Авторизация блокирована приложением ISAPI/CGI. |
| 401,501 | Доступ запрещен: слишком много запросов с одного и того же клиентского IP; Ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут предел одновременных запросов. |
| 401,502 | Запрещено: слишком много запросов с одного IP-адреса клиента; Ограничение динамического IP-адреса – достигнут максимальный предел скорости запросов. |
| 401,503 | Отказ в доступе: IP-адрес включен в список запрещенных IP |
| 401,504 | Отказ в доступе: имя хоста включено в список запрещенных |
Ошибки подобные 401
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке: 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found и 408 Request Timeout.
Также существует ряд кодов состояния HTTP на стороне сервера, например, часто встречающийся 500 Internal Server Error.
Forbidden, Unauthorized, or What Else?
How to use HTTP status code in the authorization context? When to use «401 Unauthorized» status code? When to use «403 Forbidden»? Let’s try to clarify.
Andrea Chiarelli
Senior Developer Advocate
Last Updated On: December 20, 2021
Forbidden, Unauthorized, or What Else?
How to use HTTP status code in the authorization context? When to use «401 Unauthorized» status code? When to use «403 Forbidden»? Let’s try to clarify.
Andrea Chiarelli
Senior Developer Advocate
Last Updated On: December 20, 2021
Auth0 Docs
OAuth2 And OpenID Connect: The Professional Guide
As usual, it depends 🙂. It depends on the specific scenario and also on the security level you want to provide. Let’s go a little deeper.
If you prefer, you can watch a video on the same topic:
Web APIs and HTTP Status Codes
Before going into the specific topic, let’s take a quick look at the rationale of HTTP status codes in general. Most Web APIs are inspired by the REST paradigm. Although the vast majority of them don’t actually implement REST, they usually follow a few RESTful conventions when it comes to HTTP status codes.
The basic principle behind these conventions is that a status code returned in a response must make the client aware of what is going on and what the server expects the client to do next. You can fulfill this principle by giving answers to the following questions:
This is a general principle that applies to all the HTTP status codes. For example, if the client receives a 200 OK status code, it knows there was no problem with its request and expects the requested resource representation in the response’s body. If the client receives a 201 Created status code, it knows there was no problem with its request, but the resource representation is not in the response’s body. Similarly, when the client receives a 500 Internal Server Error status code, it knows that this is a problem on the server side, and the client can’t do anything to mitigate it.
In summary, your Web API’s response should provide the client with enough information to realize how it can move forward opportunely.
Let’s consider the case when a client attempts to call a protected API. If the client provides the appropriate credentials (e.g., a valid access token), its request is accepted and processed. What happens when the client has no appropriate credentials? What status code should your API return when a request is not legitimate? What information should it return, and how to guarantee the best security experience?
Fortunately, in the OAuth security context, you have some guidelines. Of course, you can use them even if you don’t use OAuth to secure your API.
«The basic principle behind REST status code conventions is that a status code must make the client aware of what is going on and what the server expects the client to do next»
Tweet This
When to Use 400 Bad Request?
Let’s start with a simple case: a client calls your protected API, omitting a required parameter. In this case, your API should respond with a 400 Bad Request status code. In fact, if that parameter is required, your API can’t even process the client request. The client’s request is malformed.
Your API should return the same status code even when the client provides an unsupported parameter or repeats the same parameter multiple times in its request. In both cases, the client’s request is not as expected and should be refused.
Following the general principle discussed above, the client should be empowered to understand what to do to fix the problem. So, you should add in your response’s body what was wrong with the client’s request. You can provide those details in the format you prefer, such as simple text, XML, JSON, etc. However, using a standard format like the one proposed by the Problem Details for HTTP APIs specifications would be more appropriate to enable uniform problem management across clients.
For example, if your client calls your API with an empty value for the required data parameter, the API could reply with the following response:
When to Use 401 Unauthorized?
Now, let’s assume that the client calls your protected API with a well-formed request but no valid credentials. For example, in the OAuth context, this may fall in one of the following cases:
You have to use the Bearer scheme and provide the realm parameter to indicate the set of resources the API is protecting.
If the client request does not include any access token, demonstrating that it wasn’t aware that the API is protected, the API’s response should not include any other information.
On the other hand, if the client’s request includes an expired access token, the API response could include the reason for the denied access, as shown in the following example:
When to Use 403 Forbidden?
Let’s explore a different case now. Assume, for example, that your client sends a request to modify a document and provides a valid access token to the API. However, that token doesn’t include or imply any permission or scope that allows the client to perform the desired action.
In this case, your API should respond with a 403 Forbidden status code. With this status code, your API tells the client that the credentials it provided (e.g., the access token) are valid, but it needs appropriate privileges to perform the requested action.
To help the client understand what to do next, your API may include what privileges are needed in its response. For example, according to the OAuth2 guidelines, your API may include information about the missing scope to access the protected resource.
Security Considerations
When you plan how to respond to your client’s requests, always keep security in mind.
How to deal with response details
A primary security concern is to avoid providing useful information to potential attackers. In other words, returning detailed information in the API responses to attempts to access protected resources may be a security risk.
In other words, sharing this information can improve the collaboration between the client and the server, according to the basic principle of the REST paradigm. However, the same information may be used by malicious attackers to elaborate their attack strategy.
Since this additional information is optional for both the HTTP specifications and the OAuth2 bearer token guidelines, maybe you should think carefully about sharing it. The basic principle on sharing that additional information should be based on the answer to this question: how would the client behave any differently if provided with more information?
For example, in the case of a response with a 401 Unauthorized status code, does the client’s behavior change when it knows that its token is expired or revoked? In any case, it must request a new token. So, adding that information doesn’t change the client’s behavior.
Don’t let the client know.
Now, assume your client attempts to access a resource that it MUST NOT access at all, for example, because it belongs to another user. What status code should your API return? Should it return a 403 or a 401 status code?
You may be tempted to return a 403 status code anyway. But, actually, you can’t suggest any missing permission because that client has no way to access that resource. So, the 403 status code gives no actual helpful information. You may think that returning a 401 status code makes sense in this case. After all, the resource belongs to another user, so the request should come from a different user.
However, since that resource shouldn’t be reached by the current client, the best option is to hide it. Letting the client (and especially the user behind it) know that resource exists could possibly lead to Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR), an access control vulnerability based on the knowledge of resources you shouldn’t access. Therefore, in these cases, your API should respond with a 404 Not Found status code. This is an option provided by the HTTP specification:
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
For example, this is the strategy adopted by GitHub when you don’t have any permission to access a repository. This approach avoids that an attacker attempts to access the resource again with a slightly different strategy.
How to deal with bad requests
When a client sends a malformed request, you know you should reply with a 400 Bad Request status code. You may be tempted to analyze the request’s correctness before evaluating the client credentials. You shouldn’t do this for a few reasons:
Also, consider that in infrastructures with an API gateway, the client credentials will be evaluated beforehand by the gateway itself, which doesn’t know at all what parameters the API is expecting.
The security measures discussed here must be applied in the production environment. Of course, in the development environment, your API can provide all the information you need to be able to diagnose the causes of an authorization failure.
Recap
Throughout this article, you learned that:
The following cheat sheet summarizes what you learned:
Andrea Chiarelli
Senior Developer Advocate
Andrea Chiarelli
Senior Developer Advocate
More like this
Spring
Spring Boot Authorization Tutorial: Secure an API (Java)
The Confused Developer
ID Token and Access Token: What’s the Difference?
Open Standards
What Are Refresh Tokens and How to Use Them Securely
Follow the conversation
Powered by the Auth0 Community. Sign up now to join the discussion. Community links will open in a new window.
403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses
For a web page that exists, but for which a user does not have sufficient privileges (they are not logged in or do not belong to the proper user group), what is the proper HTTP response to serve?
What I’ve read on each so far isn’t very clear on the difference between the two. What use cases are appropriate for each response?
21 Answers 21
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
There’s a problem with 401 Unauthorized, the HTTP status code for authentication errors. And that’s just it: it’s for authentication, not authorization. Receiving a 401 response is the server telling you, “you aren’t authenticated–either not authenticated at all or authenticated incorrectly–but please reauthenticate and try again.” To help you out, it will always include a WWW-Authenticate header that describes how to authenticate.
This is a response generally returned by your web server, not your web application.
It’s also something very temporary; the server is asking you to try again.
So, for authorization I use the 403 Forbidden response. It’s permanent, it’s tied to my application logic, and it’s a more concrete response than a 401.
Receiving a 403 response is the server telling you, “I’m sorry. I know who you are–I believe who you say you are–but you just don’t have permission to access this resource. Maybe if you ask the system administrator nicely, you’ll get permission. But please don’t bother me again until your predicament changes.”
In summary, a 401 Unauthorized response should be used for missing or bad authentication, and a 403 Forbidden response should be used afterwards, when the user is authenticated but isn’t authorized to perform the requested operation on the given resource.
Another nice pictorial format of how http status codes should be used.
If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it.
From your use case, it appears that the user is not authenticated. I would return 401.
Something the other answers are missing is that it must be understood that Authentication and Authorization in the context of RFC 2616 refers ONLY to the HTTP Authentication protocol of RFC 2617. Authentication by schemes outside of RFC2617 is not supported in HTTP status codes and are not considered when deciding whether to use 401 or 403.
Brief and Terse
Unauthorized indicates that the client is not RFC2617 authenticated and the server is initiating the authentication process. Forbidden indicates either that the client is RFC2617 authenticated and does not have authorization or that the server does not support RFC2617 for the requested resource.
Meaning if you have your own roll-your-own login process and never use HTTP Authentication, 403 is always the proper response and 401 should never be used.
Detailed and In-Depth
The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8).
10.4.4 403 Forbidden The server understood the request but is refusing to fulfil it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated.
The first thing to keep in mind is that «Authentication» and «Authorization» in the context of this document refer specifically to the HTTP Authentication protocols from RFC 2617. They do not refer to any roll-your-own authentication protocols you may have created using login pages, etc. I will use «login» to refer to authentication and authorization by methods other than RFC2617
So the real difference is not what the problem is or even if there is a solution. The difference is what the server expects the client to do next.
401 indicates that the resource can not be provided, but the server is REQUESTING that the client log in through HTTP Authentication and has sent reply headers to initiate the process. Possibly there are authorizations that will permit access to the resource, possibly there are not, but let’s give it a try and see what happens.
Checks are usually done in this order:
UNAUTHORIZED: Status code (401) indicating that the request requires authentication, usually this means user needs to be logged-in (session). User/agent unknown by the server. Can repeat with other credentials. NOTE: This is confusing as this should have been named ‘unauthenticated’ instead of ‘unauthorized’. This can also happen after login if session expired. Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja)
FORBIDDEN: Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but refused to fulfill it. User/agent known by the server but has insufficient credentials. Repeating request will not work, unless credentials changed, which is very unlikely in a short time span. Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja) in the case that revealing the presence of the resource exposes sensitive data or gives an attacker useful information.
NOT FOUND: Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not available. User/agent known but server will not reveal anything about the resource, does as if it does not exist. Repeating will not work. This is a special use of 404 (github does it for example).
As mentioned by @ChrisH there are a few options for redirection 3xx (301, 302, 303, 307 or not redirecting at all and using a 401):
According to RFC 2616 (HTTP/1.1) 403 is sent when:
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead
In other words, if the client CAN get access to the resource by authenticating, 401 should be sent.
Assuming HTTP authentication (WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers) is in use, if authenticating as another user would grant access to the requested resource, then 401 Unauthorized should be returned.
403 Forbidden is used when access to the resource is forbidden to everyone or restricted to a given network or allowed only over SSL, whatever as long as it is no related to HTTP authentication.
If HTTP authentication is not in use and the service has a cookie-based authentication scheme as is the norm nowadays, then a 403 or a 404 should be returned.
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The origin server MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.4) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource. If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.1). If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
The semantics of 403 (and 404) have changed over time. This is from 1999 (RFC 2616):
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead.
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
Thus, a 403 (or a 404) might now mean about anything. Providing new credentials might help. or it might not.
I believe the reason why this has changed is RFC 2616 assumed HTTP authentication would be used when in practice today’s Web apps build custom authentication schemes using for example forms and cookies.
Как быстро исправить ошибку 401 (5 методов)
Страница с ошибкой при обращении к WordPress-сайту всегда вызывает неудобства, вне зависимости от того, ваш это сайт или чужой. Как и в случае со многими другими кодами ответов HTTP, ошибка 401 не содержит детальных данных для диагностики и решения проблемы.
Ошибка 401 может появиться в любом браузере. В большинстве случаев ее легко решить.
В этой статье мы расскажем, что означает 401 ошибка, почему она происходит, и какие методы ее устранения существуют.
Код ошибки 401 – что это?
Коды состояния HTTP 400 возникают в случае проблем с выполнением запросов. В частности, ошибка 401 появляется, когда браузер отказывает вам в доступе к странице, которую вы хотите посетить.
В результате вместо загрузки страниц браузер выведет сообщение об ошибке. Ошибки 401 могут возникать в любом браузере, потому отображаемое сообщение может варьироваться.
К примеру, в Chrome и Edge вы, скорее всего, увидите иконку бумаги с простым сообщением о том, что запрашиваемая страница не отвечает. Вы увидите фразу «HTTP Error 401». Вам будет предложено связаться с владельцем сайта, если ошибка не пропадет:
В иных случаях и в других браузерах вы можете получить менее дружелюбное предупреждение. К примеру, может выводиться пустая страница с сообщением «401 Authorization Required»:
Другие вариации текста:
Эти ошибки часто появляются на сайтах, где требуется вводить данные для входа. В большинстве случаев это означает, что что-то не так с учетными данными. Возможно, браузер перестал считать их действительными.
Эта ошибка похожа на HTTP 403 Forbidden Error, когда доступ к сайту для пользователя запрещен. Однако, в отличие от ошибки 403, сообщение об ошибке 401 указывает, что процесс аутентификации завершился неудачно.
Код ошибки передается через заголовок WWW-Authenticate, который отвечает за определение метода аутентификации, используемого для предоставления доступа к веб-странице или ресурсу.
Что вызывает ошибку 401
Если вы столкнулись с кодом ошибки в кодах 400, вы должны знать, что проблема произошла на стороне клиента (либо на стороне браузера). Случается, что виновником проблемы является браузер, но так бывает не всегда. Об этом мы еще расскажем позже.
Ошибки 401 возникают на ресурсах с ограниченным доступом – к примеру, на страницах, защищенных паролем. Потому можно предположить, что причина проблемы связана с данными аутентификации.
Устаревшие Cookie и кэш браузера
Одной из наиболее распространенных причин возникновения ошибки 401 является то, что кэш и файлы cookie вашего браузера устарели, что не позволяет выполнить авторизацию. Если ваш браузер использует недействительные данные для авторизации (либо вообще их не использует их), сервер отклонит запрос.
Несовместимые плагины
Также бывают ситуации, когда ошибка вызвана несовместимостью плагинов или какими-либо сбоями в них. К примеру, плагин безопасности может ошибочно принять вашу попытку входа за вредоносную активность, а потому будет возвращена ошибка 401 для защиты страницы.
Неверный URL или устаревшая ссылка
Бывает, что источником проблемы является незначительная оплошность. К примеру, был неверно введен URL, ссылка была устаревшей и т.д.
Как исправить ошибку 401 (5 методов)
Теперь, когда мы разобрались с причинами ошибки 401, пришло время обсудить, как ее устранить.
Давайте рассмотрим 5 методов, которые вы можете использовать.
Начнем с самого простого потенциального решения: убедитесь, что вы использовали верный URL. Это может выглядеть банально, но 401 ошибки нередко появляются, если URL-адрес был введен неправильно.
Еще один вариант: ссылка, которую вы использовали для перехода на запрашиваемую страницу, указывает на неправильный URL. К примеру, ссылка устарела, ведет на страницу, которой больше нет (и редиректов не задано).
Стоит тщательно перепроверить URL-адрес, который вы использовали. Если вы набирали адрес самостоятельно, убедитесь, что все написано безошибочно. Если вы переходили по ссылке, убедитесь в том, что она ведет на страницу, к которой вы хотите получить доступ (либо попробуйте перейти на эту страницу непосредственно через сайт).
Кэш браузера предназначен для улучшения процесса взаимодействия с сайтами в сети за счет сокращения времени загрузки страниц. К сожалению, иногда это может вести к нежелательным последствиям.
Как мы уже говорили выше, одной из распространенных причин появления ошибки 401 являются устаревшие или неправильные данные кэша или cookies. Потому, если URL введен верно, следующий шаг – чистка кэша браузера.
В итоге вы удалите любую недействительную информацию, которая хранится локально в вашем браузере и может приводить к прерываниям процесса аутентификации. Аналогично, файлы cookie вашего браузера могут содержать аутентификационные данные, которые нужно обновить.
Если вы пользуетесь Chrome, вам нужно щелкнуть по иконке с меню в правом верхнем углу браузера и выбрать пункт Settings. В разделе «Privacy and security» нажмите «Clear browsing data:»
Далее вводим URL требуемого сайта и очищаем для него данные.
В других браузерах процесс очистки кэша и cookie может отличаться. К примеру, в Firefox нужно щелкать по иконке с библиотекой и выбирать History > Clear Recent History:
Информацию по остальным браузерам вы можете найти в поисковиках.
Еще один метод, который вы можете попробовать для устранения ошибки 401 – это очистка DNS. Эта причина встречается относительно редко, но стоит попробовать и такой подход, особенно если первые два ничего не дали.
Чтобы очистить DNS, перейдите в Windows к меню «Пуск» и там уже введите в строку поиска cmd. Нажмите Enter. Откроется командная строка. Далее вставьте команду ipconfig/flushdns, после чего снова нажмите Enter.
Если вы пользуетесь Mac, вы можете открыть командную строку следующим образом: Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal.
Проблема может возникать и по вине плагинов.
Некоторые плагины, особенно связанные с безопасностью, могут выдавать ошибку 401 при подозрении на вредоносную активность. Также у них могут быть проблемы с совместимостью. Потому лучше всего деактивировать все плагины и посмотреть, будет ли страница работать.
Вы можете деактивировать все плагины разом, перейдя в раздел Plugins > Installed Plugins в консоли WordPress. Выберите все плагины и в меню Bulk Actions задайте Deactivate, после чего щелкните по кнопке Apply:
После этого попробуйте перезагрузить страницу с ошибкой. Если ошибка пропала, вы можете вручную по одному активировать плагины заново, чтобы выявить виновника всех бед.
Далее вы уже можете либо удалить плагин, либо написать его разработчикам, чтобы они предоставили рабочее решение.
Если проблема все еще остается, то в таком случае она может быть связана с ошибками на сервере. А значит, исправить ее будет чуть сложнее.
Как мы уже писали ранее, ответ 401 передается через заголовок WWW-Authenticate, который отображается как “WWW-Authenticate: realm= ”. Он включает в себя строки данных, указывающие на то, какой тип аутентификации требуется для предоставления доступа.
Вам нужно посмотреть, был ли отправлен ответ в WWW-Authenticate, а точнее какая схема аутентификации была использована. По крайней мере, это позволит вам приблизиться на один шаг к решению.
Перейдите на страницу с ошибкой 401 и откройте консоль разработчика в Chrome. Вы можете щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на странице и выбрать Inspect (Ctrl+Shift+J).
Далее перейдите на вкладку Network и перезагрузите страницу. Это позволит сгенерировать список ресурсов. Выберите заголовок Status, чтобы отсортировать таблицу, и найдите код 401:
Выберите данную запись, после чего перейдите на вкладку Headers. В Response Headers найдите заголовок WWW-Authenticate:
Информация, представленная в заголовке ответа, в частности, в схеме аутентификации, даст вам больше сведений о том, что произошло, и укажет на решение. Это позволит вам понять, какой тип аутентификации требуется серверу.
К примеру, в приведенном выше примере мы видим, что схема аутентификации задана как «Basic». Это означает, что запрос аутентификации требует только ID и password. Для получения более подробной информации и инструкций мы рекомендуем обратиться к HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry.
How to Fix a 401 Unauthorized Error
Methods to fix a 401 Unauthorized error
The 401 Unauthorized error is an HTTP status code that means the page you were trying to access cannot be loaded until you first log in with a valid user ID and password.
If you’ve just logged in and received the 401 Unauthorized error, it means that the credentials you entered were invalid for some reason.
401 Unauthorized error messages are often customized by each website, especially very large ones, so keep in mind that this error may present itself in more ways than these common ones:
The 401 Unauthorized error displays inside the web browser window, just as web pages do. Like most errors like these, you can find them in all browsers that run on any operating system.
How to Fix the 401 Unauthorized Error
Check for errors in the URL. It’s possible that the 401 Unauthorized error appeared because the URL was typed incorrectly or the link that was selected points to the wrong URL—one that is for authorized users only.
If you’re sure the URL is valid, visit the website’s main page and look for a link that says Login or Secure Access. Enter your credentials here and then try the page again.
If you don’t have credentials or have forgotten yours, follow the instructions provided on the website for setting up an account or resetting your password.
Do you usually struggle to remember your passwords? Consider keeping them in a password manager so that you only have to remember one password.
Reload the page. As simple as it might seem, closing down the page and reopening it might be enough to fix the 401 error, but only if it’s caused by a misloaded page.
Delete your browser’s cache. There might be invalid login information stored locally in your browser that’s disrupting the login process and throwing the 401 error. Clearing the cache will remove any problems in those files and give the page an opportunity to download fresh files directly from the server.
If you’re sure the page you’re trying to reach shouldn’t need authorization, the 401 Unauthorized error message may be a mistake. At that point, it’s probably best to contact the website owner or other website contact and inform them of the problem.
The web site owner of some websites can be reached via email at webmaster@website.com, replacing website.com with the actual website name. Otherwise, find a Contact page for specific contact instructions.
Other Ways You Might See 401 Errors
Web servers running Microsoft IIS might give more information about the 401 Unauthorized error, such as the following:
| Microsoft IIS 401 Error Codes | |
|---|---|
| Error | Explanation |
| 401.1 | Logon failed. |
| 401.2 | Logon failed due to server configuration. |
| 401.3 | Unauthorized due to ACL on resource. |
| 401.4 | Authorization failed by filter. |
| 401.5 | Authorization failed by ISAPI/CGI application. |
| 401.501 | Access Denied: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Concurrent request rate limit reached. |
| 401.502 | Forbidden: Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction Maximum request rate limit reached. |
| 401.503 | Access Denied: the IP address is included in the Deny list of IP Restriction |
| 401.504 | Access Denied: the host name is included in the Deny list of IP Restriction |
You can learn more about IIS-specific codes on Microsoft’s the HTTP status code in IIS 7 and later versions page.
Errors Like 401 Unauthorized
The following messages are also client-side errors and so are related to the 401 Unauthorized error: 400 Bad Request, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not Found, and 408 Request Timeout.
A number of server-side HTTP status codes also exist, like the often-seen 500 Internal Server Error.
Friendly HTTP 401 Status Code Message?
I’m a developer not a wordsmith and as such I’m stuck.
We have a subscription based site whereby users may well come across our 401 page.
We’ve decided that the IIS 401;2 page needs replacing.
Does anyone have any examples or advise about writing a good non offensive 401 page?
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Through a series of highly sophisticated and complex algorithms, this system has determined that you are not presently authorized to use this system function. It could be that you simply mistyped a password, or, it could be that you are some sort of interplanetary alien-being that has no hands and, thus, cannot type. If I were a gambler, I would bet that a cat (an orange tabby named Sierra or Harley) somehow jumped onto your keyboard and forgot some of the more important pointers from those typing lessons you paid for. Based on the actual error encountered, I would guess that the feline in question simply forgot to place one or both paws on the appropriate home keys before starting. Then again, I suppose it could have been a keyboard error caused by some form of cosmic radiation; this would fit nicely with my interplanetary alien-being theory. If you think this might be the cause, perhaps you could create some sort of underground bunker to help shield yourself from it. I don’t know that it will work, but, you will probably feel better if you try something.
And don’t get me started on all the cool 404 pages out there.
How to Quickly Fix the 401 Unauthorized Error (5 Methods)
Trying to access a WordPress site and being met with an error page is at best inconvenient, whether that site is yours or someone else’s. As with many HTTP response codes, part of what makes a 401 error so frustrating is the lack of information it offers for diagnosing and resolving the issue.
The 401 error can happen with any browser, so it’s a pretty common issue people face. In most cases, this problem is relatively simple and straightforward to fix.
In this post, we’ll explain what 401 error messages are and why they happen. Then, we’ll walk you through five methods you can use to fix them.
Let’s get started!
What is the 401 Error Code?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the error 401 Unauthorized as:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
An Introduction to the 401 Error Code
HTTP 400 status codes are encountered when there is a problem making a request. A 401 error, in particular, happens when your browser denies you access to the page you’re trying to visit.
As a result, instead of loading the web page, the browser will load an error message. 401 errors can happen within any browser so the message appearing may differ.
For example, in Chrome or Edge, you’ll likely see a paper icon along with a simple message telling you that the page in question isn’t working. It will include the phrase “HTTP Error 401” at the bottom, and instruct you to contact the site’s owner if the problem persists:

At other times and in other browsers, you might get a slightly less friendly warning that’s just a blank page with a “401 Authorization Required” message:

Other variations include:
These errors occur on websites that require a login in order to access them. In most cases, it means that something is either wrong with the credentials or with the browser’s ability to read them as valid.
This is similar to HTTP 403 Forbidden Error, in that access isn’t permitted to the user. However, unlike with the 403 error, the 401 error message indicates that the authentication process failed.
The code is sent via the WWW-Authenticate header, which is responsible for identifying the authentication method used for granting access to a web page or resource.
What Causes a 401 Error?
If you encounter an error code in the 400s, you know you’re dealing with a client-side (or browser-side) issue. While the problem may be happening within your browser, however, it doesn’t necessarily always mean that’s the culprit, which we’ll explain in more detail later.
401 errors occur on restricted resources, such as password-protected pages of your WordPress site. So it’s safe to assume that the cause of the problem has something to do with the authentication credentials.
Outdated Browser Cache and Cookies
One of the most common reasons you might experience a 401 error is that your browser’s cache and cookies are out of date, preventing the authorization from successfully going through. If your browser isn’t using the valid authentication credentials (or any at all), the server will reject the request.
Plugin Incompatibility
At other times, this error is caused by a plugin incompatibility or error. For example, a firewall or security plugin can mistake your login attempt as malicious activity, and return a 401 error to protect the page.
Incorrect URL or Outdated Link
It’s also possible that the source of the problem can be attributed to a minor mistake. Common culprits in this category include an incorrectly-typed URL or an outdated link.
How to Fix the 401 Error (5 Methods)
Now that we’ve gone through a bit of background on the 401 error, it’s time to discuss how you can resolve it.
Let’s take a look at five methods you can use:
1. Look for Errors in the URL
We’ll start off with the easiest potential fix: making sure you used the correct URL. This may sound simple, but 401 errors can sometimes appear if the URL wasn’t correctly entered in.
Another possibility is that the link you used to visit the page in question points to the wrong URL. For example, it might be outdated, or leading to a page that no longer exists (and no redirects are in place).
Therefore, it’s worth double-checking the URL you used. If you typed it in yourself, verify that you spelled everything correctly. If you clicked on a link, confirm that it’s pointing to the page you’re trying to access (or try to visit that page directly through the website).
Sign Up For the Newsletter
Want to know how we increased our traffic over 1000%?
Join 20,000+ others who get our weekly newsletter with insider WordPress tips!
2. Clear Your Browser’s Cache
Your browser’s cache is designed to improve your online experience, by reducing page loading times. Unfortunately, sometimes it can also cause unwanted interruptions.
As we mentioned earlier, one of the common causes of the 401 error is outdated or incorrect cache data or cookies. Therefore, if you don’t notice any issues with the page’s URL, the next step is to clear your browser’s cache.
This will clean out any invalid information that’s locally stored in your browser, which could be interrupting the authentication process. Similarly, your browser’s cookies might contain authentication data that simply needs to be refreshed.
If you’re a Google Chrome user, you can do this by clicking on the menu icon in the top-right corner of the browser, and then going to Settings. Under the Privacy and security section, click on Clear browsing data:

A new window will open. Under the Basic tab, make sure all three boxes are selected, and then select Clear data:

This process will look a little different in other browsers. For example, in Mozilla Firefox, you would click on the library icon in the top-right corner of the browser, followed by History > Clear Recent History:

In the panel that opens next, select Everything in the drop-down menu at the top, make sure “Cache” is selected, and then click on the Clear Now button:

If you’re using a different browser, please refer to this guide for clearing the cache
3. Flush Your DNS
Another method you can try to resolve the 401 error is flushing your Domain Name Server (DNS). While this is a rarer issue, it can be a possible cause, so it’s worth giving it a try if the first two solutions don’t work.
Tired of subpar level 1 WordPress hosting support without the answers? Try our world-class support team! Check out our plans

On a Mac, you can do this by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities > Terminal:

4. Deactivate Your WordPress Plugins
The problem causing your 401 error might not be due to your browser. If you’re having trouble accessing your WordPress site, it’s also possible that one or more plugins are to blame.
Some plugins, especially security-focused plugins, are configured to show a 401 error when they suspect suspicious login activity that might indicate an attack. Others might just be suffering from compatibility issues. Therefore, it’s a good idea to deactivate all of your WordPress plugins and see if that resolves the issue.
You can deactivate your plugins all at the same time in your dashboard, by going to Plugins > Installed Plugins. Check the box at the top to select all of them. Then under the Bulk Actions drop-down menu, select Deactivate and click on the Apply button:

After that, try reloading the page that returned the 401 error to see if this has resolved the issue. If it has, you can manually activate each plugin one at a time, in order to determine which one is causing the problem.
Then you can remove that plugin, replace it with a new one, or contact its developer for assistance.
5. Check the WWW-Authenticate Header Response
At this point, if the issue hasn’t been fixed, it may be caused by a server-side problem. This means our last fix will be a bit more involved.
As we saw earlier, the 401 response is sent through the WWW-Authenticate header, which appears as “WWW-Authenticate: realm= ”. It includes ‘challenges’, or strings of data that indicate what type of authentication is required in order for access to be granted.
In a nutshell, you’ll want to check and see if the header response was sent, and more specifically, what authentication scheme was used. At the very least, this can help narrow down the cause of the problem, and bring you one step closer to a solution.
To do this, go to the web page that’s displaying the 401 error, and access the developer console in Chrome. You can right-click on the page and select Inspect, or use Ctrl+Shift+J.
Next, click on the Network tab and reload the page. This will generate a list of resources. Select the Status header to sort the table and locate the 401 status code:

Select that entry, and then click on the Headers tab. Under Response Headers, locate the WWW-Authenticate header:

The information that is present in the response header, particularly the authentication schemes, can give you more information about what’s happening and point you towards a solution. It can help you understand what type of authentication the server is expecting.
For example, in the above example, we can see that the authentication scheme is “Basic”. This means the authentication request should only require an ID and password. For more detailed information and instructions on how to use this information, we recommend referring to the HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry.
Summary
When your browser and server have trouble communicating or authenticating requests, you’re sometimes forced to deal with errors such as the 401 error. While this problem is irritating, the message is usually temporary and fixable.
Here are five methods you can use to fix the 401 error:
Save time, costs and maximize site performance with:
All of that and much more, in one plan with no long-term contracts, assisted migrations, and a 30-day-money-back-guarantee. Check out our plans or talk to sales to find the plan that’s right for you.
Error 401: Unauthorized – No access to the website
Anyone who searches the internet will encounter not only interesting content, but occasionally also error messages. For many, this can be frustrating: Not only can you not visit the requested page, but you also don’t know what the displayed status code actually means. The meaning of the 401 error is quickly clarified, though: You don’t have access rights to the requested page. The source of this error is usually found rather quickly. Here we explain how you can avoid the problem and how this error occurs.
Why wait? Grab your favorite domain name today!
What does status 401 mean?
When you surf the internet, communication takes place between the client (your web browser) and the web server. Using HTTP, the underlying internet protocol, the browser, and client exchange status codes with one another. A large part of these status messages isn’t seen when you’re surfing the net, since as long as everything is running smoothly they aren’t displayed.
The HTTP status codes are divided into groups: The first three groups are those that generally aren’t displayed to you in the browser. All codes in the 100s range describe ongoing requests. The codes 200 to 226 indicate that the browser’s request was successfully performed. The messages given in the 300s, though, refer to redirections. What is displayed to you from time to time, though, are the error messages: All status messages from the 500s range describe errors on the server side. The errors 400 to 499 note problems related to the client.
So with a 401 there is also an HTTP code that indicates an error in the client. In this sense, “client” can have very different meanings for the error message, since it just means the instance of communication with the webserver. This could be the browser, but could also be the router or even the internet provider used to make the connection. In many cases, however, the internet user has caused the error themselves.
Sometimes, instead of “401 Unauthorized” you could also get the message “401 Authorization Required.” Both basically mean that you don’t have permission for the requested website and must log in first. If the webserver runs with Microsoft IIS, even more specific status codes are often displayed:
In the best-case scenario, you land on a specially designed error page that describes directly what you have to do.
How can you correct the 401 error?
In most situations, you can correct the 401 error pretty easily: The affected internet page has a section that is only released following authorization. So to access the desired web page, you need to enter your log-in data in the corresponding area. If you don’t have an account on the website yet, you need to create one and register with it. You will most likely find hyperlinks for this on the start page or in a section of the header. The error page is then displayed if you try to skip such a login step and enter the link to the blocked page directly in your web browser.
This is why you can also get an error message if you follow an external link. If the page hidden behind the link is located in a password-protected area, then it’s highly likely that your browser will display a 401 error. Then, it’s best to either go directly to the home page or try to reach the next-highest level within the folder structure of the website. In the example example.com/folder1/folder2/folder3 you could try out example.com/folder1/folder2 next. Maybe the upstream file is already accessible to you.
In case you’ve generated the error by typing it in your browser, you should check the URL again: You may have swapped just one letter or one digit, and therefore entered the password-protected area.
But the error can even be encountered when you’ve already tried to login. Some websites display the 401 status code if you’ve simply entered the wrong login information. You may have mistyped your password, username, or e-mail address. Go back a page and enter your data once again.
To make mistakes is human: So it can definitely occur that you’ve forgotten your login data. In this case, you have to contact the website operator. This can tell you your username or reset your password. Many websites have an automatic application set up for this. It will send you a link via e-mail where you can create a new password.
If you regularly have trouble remembering your passwords, you should consider using a password manager. This allows you to keep track of even the most complex passwords.
Sometimes, it could be the case that you’ve done everything right: You logged in properly using the correct form, the data entered was correct, and yet you’re still greeted with a 401 error code. It’s probably an error with the server then, which the system has just interpreted as a 401 error. In such situations, which can also occur in the course of other error codes, two solutions have proven themselves as promising in the past:
If you were able to access the page in question in the past and there was no password protection, you can still access the content of the website despite the error by using a small detour. Google creates a cache for websites that internally saves a temporary copy of the site. In the Google search bar, simply enter cache:http://example.com/ and instead of “example.com” and enter the URL in question to access the saved version. This can also be a subpage. A header back informs you of when the copy is from. Remember that you won’t find any current information there, and instead only see the copy of a previous page version. If you want to go further back into the past of the website, you can access the archive of the Wayback Machine. There, you’ll find some decades-old versions of websites.
401 vs. 403: What’s the difference?
The two status codes have very different causes: While 401 means “Authorization Required,” the 403 status message usually contains the addition “Forbidden”: Access is not allowed. As we noted, with the 401 error the system is informing you that you have to log on to view the page. As such, there should be a login for you on a higher level. This is not provided with a 403 error. The website operator forbids access to this area of the website, and offers no possibility to register for it. These pages or directories are for internal use only and shouldn’t be accessed by external internet users.
Error 502 Bad Gateway: Where’s the problem?
HTTP status codes emerge when something isn’t running properly on the internet. In this respect, the 502 Bad Gateway error is no exception. But this familiar error message can be particularly tricky: It’s not actually clear where the source of the problem lies. In the chain of gateways along which internet requests run, the error could occur at a number of different points. This article explains.
HTTP 503 (Service Unavailable): meaning and troubleshooting
It’s very likely that you’ve stumbled on the ‘HTTP Error 503 The service is unavailable’ notification or something similar during your daily browsing. The error message appears whenever a web server can’t display the website that the user is trying to access. There are many reasons for these notifications, just as there are many solutions. It’s your responsibility as the website operator to.
HTTP 400: Bad Request explained
Internet users are often confronted with error messages. HTTP status codes can be especially annoying, and even more so if you don’t understand what they mean. The message ‘HTTP 400 – Bad Request’ is a mystery for many internet users, but luckily it can be solved in most cases. We explain what the error message means and how to fix the error.
HTTP Error “405 Method Not Allowed”: How to solve the problem
HTTP is indispensable as a mediator between the browser and web server: Both communicate with each other using the transmission protocol on the application layer by sending various types of messages. With an HTTP request, for example, the browser can request a resource or return its own data to the server. If one of these HTTP methods doesn’t work, error 405 (Method Not Allowed) occurs. But what.
HTTP 408: how to fix the timeout error
Permanent availability is one of the most important things when it comes to a website. However, even the best technical conditions do not offer a 100% guarantee that a website will constantly run smoothly. Connection errors like HTTP error 408 regularly present websites with minor and major difficulties, especially since the causes are often found on the client side. Our guide looks at the causes.
401 Unauthorized vs 403 Forbidden: Which is the right status code for when the user has not logged in? [duplicate]
After lots of Googling and Stackoverflowing, it still isn’t clear to me because many articles and questions/answers were too general (including 403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses which was not specifically for my use-case).
Question: What’s the proper HTTP Status Code when the user has not logged in and requests to see some pages that should be shown only to logged-in users?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The exact satisfying one-time-for-all answer I found is:
401 Unauthorized
While we know first is authentication (has the user logged-in or not?) and then we will go into authorization (does he have the needed privilege or not?), but here’s the key that makes us mistake:
But isn’t “401 Unauthorized” about authorization, not authentication?
Back when the HTTP spec (RFC 2616) was written, the two words may not have been as widely understood to be distinct. It’s clear from the description and other supporting texts that 401 is about authentication.
So maybe, if we want to rewrite the standards! focusing enough on each words, we may refer to the following table:
It depends on the mechanism you use to perform the login.
The spec for 403 Forbidden says:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
While 401 Unauthorized is not defined in the main HTTP status codes spec but is in the HTTP Authentication spec and says:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
So if you are using WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers as your authentication mechanism, use 401. If you are using any other method, then use 403.
HTTP Status Code 401: What Is the 401 «Unauthorized» Error?
Status Code 401: «Unauthorized» Error
HTTP Status Code 401: «Unauthorized» Error
Usually, this means the user’s login credentials aren’t working. The user entered an incorrect password, or the server doesn’t know who the user is, and is asking them to try and log in again.
You’ll often see this error on membership sites or communities that require a username and password, or some other type of login or authentication. When this happens, giving the client a 401 response is totally fine.
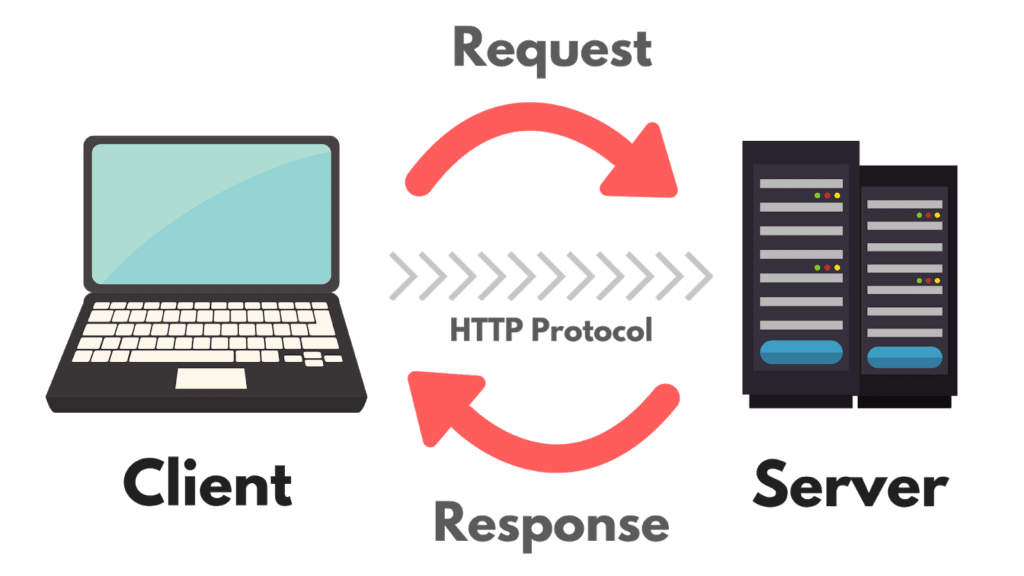
The HTTP Protocol
Let’s talk about how the HTTP protocol works.
At its very foundation, the Internet is made up of two core things: clients and servers.
Any time you click on your browser, you are accessing the Internet through a web client. It may be Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Internet Explorer.
When you visit a website, you are making a request to a web server.
Facebook.com, ClickMinded.com, MarthaStewart.com/1525880/marthas-chocolate-chip-cookies, all of these sites have their own home address. It’s called an IP address.
Your home address might be 123 Main Street, New York, NY 10001, and Facebook’s address happens to be 66.220.144.0.
Whenever you visit a page on the web, you are requesting a whole bunch of documents from that website’s server. Maybe those documents are HTML, CSS, images, a PDF—whatever it is, the basic relationship stays the same: you (the client), make a request, and the website (the server) responds to that request.
The language you are using to make these requests is called the HTTP protocol. These protocols are really just standards that everyone on the web has agreed to. Just like English, Spanish and Chinese are all languages that have an understood protocol, HTTP is just a bunch of standards and an understood protocol.
There are a number of different web protocols out there – and you might be familiar with some of them:
HTTP Status Codes
Now that we understand what the HTTP protocol is, let’s talk about HTTP status codes. Status codes let us know whether the HTTP request was a success, a failure, or something in between.
Let’s take a look at the five core status codes:
Let’s briefly go over each status code block and what they mean.
1xx Status Codes
These are informational requests. The server hasn’t fully completed the request yet and it’s still processing the information. You will not see these codes often. They include:
2xx Status Codes
These are successful requests, which means everything is okay. They include:
3xx Status Codes
These are redirects. These are shown when you request an address, but you are sent somewhere else. These can be good or bad. They include:
4xx Status Codes
These are client errors. That means something went wrong with the request (client/user) and not the response (website/server). They include:
5xx Status Codes
These are server errors. That means something went wrong with the response (website/server) and not the request (client/user). They include:
In Conclusion
Looking for more on a particular status code? We have a series of short guides on every HTTP response, so you can optimize your digital marketing strategy. Grab them here:
What is 401 Unauthorized Error? How to Fix it? (4 Easy Fixes)
Facing 401 Unauthorized Error?
Here’s the fix. But first, listen to this:
Тем не менее, эти неудобства выдерживают и продолжают беспокоить людей даже сегодня.
Но что именно эти коды ошибок появляются из ниоткуда и не объясняют, почему они появились в первую очередь?
Проще говоря, Интернет или Всемирная паутина функционируют на основе прикладного протокола, предназначенного для распределенных и совместных гипермедиа информационных систем, иначе называемых HTTP или протокол передачи гипертекста.
Другими словами, HTTP обеспечивает связь между клиентами и серверами, что позволяет беспрепятственно передавать данные между ними.
Типы ошибок 4xx
Ошибки или коды состояния, начинающиеся с цифры 4, часто относятся к ошибкам клиента. Другими словами, проблемы имеют отношение к клиентским запросам или напрямую связаны с клиентами.
Более того, эти ошибки могут указывать на временную или постоянную ситуацию. Вот несколько примеров 400 кодов ошибок.
Теперь, когда мы лучше понимаем эти надоедливые коды ошибок, пришло время сосредоточиться на 401 и как избавиться от него.
Исправление кода ошибки 401: точка зрения пользователя
Как упоминалось ранее, если вы сталкиваетесь с ошибкой 401, это обычно означает, что вы указали неверные учетные данные для входа, которые сервер не смог распознать.
Тем не менее, что происходит, когда вы фактически предоставляете правильные учетные данные для входа, но сервер по-прежнему предоставляет вам неавторизованное сообщение?
Это указывает на более глубокую проблему, чем простая опечатка. Это означает, что веб-сервер, возможно, не получил ваши учетные данные из-за проблемы с браузером, поэтому он решил немного больше с вами связываться.
Есть несколько способов решить эту проблему, и вот примеры каждого из них.
1. Проверьте URL
2. Проверьте свои учетные данные
3. Очистить историю просмотров и куки
4. Флеш DNS
Исправление ошибки 401: взгляд веб-мастера
Теперь, когда мы рассмотрели, что такое неавторизованная ошибка 401 и как ее исправить на стороне клиента, давайте посмотрим, что могут сделать веб-мастера, чтобы избавиться от этих ошибок.
Откат к предыдущей версии
Влияние ошибок на пользователей
Тем не менее, страница ошибки и сообщение могут быть сделаны интересными и даже интересными, чтобы минимизировать и смягчить разочарование пользователей.
Вот почему разработчики создают собственные страницы для сообщений об ошибках. Например, вы можете изменить метаописания для страниц с ошибками, чтобы предоставить пользователям контекст для этой ошибки, а также инструкции для возможных решений данной проблемы.
But where’s the fun in that? Indeed, a dull message describing a solution to the error may be off-putting, to say the least. That’s why developers oftentimes go a step further to ease the users’ pain.
В любом случае, даже неудобство может стать возможностью изменить ситуацию и превратить разочарование пользователей в не слишком большое разочарование.
Заключение
В конце концов, все сводится к тому, насколько вы креативны и как вы планируете подходить ко всем ошибкам. Ошибки будут существовать независимо от того, как сильно вы пытаетесь их избежать.
Само собой разумеется, что по крайней мере вы можете сделать все возможное, чтобы исправить их, прежде чем пользователи прибегнут к факелам и вилам.
Несанкционированная ошибка 401 встречается довольно часто и в основном является результатом неспособности пользователя терпеливо вводить свои учетные данные для входа. Тем не менее, эта ошибка может произойти и по другим причинам.
Вот почему важно понимать, как подойти к проблеме, а также понять, как правильно ее решить.
401 Unauthorized vs 403 Forbidden: Which is the right status code for when the user has not logged in? [duplicate]
After lots of Googling and Stackoverflowing, it still isn’t clear to me because many articles and questions/answers were too general (including 403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses which was not specifically for my use-case).
Question: What’s the proper HTTP Status Code when the user has not logged in and requests to see some pages that should be shown only to logged-in users?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The exact satisfying one-time-for-all answer I found is:
401 Unauthorized
While we know first is authentication (has the user logged-in or not?) and then we will go into authorization (does he have the needed privilege or not?), but here’s the key that makes us mistake:
But isn’t “401 Unauthorized” about authorization, not authentication?
Back when the HTTP spec (RFC 2616) was written, the two words may not have been as widely understood to be distinct. It’s clear from the description and other supporting texts that 401 is about authentication.
So maybe, if we want to rewrite the standards! focusing enough on each words, we may refer to the following table:
It depends on the mechanism you use to perform the login.
The spec for 403 Forbidden says:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
While 401 Unauthorized is not defined in the main HTTP status codes spec but is in the HTTP Authentication spec and says:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
So if you are using WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers as your authentication mechanism, use 401. If you are using any other method, then use 403.
What causes «HTTP status 401: OK»
I have an ASP.NET Web Service, when I call it occasionally it returns the correct response, other times it is returning the exception The request failed with HTTP status 401: OK. Can someone please provide me with some reasons why this would be occurring? As I can’t seem to find anything on HTTP 401 and a message of OK since 200 is OK and 401 is Unauthorized. Why would my Web Service hosted in IIS6 be returning this?
Here’s the direct exception details:
I will be trying to get a WireShark packet trace for this error when I am provided with it.
Both the client and the Web Service are code that we maintain. The exception only occurs intermittently and not always, the credential details passed through are valid AD user details for an account and IIS site is using Windows Authentication.
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
I have found the cause and have an answer.
Due to the multi-threaded nature of the problem we had it occur very intermittently.
Solution was to write a new proxy class that encompass our auto-generated ws proxy class (from the WSDL) and implementing a SYNCLOCK object over every method within this new proxy class.
The problem also seemed to go away when I was using the server name rather than a DNS name because each separate thread call went on a different TCP pipe.
Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is possible but has failed or not yet been provided.
This means you don’t not have permission for the resource you are trying to access, and that authenticating may make a difference. I don’t think the OK is relavent, though it is unusual. Check the actual Http Status code in Fiddler to be sure.
The request was a legal request, but the server is refusing to respond to it. Unlike a 401 Unauthorized response, authenticating will make no difference.
Is the service on a farm? It could be one server is not configured correctly.
Based on your last comment you should check there are no resource leaks causing the unexpected behaviour. If your using a database make sure you are disposing of disposable objects etc, profile the server to monitor memory use. Consider async services to keep the thread pool free if you have long running requests. Check event logs.
I think I may have seen similar behaviour when IIS can’t handle authenticated traffic, it just bombs out with a 401. I never noticed the OK, but could well occur in this scenario.
Разница между кодами ответов 403 и 401
В чём отличия между этими кодами ответов? Оба говорят об отсутствии прав доступа
4 ответа 4
Если запрос уже включал учетные данные авторизации, то ответ 401 указывает, что авторизация для этих учетных данных была отклонена.
Сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его выполнить.
Код ответа на статус ошибки «HTTP 403 Forbidden» указывает, что сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его авторизовать.
Этот статус похож на 401, но в этом случае повторная аутентификация не будет иметь никакого значения. Доступ запрещен и привязан к логике приложения (например, неверный пароль).
Так же, не запрещено ошибки програмно генерировать и светить не в том случае для которого они предназначены, но как правило эти две используются для перечисленных целей.
Всё ещё ищете ответ? Посмотрите другие вопросы с метками http или задайте свой вопрос.
Похожие
Подписаться на ленту
Для подписки на ленту скопируйте и вставьте эту ссылку в вашу программу для чтения RSS.
Нажимая «Принять все файлы cookie» вы соглашаетесь, что Stack Exchange может хранить файлы cookie на вашем устройстве и раскрывать информацию в соответствии с нашей Политикой в отношении файлов cookie.
Repeated status codes «401» and «200» when using MAPI over HTTP
Symptoms
Cause
MAPI over HTTP uses two client-server sessions, one for change notifications that is opened when Outlook starts, and one for sending/receiving data that is established on demand. The MAPI and HTTP sessions are on different layers. When the «send data» or «receive data» MAPI sessions are established, a new HTTP session is created, and authentication occurs at the beginning of the HTTP session.
The HTTP sessions authentication Request for Comment (RFC) describes the expected protocol sequence. This includes sending an empty authentication request so that the server responds by using the authentication protocols that it supports. This lets the client choose the appropriate authentication type. The repeated «401» and «200» status codes are expected as part of this process.
Workaround
You can disable the automatic proxy setting to reduce the number of HTTP «401» responses. To do this, change or add the following registry value:
Key: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\16.0\Common\Internet\
Value name: EnableHttpAccessTypeAutomaticProxy
Type: REG_DWORD
Value data: 0
After you set this registry value, proxy configuration is handled by Outlook instead of Microsoft Windows HTTP Services (WinHTTP). This enables Outlook to retain the server configuration and pre-authenticate future requests.
What is 401 Unauthorized Error? How to Fix it? (4 Easy Fixes)
Facing 401 Unauthorized Error?
Here’s the fix. But first, listen to this:
Undoubtedly, you’ve come across an error or two while browsing your favorite websites online. These errors are a common nuisance that both webmasters and consumers don’t like to see.
Still, these inconveniences manage to endure and continue to bother people even today.
But what exactly are these error codes that keep popping up out of nowhere and without explaining why they’ve appeared in the first place?
Simply put, the Internet or the World Wide Web functions based on the application protocol designed for distributed and collaborative hypermedia information systems, otherwise known as HTTP or Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
In other words, HTTP enables communication between clients and servers thus allowing seamless transfer of data between the two.
However, when there’s a communication issue somewhere along the way, an error occurs marked as a response status code. The most common errors are the 4xx ones that represent an issue or a problem. With that in mind, let’s focus on the 401 unauthorized error and how to fix it.
Types of 4xx errors
Errors or status codes that start with the number 4 oftentimes refer to client errors. In other words, issues have something to do with client requests or are directly caused by the clients themselves.
What’s more, these errors may indicate if the situation is temporary or permanent. Here are a few examples of 400 error codes.
Now that we have a better understanding of these pesky error codes, it’s time to focus on the 401 one and how to get rid of it.
Fixing the 401 error code: The user perspective
As mentioned before, if you experience the 401 error, it usually means that you’ve provided incorrect login credentials that server couldn’t recognize.
However, what happens when you do, in fact, provide correct login credentials but the server still provides you with an unauthorized message?
This indicates a deeper issue than a simple typo. It means that the web server may not have received your credentials due to browser issue so it decides to mess with you a bit more.
There are a few ways you can try to fix this problem and here are examples of each of them.
1. Check the URL
2. Check your login credentials
3. Clear browsing history and cookies
4. Flush DNS
Fixing the 401 error: The webmaster perspective
Now that we covered what a 401 unauthorized error is and how to fix it from a client-side, let’s have a look at what webmasters can do to get rid of these errors.
Roll back to the previous version
The impact of errors on users
Errors are quite an inconvenience, to put it mildly. They can irritate users and have a major negative impact on their satisfaction and overall experience, even though the error occurred because users made a mistake.
However, an error page and message can be made interesting and even entertaining, in order to minimize and mitigate users’ frustration.
That’s why developers create custom pages for error messages. For instance, you can alter the meta descriptions for error pages to give users context behind the error, as well as instructions to possible solutions to the problem at hand.
But where’s the fun in that? Indeed, a dull message describing a solution to the error may be off-putting, to say the least. That’s why developers oftentimes go a step further to ease the users’ pain.
In any event, even an inconvenience can be an opportunity to turn things around and turn user frustration into not-so-much-frustration.
Conclusion
In the end, it comes down to how creative you are and how you plan to approach the entire error thing. Errors will continue to exist no matter how hard you try to avoid them.
It goes without saying that at least you can do is to do your best to fix them before users resort to torches and pitchforks.
The 401 unauthorized error is quite common and mostly a result of a user’s inability to patiently type in their login credentials. Still, this error can happen for other reasons as well.
That’s why it’s important to understand how to approach the problem, as well as understand how to properly solve it.
HTTP 401 Error vs HTTP 403 Error – Status Code Responses Explained
We’ve covered the 403 (Forbidden) HTTP Error code in some detail before, but it also has a near identical sibling.
So what exactly is the difference between the 401 (Unauthorized) and 403 (Forbidden) status codes? Surely they mean the same thing? Let’s take a closer look!
RFC Standards
The most up to date RFC Standard defining 401 (Unauthorized) is RFC 7235
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The user agent MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field.
Whereas 403 (Forbidden) is most recently defined in RFC 7231
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access.
Common Causes
As mentioned in the previous article, the 403 error can result when a user has logged in but they don’t have sufficient privileges to access the requested resource. For example, a generic user may be attempting to load an ‘admin’ route.
The most obvious time you’d encounter a 401 error, on the other hand, is when you have not logged in at all, or have provided the incorrect password.
These are the two most common causes for this pair of errors.
Less Common Causes
There are some instances where it’s not quite as straightforward as that, though.
403 errors can occur because of restrictions not entirely dependent on the logged in user’s credentials.
For example, a server may have locked down particular resources to only allow access from a predefined range of IP addresses, or may utilize geo-blocking. The latter can be potentially circumvented with a VPN.
401 errors can occur even if the user enters the correct credentials. This is rare, and might be something you only really encounter while developing your own authenticated back ends. But if the authorization header is malformed it will return a 401.
I have run in to this problem myself when testing APIs under development with Postman and forgetting the correct syntax for auth headers!
That’s it
I hope this clears up any confusion surrounding these very similar errors.
If you found this helpful, or wish to challenge or extend anything raised here, feel free to contact me on Twitter @JacksonBates.
Lead Software Engineer and consultant freelancer in Melbourne, Australia. Formerly a teacher. I work at gracepapers.com.au, helping parents juggle their family and work lives!
If you read this far, tweet to the author to show them you care. Tweet a thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
freeCodeCamp is a donor-supported tax-exempt 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization (United States Federal Tax Identification Number: 82-0779546)
Donations to freeCodeCamp go toward our education initiatives, and help pay for servers, services, and staff.
About
Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is possible but has failed or not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource.
The request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field1 containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The user agent MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field2. If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
401 Unauthorized vs 403 Forbidden: Which is the right status code for when the user has not logged in? [duplicate]
After lots of Googling and Stackoverflowing, it still isn’t clear to me because many articles and questions/answers were too general (including 403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses which was not specifically for my use-case).
Question: What’s the proper HTTP Status Code when the user has not logged in and requests to see some pages that should be shown only to logged-in users?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The exact satisfying one-time-for-all answer I found is:
401 Unauthorized
While we know first is authentication (has the user logged-in or not?) and then we will go into authorization (does he have the needed privilege or not?), but here’s the key that makes us mistake:
But isn’t “401 Unauthorized” about authorization, not authentication?
Back when the HTTP spec (RFC 2616) was written, the two words may not have been as widely understood to be distinct. It’s clear from the description and other supporting texts that 401 is about authentication.
So maybe, if we want to rewrite the standards! focusing enough on each words, we may refer to the following table:
It depends on the mechanism you use to perform the login.
The spec for 403 Forbidden says:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
While 401 Unauthorized is not defined in the main HTTP status codes spec but is in the HTTP Authentication spec and says:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
So if you are using WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers as your authentication mechanism, use 401. If you are using any other method, then use 403.
Какой http-код использовать для неавторизованного пользователя, 401 или 403?
В чём разница в http-кодах 401 и 403?
1 ответ
Response c кодом 401 или 403 означает, что клиент не может просмотреть страницу, т.к. недостаточно прав для этого.
Переведём официальную документацию, чтобы понять, какой http-код лучше использовать (401 vs 403).
Код 401 Unauthorized
The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8). If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user SHOULD be presented the entity that was given in the response, since that entity might include relevant diagnostic information. HTTP access authentication is explained in «HTTP Authentication: Basic and Digest Access Authentication».
Для выполнения запроса пользователь должен быть авторизован. Ответ должен включать заголовок с полем «WWW-Authenticate», где через запятую должны быть перечислены параметры, необходимые для авторизации. При ответе с кодом 401 пользователь может повторить свой запрос. Клиент должен выполнить условия авторизации, после чего сделать повторный запрос.
Код 403 Forbidden.
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead.
Сервер понял запрос, но не захотел его выполнять. Нет разрешения на запрос и запрос не должен быть повторён. Сервер должен объяснить клиенту, почему запрос не может быть выполнен (это касается всех методов, кроме HEAD). Если сервер не хочет описывать причину не выполнения запроса клиенту, то сервер должен возвращать http-статус 404 Not Found вместо 403 Forbidden.
Подведём итог, использовать 401 или 403?
Если клиент может получить доступ к странице (например, пройдя авторизацию), то нужно возвращать http-код 401. 401 нужно возвращать при отсутствующей или просроченной авторизации.
Если мы знаем, что доступ к странице для клиента закрыт, не может быть получен, то нужно возвращать http-код 403. Код 403 также следует возвращать, если клиент авторизован, но у него недостаточно прав для просмотра данной страницы.
Т.е. 403 код говорит «Извините, я знаю кто вы (вы авторизованы). Но, к сожалению, у вас нет прав для доступа к данному ресурсу. Возможно, вам нужно обратиться к администратору ресурса за получением разрешений.» Клиенту не имеет смысл повторять запрос.
401 Unauthorized vs 403 Forbidden: Which is the right status code for when the user has not logged in? [duplicate]
After lots of Googling and Stackoverflowing, it still isn’t clear to me because many articles and questions/answers were too general (including 403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses which was not specifically for my use-case).
Question: What’s the proper HTTP Status Code when the user has not logged in and requests to see some pages that should be shown only to logged-in users?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The exact satisfying one-time-for-all answer I found is:
401 Unauthorized
While we know first is authentication (has the user logged-in or not?) and then we will go into authorization (does he have the needed privilege or not?), but here’s the key that makes us mistake:
But isn’t “401 Unauthorized” about authorization, not authentication?
Back when the HTTP spec (RFC 2616) was written, the two words may not have been as widely understood to be distinct. It’s clear from the description and other supporting texts that 401 is about authentication.
So maybe, if we want to rewrite the standards! focusing enough on each words, we may refer to the following table:
It depends on the mechanism you use to perform the login.
The spec for 403 Forbidden says:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
While 401 Unauthorized is not defined in the main HTTP status codes spec but is in the HTTP Authentication spec and says:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
So if you are using WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers as your authentication mechanism, use 401. If you are using any other method, then use 403.
HTTP authentication
HTTP provides a general framework for access control and authentication. This page is an introduction to the HTTP framework for authentication, and shows how to restrict access to your server using the HTTP «Basic» schema.
The general HTTP authentication framework
RFC 7235 defines the HTTP authentication framework, which can be used by a server to challenge a client request, and by a client to provide authentication information.
The challenge and response flow works like this:
The general message flow above is the same for most (if not all) authentication schemes. The actual information in the headers and the way it is encoded does change!
Warning: The «Basic» authentication scheme used in the diagram above sends the credentials encoded but not encrypted. This would be completely insecure unless the exchange was over a secure connection (HTTPS/TLS).
Proxy authentication
The same challenge and response mechanism can be used for proxy authentication. As both resource authentication and proxy authentication can coexist, a different set of headers and status codes is needed. In the case of proxies, the challenging status code is 407 (Proxy Authentication Required), the Proxy-Authenticate response header contains at least one challenge applicable to the proxy, and the Proxy-Authorization request header is used for providing the credentials to the proxy server.
Access forbidden
In all cases, the server may prefer returning a 404 Not Found status code, to hide the existence of the page to a user without adequate privileges or not correctly authenticated.
Authentication of cross-origin images
A potential security hole (that has since been fixed in browsers) was authentication of cross-site images. From Firefox 59 onwards, image resources loaded from different origins to the current document are no longer able to trigger HTTP authentication dialogs (bug 1423146), preventing user credentials being stolen if attackers were able to embed an arbitrary image into a third-party page.
Character encoding of HTTP authentication
Browsers use utf-8 encoding for usernames and passwords.
WWW-Authenticate and Proxy-Authenticate headers
The WWW-Authenticate and Proxy-Authenticate response headers define the authentication method that should be used to gain access to a resource. They must specify which authentication scheme is used, so that the client that wishes to authorize knows how to provide the credentials.
The syntax for these headers is the following:
Here, is the authentication scheme («Basic» is the most common scheme and introduced below). The realm is used to describe the protected area or to indicate the scope of protection. This could be a message like «Access to the staging site» or similar, so that the user knows to which space they are trying to get access to.
Authorization and Proxy-Authorization headers
The Authorization and Proxy-Authorization request headers contain the credentials to authenticate a user agent with a (proxy) server. Here, the is needed again followed by the credentials, which can be encoded or encrypted depending on which authentication scheme is used.
Authentication schemes
The general HTTP authentication framework is the base for a number of authentication schemes.
IANA maintains a list of authentication schemes, but there are other schemes offered by host services, such as Amazon AWS.
Some common authentication schemes include:
Basic
See RFC 7617, base64-encoded credentials. More information below.
Bearer
See RFC 6750, bearer tokens to access OAuth 2.0-protected resources
Digest
See RFC 7616. Firefox 93 and later support the SHA-256 algorithm. Previous versions only support MD5 hashing (not recommended).
HOBA
See RFC 7486, Section 3, HTTP Origin-Bound Authentication, digital-signature-based
Mutual
Negotiate / NTLM
VAPID
SCRAM
AWS4-HMAC-SHA256
See AWS docs. This scheme is used for AWS3 server authentication.
Schemes can differ in security strength and in their availability in client or server software.
The «Basic» authentication scheme offers very poor security, but is widely supported and easy to set up. It is introduced in more detail below.
Basic authentication scheme
The «Basic» HTTP authentication scheme is defined in RFC 7617, which transmits credentials as user ID/password pairs, encoded using base64.
Security of basic authentication
As the user ID and password are passed over the network as clear text (it is base64 encoded, but base64 is a reversible encoding), the basic authentication scheme is not secure. HTTPS/TLS should be used with basic authentication. Without these additional security enhancements, basic authentication should not be used to protect sensitive or valuable information.
Restricting access with Apache and basic authentication
Restricting access with Nginx and basic authentication
Access using credentials in the URL
Many clients also let you avoid the login prompt by using an encoded URL containing the username and the password like this:
Коды ошибок REST API для партнеров
Ошибки в интерфейсах REST API партнеров возвращаются с использованием стандартных кодов состояния HTTP, а также объекта ответа JSON с ошибкой.
Коды состояния HTTP
В представленной ниже таблице перечислены и описаны коды состояния HTTP, которые могут быть возвращены этими интерфейсами.
| Код состояния | Сообщение о состоянии | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| 400 | Ошибка запроса | Не удалось обработать запрос, так как он представлен в неправильном формате или является некорректным. |
| 401 | Не авторизовано | Необходимые данные для проверки подлинности отсутствуют или не являются допустимыми для ресурса. |
| 403 | Запрещено | Отказано в доступе к запрашиваемому ресурсу. Возможно, у пользователя недостаточно разрешений. Внимание! Код состояния HTTP 403; Forbidden error=insufficent_claims может возвращаться, если к ресурсу применены политики условного доступа. Дополнительные сведения о Microsoft Graph и условном доступе см. в статье Руководство разработчика по условному доступу в Azure Active Directory. |
| 404 | Не найдено | Запрашиваемый ресурс не существует. |
| 405 | Метод не разрешен | Метод HTTP в запросе не разрешено использовать для ресурса. |
| 406 | Недопустимо | Эта служба не поддерживает формат, запрашиваемый в заголовке Accept. |
| 409 | Conflict | Текущее состояние конфликтует с ожиданиями запроса. Например, указанная родительская папка не существует. |
| 410 | Потеряно | The requested resource is no longer available at the server. |
| 411 | Требуется длина | В запросе необходимо указать заголовок Content-Length. |
| 412 | Необходимое условие не выполнено | Необходимое условие, указанное в запросе (например, заголовок if-match), не соответствует текущему состоянию ресурса. |
| 413 | Размер запрашиваемой сущности слишком большой | Размер запроса превышает ограничение. |
| 415 | Неподдерживаемый тип носителя | Тип контента запроса не поддерживается службой. |
| 416 | Запрошенный диапазон невыполним | Заданный диапазон байтов недопустим или недоступен. |
| 422 | Необрабатываемый объект | Не удалось обработать запрос, так как он является семантически некорректным. |
| 423 | Заблокировано | Запрашиваемый ресурс заблокирован. |
| 429 | Слишком много запросов | Клиентское приложение было отрегулировано, и ему не следует пытаться повторить запрос, пока не пройдет определенное время. |
| 500 | Внутренняя ошибка сервера | При обработке запроса возникла внутренняя ошибка сервера. |
| 501 | Не реализовано | Запрашиваемая функция не реализована. |
| 503 | Служба недоступна | Служба временно недоступна для обслуживания или перегружена. Вы можете повторить запрос по прошествии времени, которое можно указать в заголовке Retry-After. |
| 504 | Истекло время ожидания шлюза | Сервер, работающий в качестве прокси-сервера, при попытке выполнить запрос не получил своевременный ответ, необходимый для доступа, от сервера, находящегося выше в иерархии. Может возникать вместе с ошибкой 503. |
| 507 | Недостаточно места в хранилище | Достигнута максимальная квота хранилища. |
| 509 | Превышен предел пропускной способности | Приложение было отрегулировано из-за превышения максимальной пропускной способности. Приложение может повторить запрос по прошествии дополнительного времени. |
Ответ об ошибке — это отдельный объект JSON, содержащий одно свойство с именем error. Этот объект содержит все сведения об ошибке. Вы можете использовать возвращаемые в нем данные вместо кода состояния HTTP или вместе с ним. Ниже представлен пример полного текста ошибки JSON.
Тип ресурса ошибки
Ответ об ошибке — это отдельный объект JSON, содержащий одно свойство с именем error. Этот объект содержит все сведения об ошибке. Вы можете использовать возвращаемые в нем данные вместо кода состояния HTTP или вместе с ним. Ниже представлен пример полного текста ошибки JSON.
В приведенных ниже таблице и примере кода описывается схема ответа об ошибке.
| Имя | Тип | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| code | строка | Всегда возвращается. Указывает тип возникшей ошибки. Не принимает значение null. |
| message | строка | Всегда возвращается. Содержит подробное описание ошибки и дополнительные сведения для отладки. Не принимает значение null, не может быть пустым. Максимальная длина: 1024 символа. |
| innerError | объект | Необязательный элемент. Дополнительный объект ошибки, который может быть более подробным, чем ошибка верхнего уровня. |
| target | строка | Целевой объект, в котором возникла ошибка. |
Свойство Code
Свойство code содержит одно из перечисленных ниже возможных значений. Приложения должны быть готовы к обработке любой из этих ошибок.
| Код | Описание |
|---|---|
| accessDenied | У вызывающей стороны нет разрешения на выполнение действия. |
| generalException | Возникла неопределенная ошибка. |
| InvalidRequest | Запрос представлен в неправильном формате или является некорректным. |
| itemNotFound | Ресурс не найден. |
| preconditionFailed | Необходимое условие, указанное в запросе (например, заголовок if-match), не соответствует текущему состоянию ресурса. |
| resourceModified | Обновляемый ресурс изменился с момента последнего считывания. Как правило, это связано с несовпадением eTag. |
| serviceNotAvailable | Служба недоступна. Повторите попытку через некоторое время. Возможно, задан заголовок Retry-After. |
| unauthenticated | Вызывающий объект не прошел проверку подлинности. |
Свойство Message
Объект InnerError
Объект innererror может рекурсивно содержать другие объекты innererror с дополнительными, более конкретными кодами ошибок. При обработке ошибки приложения должны циклически просматривать все доступные коды ошибок и использовать наиболее подробный из них, который понятен приложению.
Correct HTTP status code for login form?
I am implementing the authentication for an app, and I am using a pluggable system with «authentication methods». This allows me to implement both HTTP Basic as well as HTML-based authentication.
With HTTP Basic/Digest auth the server sends a 401 Unauthorized response header. However, according to the HTTP/1.1 RFC:
The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource.
Since I do not know of any «html» WWW-Authenticate header, sending a 401 with an HTML login form seems inappropriate. Is there any alternative to this? I want to design my app in a RESTful way.
What is the correct HTTP Status code (and headers) for an HTML-based login form? And what is the correct code when the login fails?
Note: I am not interested in Digest Authentication.
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
For HTML I think you should respond with a 400.
This may be true for non-HTML requests as well, since 401 is as far as I understand it more designed to respond to a request to content that requires authentication, not to respond to an authentication request.
HTML does not always allow for pure use of RESTful APIs, so it’s ok to cut corners here and there imo, but maybe there is a better way I’m not seeing in this particular case.
When requesting the login form which is a public page, you get what you want, so it’s a 200 status code :
When requesting for a page that needs a http level authentication that you didn’t initiated (basic http, ssl certificate, etc.), the application must tell the browser itself that it needs to initiate this authentication for you :
When the authentication is a cookie-based session, you already have a cookie (if it’s not the case, you will get one with the set-cookie header when requesting the page) but this cookie doesn’t tell that you are allowed to access the /secured uri. So if you try to access this uri, you should get a «403 forbidden» status. Then the «log in» action is no more than just changing the state of the application with a POST request to make the application grant access for this cookie, so.
Log in with bad credentials:
Log in with good credentials but not enough permissions :
Log in with good credentials and enough permissions :
This is a tricky question, largely because the most well-established HTTP clients used by people are browsers. According to the RFC, the WWW-Authenticate header can contain anything. Basic and digest authentication are just two examples of further standardised challenge/response mechanisms. You can simply specify a challenge like html-form > and return the 401 along with an HTML form. Also, recall from the spec that multiple challenges can be specified within the same WWW-Authenticate header, but I don’t have any experience testing browsers extensively with different schemes.
@2016-02-17 Updated
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The user agent MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.2). If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
If you want to handle if no permission right, you may need 403 Forbidden [RFC7231]
HTTP 422 is used for WebDAV, but the meaning might fit the needs. (Not suggested for most cases)
For more information, please see the comment of Cássio Mazzochi Molin below.
@2016-02-12 **Updated** *(This is the reference to the accepted answer.)*
HTTP 422 is used for WebDAV, but the meaning might fit the needs. HTTP 401 is for authorization. And is not suitable for authentication.
HTTP 422 is now better choice other than 400 / 401. HTTP 422 is an alternative choice.
How to deal with 401 Unauthorized response i Jmeter V3.0 or lower?
I am trying to login the-internet.herokuapp.com/basic_auth using admin:admin as credentials.
I am using Jmeter v3.0 and I added HTTP Authorization manager, Cookie manager and also added the name and value in header manager as shown in the image, but I am still getting 401 unauthorized response.
I tried the same thing in a different system with Jmeter v3.1 and its working.
Does anyone know how to resolve issue with Jmeter v3.0 or lower?
1 Answer 1
I cannot reproduce your problem using JMeter 3.0 and only having HTTP Authorization Manager added apart from the HTTP Request:
Here is a full Test Plan just in case:
I would recommend removing your Authorization header from the HTTP Header Manager just in case.
See How to Use HTTP Basic Authentication in JMeter article for more details on bypassing basic access authentication in JMeter tests.
It is hightly recommended to use the latest JMeter versions where possible as newer versions normally come with bug fixes, performance improvements and brand new features so consider upgrading to JMeter 3.2 (or whatever is the latest version available at the JMeter Downloads page)
Ошибка сервера 401: что это за ошибка и как ее исправить
Вы здесь
Главная Отзыв на госсайт: Федеральная налоговая службане могу войти в личный кабинет. вчера регистрировался, а сейчас при вводе пароля на странице <«status»:0,»error»:»Maintenance. Sorry…»>Дата публикации: 01 марта 2020 г., 00:08Тип отзыва: ПроблемаМодерация: Системный Администратор 01.03.2020 — 08:50 Ответил куратор: Иванова Любовь ЕвгеньевнаДата ответа: 03 марта 2020, 09:56 г. Текущий статус: Обработан
Уважаемый пользователь сайта!
При наличии вопросов по работе интернет-сервисов Вы можете обращаться в службу технической поддержки через сервис «Техническая поддержка сервисов», размещенный в разделе «Все сервисы» (https://www.nalog.ru/rn77/service/service_feedback/). Обращениям присваиваются регистрационные номера, своевременность их исполнения тщательно контролируется. В случае необходимости специалисты службы технической поддержки связываются с налогоплательщиком для мониторинга текущей ситуации и оперативного исправления выявленных сбоев.
Данный виджет разработан с целью предоставления возможности налогоплательщикам оценить работу сайта.
Оказал ли куратор необходимую помощь?
Ваше мнение очень важно при доработке и совершенствовании АИС «Мониторинг Госсайтов»
Большое количество налогоплательщиков сталкивается с ошибкой «Проверка защищенного соединения с сервером личного кабинета индивидуального предпринимателя». В этом случае пользователи не могут попасть в личный кабинет и воспользоваться его функциями. Рассмотрим, что делать в этой ситуации далее в статье.
Антивирус – причина ошибки «Проверка защищенного соединения»
Ошибка возникает при посещении сайтов для оплаты налогов, а также при регистрации на них. С этим вопросом пользователи часто обращаются в техническую поддержку сервиса. В первую очередь в поддержке советуют отключить на время антивирусное программное обеспечение. Это можно сделать на панели быстрого доступа внизу экрана Windows. При установке антивируса в браузер, который используется по умолчанию, добавляется специальное расширение. Оно служит для блокирования подозрительных сайтов, а также тех сайтов, которые занесены в базу данных антивируса.
Расширение отключается достаточно просто, необходимо зайти в настройки браузера, найти пункт с расширением и напротив установить статус «Выключено». После этого попытаться снова зайти на сайт, где возникала ошибка «Проверка защищенного соединения личного кабинета ИП». Сайт, на который вы пытаетесь зайти, должен быть внесен в надежные узлы браузера. Это тоже можно сделать в настройках. Если ошибка возникает при попытке зайти в ЛК на nalog.ru, необходимо:
Для тех, кто использует антивирус ESET, необходимо сделать еще кое-что:
При проверке декларации может возникать ошибки 0000000002 и 0400300003.
Настроить браузер для устранения ошибки «Проверки защищенного соединения»
Чтобы устранить ошибку «Проверка защищённого соединения с сервером личного кабинета юридического лица», необходимо произвести некоторые настройки браузера и операционной системы.
Можно воспользоваться браузером Safari вместо IE. Также, можно использоваться более новую версию КриптоПро 4.0. Скачать ее нужно только с официального сайта. Демо-версией вы сможете пользоваться 3 месяца без ввода лицензионного ключа.
Другие методы устранения дисфункции
Нередко, ошибка возникает не только при соединении с сервером личного кабинета индивидуального предпринимателя, но и с сервером личного кабинета юридического лица. Причиной ошибки «Проверка защищенного соединения» могут являться настройки КриптоПро. Здесь нужно зайти на вкладку «Настройки TLS» и убрать флажок с чек-поинта «Не использовать устаревшие cipher suite».
После этого нужно перезагрузить компьютер. Можно попытаться установить вручную сертификат, для этого:
Следования вышеописанным рекомендациям в большинстве случаев помогут решить ошибку «Проверка защищенного соединения с личным кабинетом на сайте».

Заполнение в личном кабинете на сайте налоговой заявления о возврате излишне уплаченного НДФЛ, как налогового агента, ведет к неправильному заполнению. Оказывается, нужно ножками идти в инспекцию.
Поделились в «Красном уголке бухгалтера».
«Отхватил адреналинчику, занесло неправедными путями в налоговую. Основной вопрос был в возврате дважды уплаченного, как налоговый агент НДФЛ. Честно, больше месяца прождал денежек или какой-либо бумажки от налоговиков, вот и дополз до них с распечатанным из ЛК ИП заявлением на возврат и квитанцией о приеме заявления. Все тихо, спокойно, народу практически нет, температуру больше не измеряют, в зал пускают только когда номер талона высветиться и не более 20 человек одновременно. Заявление на возврат заполнял в ЛК ИП, все ставится автоматом: статус плательщика — 4 (налоговый агент), 1 — излишне уплаченный, 1 — налог, номер счета для возврата 4 — налогового агента, получатель — 2 физическое лицо (исходя из 1 — организация (ответственный участник консолидируемой группы налогоплательщиков) и 3 — орган, осуществляющий открытие и ведение лицевых счетов, программа автоматом приравнивает ИП к физлицам. Что здесь неправильно программа заполнила, что они заявление разнесли как заявление на возврат личного НДФЛ физлица (типа по 3-ндфл)? Не видят они в своем заявлении статуса налогового агента, говорят программа в ЛК ИП заполняет неправильно и нужно на бумажке им подавать с другим статусом, которого они не нашли в заявлении из ЛК (то ли 2 то ли 13, запутался). И отказ на возврат, говорят инспектор выгрузил, вот только его нет ни в ЛК ИП, ни в ЛК ФЛ и из ФНС РФ прилетело только сообщение об отправки квитанции, об исполнении ничего не было».
Зачем вообще нужны сервисы, если они заполняют неправильно и все равно нужно идти в инспекцию на прием?
Вот что пишут в комментариях:
«Вечно у них со статусом 2 проблема, подайте на бумаге».
«Есть подозрение что действительно может лучше не с ЛК делать заявления, а просто им письмом. И у юрлиц в ЛК чудеса бывают, а с физиками тем более».
«Так заполнение от этого не изменится, статусы такие же поставлю в заявлении. Кто им мешает снова на физика все отнести? Про 13-й статус в заявлении вообще ничего нет. Не пойму, где по их мнению ошибка в заявлении».
«Ну сделайте им и 2 и 13 в конце концов, пусть выбирают. Но с 2 завернули ведь, нужно тогда пробовать дальше. А что делать?».
«Так куда его сунуть, этот 13? Нет в форме такого статуса. Юридические лица и ИП могут указываться в заявлении коды 01 и 02. Физлицам лучше указать код 02 при возврате налогов. У меня код 2 стоит, в остальных местах налоговый агент указан».
В общем, стоит писать в техподдержку. А если все заполнено правильно, по их мнению, писать жалобу в Управление. Чего автор и хочет сделать.
Записаться 8645 12350 ₽ –30%
Подборка полезных мероприятий
03 авг в 2020 18K
Попробуем разобраться с наиболее распространенными причинами возникновения данной ошибки кода HTTP-соединения и обсудим способы их решения.
Причины появления ошибки сервера 401 и способы ее устранения на стороне пользователя
При доступе к некоторым сайтам (или отдельным страницам этих сайтов), посетитель должен пройти определенные этапы получения прав:
Большинство пользователей сохраняют свои данные по умолчанию в истории браузеров, что позволяет быстро идентифицироваться на наиболее часто посещаемых страницах и синхронизировать настройки между устройствами. Данный способ удобен для серфинга в интернете, но может привести к проблемам с безопасностью доступа к конфиденциальной информации. При наличии большого количества авторизованных регистрационных данных к различным сайтам используйте надежный мастер-пароль, который закрывает доступ к сохраненной в браузере информации.
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления ошибки с кодом 401 для рядового пользователя является ввод неверных данных при посещении определенного ресурса. В этом и других случаях нужно попробовать сделать следующее:
Некоторые крупные интернет-ресурсы с большим количеством подписчиков используют дополнительные настройки для обеспечения безопасности доступа. К примеру, ваш аккаунт может быть заблокирован при многократных попытках неудачной авторизации. Слишком частые попытки законнектиться могут быть восприняты как действия бота. В этом случае вы увидите соответствующее сообщение, но можете быть просто переадресованы на страницу с кодом 401. Свяжитесь с администратором сайта и решите проблему.
Иногда простая перезагрузка проблемной страницы, выход из текущей сессии или использование другого веб-браузера полностью решают проблему с 401 ошибкой авторизации.
Устранение ошибки 401 администратором веб-ресурса
Для владельцев сайтов, столкнувшихся с появлением ошибки отказа доступа 401, решить ее порою намного сложнее, чем обычному посетителю ресурса. Есть несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут в этом:
Где в поле /oldpage.html прописывается адрес проблемной страницы, а в http://site.com/newpage.html адрес страницы авторизации.
Таким образом вы перенаправите пользователей со всех страниц, которые выдают ошибку 401, на страницу начальной авторизации.
Хотя ошибка 401 и является проблемой на стороне клиента, ошибка пользователя на стороне сервера может привести к ложному требованию входа в систему. К примеру, сетевой администратор разрешит аутентификацию входа в систему всем пользователям, даже если это не требуется. В таком случае сообщение о несанкционированном доступе будет отображаться для всех, кто посещает сайт. Баг устраняется внесением соответствующих изменений в настройки.
Дополнительная информация об ошибке с кодом 401
Веб-серверы под управлением Microsoft IIS могут предоставить дополнительные данные об ошибке 401 Unauthorized в виде второго ряда цифр:
Более подробную информацию об ошибке сервера 401 при использовании обычной проверки подлинности для подключения к веб-узлу, который размещен в службе MS IIS, смотрите здесь.
Следующие сообщения также являются ошибками на стороне клиента и относятся к 401 ошибке:
Как видим, появление ошибки авторизации 401 Unauthorized не является критичным для рядового посетителя сайта и чаще всего устраняется самыми простыми способами. В более сложной ситуации оказываются администраторы и владельцы интернет-ресурсов, но и они в 100% случаев разберутся с данным багом путем изменения настроек или корректировки html-кода с привлечением разработчика сайта.
Александр Григорьев +49 Используемые источники:
How to check for an HTTP status code of 401?
Part of Google Cloud Collective
In one of the answers that I have received here, I encountered a problem of not knowing how to pass automatically through «Google App Engines» my ID and a password to a website, on which I am a registered user and have an account. A suggestion was given to me to «check for an HTTP status code of 401, «authorization required», and provide the kind of HTTP authorization (basic, digest, whatever) that the site is asking for». I don’t know how to check for status code. Can anyone, please, tell me how to do it?
If I use this way in Google App Engine (fetching the url of my eBay summary page):
I always get «200» instead of «401»
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
In ordinary Python code, I’d probably use the lower-level httplib, e.g.:
this will show you such codes as 301 (moved permanently) and 302 (moved temporarily); higher level libraries such as urllib2 would handle such things «behind the scenes» for you, which is handy but makes it harder for you to take control with simplicity (you’d have to install your own «url opener» objects, etc).
In App Engine, you’re probably better off using urlfetch, which returns a response object with a status_code attribute. If that attribute is 401, it means that you need to repeat the fetch with the appropriate kind of authorization information in the headers.
However, App Engine now also supports urllib2, so if you’re comfortable with using this higher level of abstraction you could delegate the work to it. See here for a tutorial on how to delegate basic authentication to urllib2, and here for a more general tutorial on how basic authentication works (I believe that understanding what’s going on at the lower layer of abstraction helps you even if you’re using the higher layer!-).
HTTP Status Codes With Explanations
Amir Ghahrai
HTTP Status Codes or Response Codes are grouped into five categories. 1×× Informational, 2×× Success, 3×× Redirection, 4×× Client Error, 5×× Server Error.
This post contains the full list of HTTP status codes with a short description of the most common response codes.
When we do API testing, usually the first thing that we check on the response from an API call is the status code. It is essential that we are familiar with at least the most common status codes so we can identify issues quicker.
1×× Informational
The 1xx (Informational) class of status code indicates an interim response for communicating connection status or request progress prior to completing the requested action and sending a final response.
2×× Success
The 2xx (Successful) class of status code indicates that the client’s request was successfully received, understood, and accepted.
200 OK
The 200 (OK) status code indicates that the request has succeeded. The payload sent in a 200 response depends on the request method.
201 Created
The 201 (Created) status code indicates that the request has been fulfilled and has resulted in one or more new resources being created.
204 No Content
The 204 (No Content) status code indicates that the server has successfully fulfilled the request and that there is no additional content to send in the response payload body.
3×× Redirection
The 3xx (Redirection) class of status code indicates that further action needs to be taken by the user agent in order to fulfill the request.
301 Moved Permanently
The 301 (Moved Permanently) status code indicates that the target resource has been assigned a new permanent URI and any future references to this resource ought to use one of the enclosed URIs.
302 Found
The 302 (Found) status code indicates that the target resource resides temporarily under a different URI.
4×× Client Error
The 4xx (Client Error) class of status code indicates that the client seems to have erred.
400 Bad Request
The 400 (Bad Request) status code indicates that the server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax).
401 Unauthorized
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
403 Forbidden
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it.
404 Not Found
The 404 (Not Found) status code indicates that the origin server did not find a current representation for the target resource or is not willing to disclose that one exists.
405 Method Not Allowed
The 405 (Method Not Allowed) status code indicates that the method received in the request-line is known by the origin server but not supported by the target resource.
415 Unsupported Media Type
The 415 (Unsupported Media Type) status code indicates that the origin server is refusing to service the request because the payload is in a format not supported by this method on the target resource. The format problem might be due to the request’s indicated Content-Type or Content-Encoding, or as a result of inspecting the data directly.
5×× Server Error
The 5xx (Server Error) class of status code indicates that the server is aware that it has erred or is incapable of performing the requested method.
500 Internal Server Error
The 500 (Internal Server Error) status code indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request.
502 Bad Gateway
The 502 (Bad Gateway) status code indicates that the server while acting as a gateway or proxy, received an invalid response from an inbound server it accessed while attempting to fulfill the request.
503 Service Unavailable
The 503 (Service Unavailable) status code indicates that the server is currently unable to handle the request due to a temporary overload or scheduled maintenance, which will likely be alleviated after some delay.
504 Gateway Timeout
The 504 (Gateway Timeout) status code indicates that the server while acting as a gateway or proxy, did not receive a timely response from an upstream server it needed to access in order to complete the request.
Несанкционированные ошибки (401) при назимении API
Ссылаясь на статью о серии устранения неполадок управления API Azure,это третий сценарий лаборатории. Убедитесь, что вы следовали инструкциям по настройке лаборатории в соответствии с этим, чтобы воссоздать проблему.
Оригинальная версия продукта: Служба управления API
Исходный номер КБ: 4464930
Симптомы
API Echo внезапно начал метать различные типы HTTP 401 — несанкционированные ошибки при наводении операций под ней. Создание ресурсов и извлечение ресурсов показывают это сообщение об ошибке:
<
«statusCode»: 401,
«сообщение»: «Доступ отказано в связи с недействительным ключом подписки. Убедитесь, что для активной подписки необходимо предоставить допустимый ключ».
>
В то время как остальные операции отображаются
<
«statusCode»: 401,
«сообщение»: «Доступ отказано в связи с отсутствием ключа подписки. Обязательно включаем ключ подписки при внесении запросов в API».
>
Ожидаемый код ответа HTTP для всех операций — 200, однако тело отклика будет отличаться, так как API-ответ всегда повторяет все, что вы отправляете в качестве тела запроса в дополнение к заголовщикам.
Действия по устранению неполадок
Чтобы получить доступ к API, разработчики должны сначала подписаться на продукт. Когда они подписываются, они получают ключ подписки, который отправляется в качестве части заголовки запросов, которая хороша для любого API в этом продукте. Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key — это заголовка запросов, отправленная для ключа подписки продукта, связанного с этим API. Клавиша заполняется автоматически.
Что касается доступа к ошибке, отказано из-за недействительных ключа подписки. Убедитесь, что вы предоставляете допустимый ключ для активной подписки, ясно, что вы отправляете неправильное значение загона запроса Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key во время запроса На создание ресурсов и извлечение операций ресурсов.
Вы можете проверить ключ подписки для определенного продукта с портала разработчика APIM, переехав на страницу Profile после регистрации, как показано ниже.
Выберите кнопку Показать, чтобы увидеть ключи подписки для соответствующих продуктов, на которые вы подписаны.
Если вы проверяете отправимые с вкладки Test загонщики, вы заметите, что значение заглавного запроса Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key неверно. Возможно, вам будет интересно, как это возможно, так как AIM автоматически заполняет этот заглавный элемент запроса нужным ключом подписки.
Давайте проверим определение Frontend в статье Создание ресурсов и извлечение операций ресурсов в вкладке Design. При тщательном осмотре вы заметите, что эти операции получили неправильное кодовое значение заглавного заглавного запроса Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key, добавленного в вкладке Headers.
Вы можете удалить его, это должно решить проблему ключа недействительной подписки, но все равно вы получите недостающую ошибку ключа подписки.
Вы можете получить следующее сообщение об ошибке:
Длина контента: 152
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Sun, 29 Jul 2018 14:29:50 GMT
Vary: Origin WWW-Authenticate: AzureApiManagementKey realm=» https://pratyay.azure-api.net/echo «,name=»Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key», type=»header» <
«statusCode»: 401,
«сообщение»: «Доступ отказано в связи с отсутствием ключа подписки. Обязательно включаем ключ подписки при внесении запросов в API». >
Перейдите к APiettings Echo и проверьте, связан ли он с любым из доступных продуктов. Если нет, необходимо связать этот API с продуктом, чтобы получить ключ подписки.
Сначала разработчики должны подписаться на продукт, чтобы получить доступ к API. Когда они подписываются, они получают ключ подписки, который хорошо для любого API в этом продукте. Если вы создали экземпляр AIM, вы уже администратор, поэтому вы подписаны на каждый продукт по умолчанию.
Server returned HTTP response code: 401 for URL: https
I’m using Java to access a HTTPS site which returns the display in an XML format. I pass the login credentials in the URL itself. Here is the code snippet:
I’m creating a trust manager in the program which does not validate signed/unsigned certificates. But, on running the above program, I get the error Server returned HTTP response code: 401 for URL: https://Administrator:Password@localhost:8443/abcd
I can use the same url on my browser and it displays the xml correctly. Kindly let me know how to make this work within the Java program.
2 Answers 2
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
401 means «Unauthorized», so there must be something with your credentials.
I think that java URL does not support the syntax you are showing. You could use an Authenticator instead.
and then simply invoking the regular url, without the credentials.
The other option is to provide the credentials in a Header:
PS: It is not recommended to use that Base64Encoder but this is only to show a quick solution. If you want to keep that solution, look for a library that does. There are plenty.
customerrors for 401.2 in ASP.NET
I successfully implemented role based authorization in ASP.NET. When a person does not have the needed role he gets to see an error page for 401.2 not authorized.
What I would like to accomplish now is to have a custom 401 page in my application and have it redirected there via settings in the web.config. I tried this:
But this does not get caught. Do I have to override it in IIS instead? I hope not as that would make getting things deployed harder.
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
I ran into the same problem recently and it turns out that this is one of the quirks when using Windows Authentication.
Joshua Flanagan created a nice HttpModule a while ago that will respect the customErrors section in your web.config and redirect to the 401 error page.
The key to the solution is to intercept the EndRequest event of the page lifecycle, check for a 401 status code, and then execute your custom page.
Hands off that resource, HTTP status code 401 vs 403 vs 404
By Arnaud Lauret, May 5, 2021
Choosing HTTP status codes Series
When designing APIs, choosing HTTP status codes is not always that obvious and prone to errors, I hope this post series will help you to avoid common mistakes and choose an adapted one according to the context.
The context
But what happens if some curious and maybe malicious user scan network traffic coming out of the application? This hacker will easily understand how this “not so private” API works. With very little effort, they will succeed to generate phone numbers that actually exist in the underlying system so send GET /users/
In either case, the API should prevent accessing resources that don’t belong to the caller and signify there’s a problem with caller’s request. Note that if that sounds like a no-brainer for many people, that is actually not always the case and some APIs may return a 200 OK along with the requested data. Regularly, stories such as this one (which inspired the above use case) come out. Never forget that when creating APIs and never refrain from double check that your colleagues are also aware of that. And note also that using PII (Personnally Identifiable Information) or other sensitive data as ids can be very convenient but raises security concerns, especially if they appear in URLs as they can be logged almost everywhere. I should write a post series about API security one day ( POST /writing-ideas done!).
Use 404 when resource is none of consumer’s business (and never will)
The 404 (Not Found) status code indicates that the origin server did not find a current representation for the target resource or is not willing to disclose that one exists.
Returning a 404 Not Found means “the requested resource does not exists”. Actually, there’s a subtlety, it could mean “the requested resource actually exists but it’s none of your business, you’re not allowed to access it and never will; actually, it does not exist for you” or “the requested resource does not exist at all” but the consumer will never know what is the true reason behind this HTTP status code.
That response is the best one for the introduction’s use case, granted that users want to use this application without sharing anything with others. In that case, given that John and Emma use the application, if Emma “hacks” the API, we will never ever want her to know that /users/
But if 404 Not Found is usually my first idea when a consumer tries to access to a /resources/1234 they shouldn’t (I admit I’m a little obsess with security and prone to not show what is not needed to be shown), there are cases where it could be interesting to let them know the target resource exists.
Use 403 when consumer can do something about it
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
Returning a 403 Forbidden signifies “the requested resource actually MAY exists but you cannot access it. You MAY access it by requesting adequate rights to someone, maybe an administrator for instance”.
Never ever use 401 (don’t be fooled by its reason)
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
There are only two hard things in Computer Science: cache invalidation and naming things.
A 401 signifies there’s a problem with your credentials which usually are provided in an Authorization header (still wrong name, but at least it’s consistent with the reason). This status is made to signify “you forgot to provide an Authorization header with some credentials” or “your credentials provided in the Authorization header are invalid/expired”. In the API world, it basically says “You can’t use the API at all, come back with a valid access token”.
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
To be even more sure that 403 Forbidden is the right answer, let’s talk about Oauth 2 scopes. Indeed, dealing with resource rights access is not always, let’s say “internal business rule” driven (checking in users table that the identified user has the requested phone number for example). When consumers request an access token using the Oauth 2 framework (the token that goes into the not so well named Authorization header), they may request a token restricted to given elements thanks to scopes. For instance, when using the Github API, you may request access to public repo only or to user data only. What should happen when a consumer requests access to a resource without adapted scopes? Section 3.1 of RFC 6750 The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage is quite clear:
The request requires higher privileges than provided by the access token. The resource server SHOULD respond with the HTTP 403 (Forbidden) status code and MAY include the «scope» attribute with the scope necessary to access the protected resource.
HTTP Status code is not enough
That means two things. First 401 Unauthorized is definitely not an option in the case we are studying today. Second, HTTP status code is not enough. Indeed, 403 Forbidden could be returned because consumer lacks some scope to GET /resources/
Don’t forget DX and context
Respecting HTTP and other RFCs is important to avoid surprising developers with behaviors that are against common practices, but most important, whatever the HTTP status code you’ll choose to return, what matters above all is providing the response the most adapted for the context that will actually help the developer (and the consumer and even the end user) to know what is actually happening and help them solve the problem if they can.
Непредвиденное состояние 401.1 возвращается при использовании заголовков предварительной проверки подлинности с Internet Explorer и IIS.
В этой статье устранена проблема, из-за которой возвращается непредвиденное состояние 401.1 с заголовками предварительной проверки подлинности. Это происходит при использовании Internet Explorer для браузера в веб-приложении, размещенном в службы IIS (IIS).
Исходная версия продукта: Режим IE для Edge, службы IIS, Internet Explorer 11, 10, 9
Исходный номер базы знаний: 2749007
Симптомы
Рассмотрим следующий сценарий.
В этом сценарии службы IIS могут возвращать ответ http (HTTP) 401.1 в Internet Explorer в ответ на запрос браузера. Веб-браузер может предложить ввести имя пользователя и пароль. Кроме того, в окне браузера может отображаться сообщение об ошибке HTTP 401.1.
Причина
Такое поведение является особенностью данного продукта. Ответ 401.1 будет получен, если первый запрос веб-браузера, отправляемый в приложение IIS, содержит один из следующих заголовков:
Обходной путь
Чтобы обойти это поведение, отключите предварительную проверку подлинности в Internet Explorer или отключите проверку подлинности в режиме ядра для веб-приложения IIS.
При неправильном использовании редактора реестра могут возникнуть серьезные проблемы, которые могут потребовать переустановки операционной системы. Корпорация Майкрософт не может гарантировать, что вы сможете решить проблемы, возникающие в результате неправильного использования редактора реестра. Используйте редактор реестра на свой риск.
Чтобы изменить это поведение в Internet Explorer, используйте редактор реестра ( Regedt32.exe ), чтобы добавить значение в следующий раздел реестра:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Internet Settings/
Указанный выше раздел реестра является одним путем. он был заключен в оболочку для удобочитаемости.
Добавьте следующее значение реестра:
Чтобы изменить это поведение в IIS, отключите проверку подлинности в режиме ядра для веб-приложения IIS.
Откройте службы IIS (IIS), выполнив следующую команду из командной строки администратора:
В области « Подключения» разверните имя сервера, разверните узел, а затем сайт, приложение или веб-службу, для которых требуется отключить проверку подлинности в режиме ядра.
Прокрутите страницу до раздела «Безопасность» на панели « Главная» и дважды щелкните » Проверка подлинности».
В области проверки подлинности выберите Windows проверку подлинности.
На панели «Параметры действий» выберите «Дополнительные параметры».
Когда появится диалоговое Параметры Advanced Параметры, снимите флажок «Включить проверку подлинности в режиме ядра«.
Нажмите кнопку « ОК», чтобы закрыть диалоговое Параметры advanced Параметры.
Отключение проверки подлинности в режиме ядра может привести к сбою веб-приложений, для которых требуется проверка подлинности и делегирование Kerberos.
Дополнительные сведения
Чтобы определить, вызван ли запрос проблемой, описанной в этой статье, используйте средство Fiddler. С помощью этого средства можно просмотреть трафик HTTP-запросов и ответов для запроса, что приводит к появлению запроса в Internet Explorer. Кроме того, вам потребуются журналы IIS с сервера IIS для подтверждения состояния HTTP и кодов вложенного состояния. В следующем примере для иллюстрации этого поведения используется Internet Explorer 9:
Запустите средство Fiddler и включите запись трафика.
Перейдите к веб-приложению IIS, чтобы оно привело к появлению запроса учетных данных.
В Fiddler найдите запрос, который привело к 401. Просмотрев необработанные представления запросов и ответов, вы увидите записи, аналогичные следующим:
Исходный запрос к веб-приложению уже содержит Authorization заголовок, что приводит к ответу 401. В соответствующем журнале IIS должна отображаться запись, аналогичная следующей:
Состояние HTTP и вложенное состояние — 401.1, что сопоставляется с состоянием «Отказано в доступе » из-за недопустимых учетных данных.
Дополнительные сведения см. в следующей документации:
HTTP аутентификация
HTTP предоставляет набор инструментов для котнроля доступа к ресурсам и аутентификации. Самой распространённой схемой HTTP аутентификации является «Базовая» (Basic) аутентификация. Данное руководство описывает основные возможности HTTP аутентификации и показывает способы ограничения доступа к вашему серверу с её использованием.
Общий механизм HTTP аутентификации
В случае базовой авторизации как на иллюстрации выше, обмен должен вестись через HTTPS (TLS) соединение, чтобы обеспечить защищённость.
Прокси-аутентификация
Этот же механизм запроса и ответа может быть использован для прокси-аутентификации. В таком случае ответ посылает промежуточный прокси-сервер, который требует авторизации. Поскольку обе формы аутентификации могут сосуществовать, для них используются разные заголовки и коды статуса ответа. В случае с прокси, статус-код запроса 407 (Proxy Authentication Required) и заголовок Proxy-Authenticate (en-US), который содержит хотя бы один запрос, относящийся к прокси, а для передачи учётных данных прокси-серверу используется заголовок Proxy-Authorization (en-US).
Доступ запрещён
Аутентификация cross-origin изображений
Аутентификация с помощью изображений, загружаемых из разных источников, была до недавнего времени потенциальной дырой в безопасности. Начиная с Firefox 59, изображения, загружаемые из разных источников в текущий документ, больше не запускают диалог HTTP-аутентификации баг 1423146, предотвращая тем самым кражу пользовательских данных (если нарушители смогли встроить это изображение в страницу).
Кодировка символов HTTP аутентификации
заголовки WWW-Aутентификации и Прокси-Аутентификации
WWW-Authenticate (en-US) и Proxy-Authenticate (en-US) заголовки ответа которые определяют методы, что следует использовать для получения доступа к ресурсу. Они должны указывать, какую схему аутентификации использовать, чтобы клиент, желающий авторизоваться, знал, какие данные предоставить. Синтаксис для этих заголовков следующий:
заголовки Авторизации и Прокси-Авторизации
Заголовки запросов Authorization и Proxy-Authorization (en-US) содержат учётные данные для аутентификации агента пользователя (User Agent) на (прокси) сервере. Здесь снова требуется за которым следуют учётные данные, которые могут быть закодированы или зашифрованы в зависимости от того, какая схема аутентификации используется.
Схемы Аутентификации
Общая структура HTTP аутентификации является основной для ряда схем аутентификации. Schemes can differ in security strength and in their availability in client or server software.
IANA поддерживат список схем аутентификации, однако существуют и другие схемы предлагаемые хост-сервисами, например, Amazon AWS.
Некоторые распространенные схемы аутентификации включают:
AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 (смотреть AWS документацию).
Схемы могут различаться по степени безопасности и по их доступности в клиентском или серверном программном обеспечении.
«Базовая» (Basic) схема аутентификации обеспечивает очень низкую безопасность, но широко поддерживается и проста в настройке. Более подробно она представлена ниже.
Базовая (Basic) схема аутентификации
«Базовая» схема HTTP-аутентификации определена в RFC 7617, которая передаёт учётные данные в виде пар пользователь ID/пароль (user ID/password), закодированных с использованием base64.
Безопасность базовой аутентификации
Ограничение доступа с помощью Apache и базовой аутентификации
Ограничение доступа с помощью nginx и базовой аутентификации
Доступ используя учётные данные в URL-адресе
Многие клиенты также позволяют избежать запроса на вход в систему, используя закодированный URL, содержащий имя пользователя и пароль, как показано ниже:
Как исправить ошибку HTTP 401 неавторизованного запроса?
Вся сеть работает на основе протокола связи между браузером и веб-сервером. Когда что-то пойдет не так, вы можете увидеть в браузере различные типы кодов ошибок HTTP. Ошибка HTTP или код состояния 4xx указывает на то, что браузер отправил на сервер неправильную информацию. Веб-серверы вернут код 401, если они не могут обработать запрос из-за неправильной аутентификации.
Связанный: Исправить ошибку HTTP 400 неверного запроса.
Как исправить ошибку HTTP 401 неавторизованного запроса?
Эта проблема чаще встречается на веб-сайтах, которые предлагают вход в систему и специальный контент по подписке. Хотя в большинстве случаев причиной является неправильный вход в систему, в некоторых случаях может произойти ошибка 401 Несанкционированный запрос, даже если у вас есть действительные учетные данные для входа. В этом случае веб-сервер мог не получить ваши данные для входа из-за проблемы на стороне браузера и вернуть ошибку 401.
Если вы видите ошибку 401, выполните следующие действия, чтобы устранить ошибку. Большинство решений довольно легко исправить. Мы также отдельно сгруппировали возможные исправления для обычных пользователей и владельцев веб-сайтов. Вы можете опробовать подходящий случай.
Для обычных пользователей
1. Проверьте URL
Это наиболее частая причина ошибки 401 неавторизованный запрос. Это могло произойти, когда вы вводите URL вручную. В противном случае вы можете щелкнуть устаревший URL-адрес, отмеченный закладкой в вашем браузере. Ошибка может появиться, если страница больше не существует. Итак, проверьте URL-адрес и убедитесь, что нет орфографических ошибок и веб-страница все еще доступна.
Связанный: Исправить ошибку HTTP 404, не найденную.
2. Очистить DNS
В некоторых случаях ошибки DNS также могут вызывать ошибку 401 неавторизованный запрос. Вы можете исправить ошибку, очистив DNS.
Следуйте инструкциям в Windows:
Если вы используете macOS, очистка DNS немного отличается.
3. Очистить файлы cookie браузера.
Файлы cookie — это фрагменты информации, которые используются веб-сайтами для запоминания вашей уникальной личной информации. Во многих случаях файлы cookie также хранят информацию об аутентификации пользователя и напоминают веб-серверу об уровне авторизации, который может быть предоставлен пользователю. К сожалению, это не всегда работает гладко, и может произойти неправильная аутентификация сервера. Ошибка 401 может произойти, если веб-сервер не может распознать токен сеанса, отправленный вашим веб-браузером. Когда сервер считает, что ваш токен недействителен, вы можете получить ошибку 401 Unauthorized Request.
Гораздо проще удалить все файлы cookie полностью или только для определенных веб-сайтов. Когда вы очищаете файлы cookie, вам придется повторно ввести данные для входа в электронную почту, социальные сети и другие веб-сайты, требующие входа в систему. После очистки кеша попробуйте войти на веб-сайт и проверьте, можете ли вы получить полный доступ на этот раз без проблем.
4. Проверьте свои права доступа.
Ошибка 401 может произойти из-за неправильного входа в систему или разрешения. Например, ссылка может быть зарезервирована только для участников, и при нажатии на нее вы получите ошибку 401 неавторизованный запрос. В этом случае вам может потребоваться связаться с владельцем сайта для получения надлежащего доступа.
В других случаях вы могли вводить неверные учетные данные для входа на веб-сайт. Если вы знаете, что учетные данные верны, очистите файлы cookie и очистите DNS, как описано в предыдущих разделах. Теперь попробуйте еще раз войти на сайт.
Если вы действительно забыли пароль, найдите на сайте ссылку для сброса пароля. Обычно веб-сайт запрашивает адрес электронной почты, который вы использовали для создания учетной записи в прошлом. В некоторых случаях по ошибке включается неправильное требование аутентификации, и веб-сайт становится недоступным для пользователей, которые вошли в систему. Эту проблему может решить только администратор веб-сайта.
5. Выйдите из системы и войдите снова.
Большинству веб-сайтов требуются регулярные простои для обслуживания. Также есть вероятность, что владелец веб-сайта может вносить некоторые изменения в серверную часть, вызывая временные проблемы. Если вы столкнулись с проблемами со статусом входа в систему, выйдите из системы и войдите снова. Во многих случаях веб-сайт может снова работать нормально.
Владельцам веб-сайтов
6. Откат к предыдущей версии CMS
Большинство систем управления контентом обновляются довольно регулярно. Иногда при незначительном обновлении случайно появляются новые ошибки, в том числе необъяснимое появление ошибки 401 Unauthorized Request. Если ваши пользователи сообщают об этой проблеме после недавнего обновления CMS, вам следует рассмотреть возможность отката к предыдущей версии.
К сожалению, некоторые CMS не позволяют выполнить откат. В таком случае вам может потребоваться официальная поддержка поставщика услуг.
7. Удалите ваши изменения.
Некоторые системы управления контентом, такие как WordPress, предлагают плагины, темы, модули, виджеты и расширения. Вы можете использовать эти функции для добавления новых функций и изменения внешнего вида очень универсально. К сожалению, некоторые плагины, темы, модули, виджеты и расширения находятся в плохом состоянии. Некоторые расширения также могут привести к внесению большего количества изменений, чем необходимо.
Когда вы видите ошибку 401 после любого обновления, первое, что вы можете сделать, это удалить последний обновленный плагин и проверить результат. Следует отметить, что проблема может быть решена не сразу после удаления или перехода на более раннюю версию плагина. Это могло произойти, если плагин изменил данные в серверной базе данных или файлах PHP. Таким образом, после удаления плагина любые изменения в базе данных или файлах PHP не могут быть отменены. В таком случае вам может потребоваться вернуть содержимое к ранее работающей версии из резервной копии.
Вывод
Во многих случаях ошибка 401 Unauthorized Request возникает, когда вы пытаетесь войти в систему с неправильными учетными данными. Некоторые веб-сайты, такие как банковские сайты, могут заблокировать вашу учетную запись, если вы несколько раз попытаетесь ввести неправильный пароль. Поэтому убедитесь, что вы указали правильные данные для входа, иначе обратитесь в службу поддержки веб-сайта, чтобы решить вашу проблему. С другой стороны, если вы являетесь владельцем веб-сайта, попробуйте вернуться к своим предыдущим действиям, чтобы восстановить доступ к сайту.
Axios login request: Unauthorized, request status code 401
I’m trying to get an authorization token by making a request to an api using axios:
I’m getting always status code 401(Unauthorized):
Where I’m doing wrong?
The fact is that making the same request using python works fine:
1 Answer 1
By sending username and password in auth: <> in axios, you are doing the basic-authentication, basically sending Authorization: basic header.
As per working python program, you need to send the username and password as part of the request body. You need to serialize the body params for url-encoded content type as well.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged node.js authentication axios http-status-code-401 or ask your own question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
The request failed with HTTP status 401: Unauthorized
The request failed with HTTP status 401: Unauthorized.
How do I get around this?
5 Answers 5
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
You need to set the credentials in you application when you initialise the webService object.
Something like webService.UseDefaultCredentials = true
This will set the credentials of the request to the current user executing the application.
you can use this:
if does not work, use the below code instead of the code above
note: the username Password and domain is the user credential of the user that access to webservice
so make sure that user have permission to access to web service
maybe the user is the windows user
and you can get the domain from: right click in «MyComputer» and properties the domain is the Computer name or Workgroup
«HTTP 401» error message when you try to access web resources that require Kerberos authentication on a computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
Symptoms
Consider the following scenario:
You have a computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2.
You configure the FEATURE_USE_CNAME_FOR_SPN_KB911149 registry subkey according to the description in the following Microsoft Knowledge Base article:
You try to access a webpage or a web application that requires Kerberos authentication by using the alias (CNAME) resource record. A service principal name (SPN) is configured for the CNAME that is related to the web resource.
In this scenario, you cannot access these web resources, and you receive an error message that resembles the following:
HTTP 401
Kerberos authentication failed: gss_accept_sec_context failed: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information, Wrong principal in request
Cause
This issue occurs because the SPN for the web resources is only registered with the CNAME.
A Windows 7-based or Windows Server 2008 R2-based client computer requests a Kerberos ticket for the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the web resources. This means that the client computer requests the host (A) resource record that corresponds to the CNAME for Kerberos authentication. If the SPN is only registered with the CNAME, access to the web resources fails.
Resolution
Hotfix information
A supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that is described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing the problem described in this article. This hotfix might receive additional testing. Therefore, if you are not severely affected by this problem, we recommend that you wait for the next software update that contains this hotfix.
If the hotfix is available for download, there is a «Hotfix download available» section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section does not appear, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support to obtain the hotfix.
Note If additional issues occur or if any troubleshooting is required, you might have to create a separate service request. The usual support costs will apply to additional support questions and issues that do not qualify for this specific hotfix. For a complete list of Microsoft Customer Service and Support telephone numbers or to create a separate service request, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=supportNote The «Hotfix download available» form displays the languages for which the hotfix is available. If you do not see your language, it is because a hotfix is not available for that language.
Prerequisites
There are no prerequisites to apply this hotfix.
Registry information
To use the hotfix in this package, you do not have to make any changes to the registry.
Restart requirement
You may have to restart the computer after you apply this hotfix.
Hotfix replacement information
This hotfix does not replace a previously released hotfix.
File information
The global version of this hotfix installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and the times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and the times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time together with your current daylight saving time (DST) bias. Additionally, the dates and the times may change when you perform certain operations on the files.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 file information notes
Important Windows 7 hotfixes and Windows Server 2008 R2 hotfixes are included in the same packages. However, hotfixes on the Hotfix Request page are listed under both operating systems. To request the hotfix package that applies to one or both operating systems, select the hotfix that is listed under «Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2» on the page. Always refer to the «Applies To» section in articles to determine the actual operating system that each hotfix applies to.
The MANIFEST files (.manifest) that are installed for each environment are listed separately in the «Additional file information for Windows Server 2008 R2 and for Windows 7» section. MANIFEST files and the associated security catalog (.cat) files, are extremely important to maintain the state of the updated components. The security catalog files, for which the attributes are not listed, are signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
Friendly HTTP 401 Status Code Message?
I’m a developer not a wordsmith and as such I’m stuck.
We have a subscription based site whereby users may well come across our 401 page.
We’ve decided that the IIS 401;2 page needs replacing.
Does anyone have any examples or advise about writing a good non offensive 401 page?
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Through a series of highly sophisticated and complex algorithms, this system has determined that you are not presently authorized to use this system function. It could be that you simply mistyped a password, or, it could be that you are some sort of interplanetary alien-being that has no hands and, thus, cannot type. If I were a gambler, I would bet that a cat (an orange tabby named Sierra or Harley) somehow jumped onto your keyboard and forgot some of the more important pointers from those typing lessons you paid for. Based on the actual error encountered, I would guess that the feline in question simply forgot to place one or both paws on the appropriate home keys before starting. Then again, I suppose it could have been a keyboard error caused by some form of cosmic radiation; this would fit nicely with my interplanetary alien-being theory. If you think this might be the cause, perhaps you could create some sort of underground bunker to help shield yourself from it. I don’t know that it will work, but, you will probably feel better if you try something.
And don’t get me started on all the cool 404 pages out there.
401 seems to be used to indicate an authentication failure whereas 403 for an authorization failure (which means authentication succeeded?) In case of an oauth flow if I try to authenticate with an expired token what is the right error code that prompts the client to refresh the token and try again?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
A 401. The 401 vs 403 confusion is not new. See some discussion in a w3.org email here: https://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/ietf-http-wg/2008AprJun/0418.html, though the cited RFC 2616 has been obsoleted.
From the 401 description, though «valid» is up for interpretation:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
But even more relevant, see RFC 6750 regarding Bearer Token authentication, Section 3, last paragraph. https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6750#section-3
And in response to a protected resource request with an authentication attempt using an expired access token:
Think about the boarding process in an airport. They check 2 things:
They check your identity card. This is authentication. Online, any token or user/password couple stands for your identity card.
They check you are in the passenger list for that plane (the plane is the resource you are trying to access). This is authorization. Online, the page the user is trying to access stands for the resource.
So now when you think about an access problem (token expired, token parsing failed, invalid password, user is not allowed) and which HTTP code you should return, you just have to think «if this issue was transposed into an airport scenario and I was denied access to the plane, would this have anything to do with the identity card check step?» If yes, this is 401. If not, this is 403.
Missing token Missing identity card Rejected because of identity card check 401
Expired token Expired identity card Rejected because of identity card check 401
Malformed token Unreadable/damaged identity card Rejected because of identity card check => 401
User doesn’t have privilege for the resource Passenger is not allowed to access this plane Not rejected because of identity card check => 403
You banned a user Passenger is blacklisted Not rejected because of identity card check => 403
TL;DR: 401
Long version, in addition to crunk1 (valid) answer:
401 would mean that the token was missing or invalid. In other words, it failed validation or parsing for some reason.
403 would mean that the token was successfully validated/parsed, but then the authorization to perform the action was denied for some reason.
Now, an expired token means that the token was successfully parsed but that the expiration date set in that token is already passed. Which is somewhat in-between if you consider that checking the expiration date is part of the authorization process. Personally I believe that it is part of the token validation, not the authorization, for those reasons:
There are some cases where the resource server (the API that receives and validates the token) would not even be able to know that the token is expired, and would return a 401 instead:
Also, a 403 response would instruct the client that it is an authorization issue, so retrying with an new token carrying the same access rights doesn’t have much chance to succeed, while a 401 would pass the information that the token was not accepted, so maybe retrying with a new fresh token might work.
For those reasons, I chose to return a 401 in my implementations. But TBH this doesn’t matter much, since the token expiration is supposed to be handled by the client, based on the expires_in information returned by the AS at the same time as the token, more than by a return code from the API when the token is expired.
You might have faced below error during replay of your script, though your script has web_set_user() function. In this article we will see how to fix it using various methods.
Basically above error occurs when the application is trying to validate the simulated request with proper credentials and header information. If any critical parameters missing in the header, LoadRunner throws above error.
Table of Contents
Fix 1:
Make sure that you have added valid details in the web_set_user() function. It should have valid user identity, password, and the host & port details. It is good to incorporate the password in the encrypted format using lr_decrypt functions. Below is the perfect example of web_set_user function.
web_set_user(“mydomain\\myuserid”, lr_decrypt(“4042e3e7c8bbbcfde0f737f91f”), ” mydomain:8080″);
Fix 2:
You can try running the script using WinInet replay instead of Sockets. To change the settings, go to Runtime Settings > Preferences, check Use WinInet replay instead of Sockets (Windows only)
Fix 3:
If above two fixes doesn’t work, you need to compare and validate the complete request of LoadRunner and the complete request from Fiddler.
Run the script in LoadRunner by turning on the extended log (preferably with Parameter Substitution and Data returned by server) and capture the request headers, cookies, etc.
Now, open Fiddler and manually navigate the business flow and then compare the request header information with LoadRunner info. If there is a mismatch, you need to incorporate it in the LoadRunner script. E.g. Fiddler request headers had authorization headers, accept encoding etc. You need to use web_add_header function to add the details to the script. If you use any other methods to fix unauthorized error, please let me know in the comments section.
If you like my article, please do share in your favorite social media. Please do not forget to subscribe to my weekly newsletter, it is FREE.
HTTP status code 401 even though I’m sending credentials in the request
Recently i have introduced JWT authentication to my Springboot and Angualr2 based App. In There i tried to do a POST request by passing the JWT token as below in my Angualr code
However in the server side it returns status code 401. The issue is in the Springboot side it checks the authorization header as below and it returns null
Then i had a look at the request header and it has the authorization header under Access-Control-Request-Headers as below. But it is not visible to the server side.
Then i read further and found that this could be an issue with CORS configuration. So i have modified my CORS configuration filter to have addExposedHeader as below
Still the server complains that it can not find the Authorization header. Did i miss any thing here? Appreciate your help
After reading the sideshowbarker’s comment below, i was able to understand the basics behind the issue. In My Project I have a JWT token filter and inside that it always checks the Authorization header. Then i have modified it as below and now it works as expected
1 Answer 1
You need to configure the server to not require authorization for OPTIONS requests (that is, the server the request is being sent to — not the one serving your frontend code).
That’s because what’s happening is this:
The Access-Control-Request-Headers and Access-Control-Request-Method request headers show in the question indicate the browser’s doing a CORS preflight OPTIONS request.
So you must figure out what part of the server-side code on the server the request is being sent to causes it to require authorization for OPTIONS requests, and change that so it instead responds to OPTIONS with a 200 or 204 success response without requiring authorization.
an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’ #318
Comments
ukomiljon commented Nov 24, 2017
Severity Code Description Project File Line Suppression State
Error CS0006 Metadata file ‘E:\Grial-marketezi\Grial\starter\marketezi\bin\Debug\marketezi.dll’ could not be found marketezi.iOS E:\Grial-marketezi\Grial\starter\marketezi.iOS\CSC 1 Active
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi.Droid: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi.Droid: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi.iOS: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi.iOS: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Repeater’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Repeater.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Repeater.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Repeater’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Tab’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Tab.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Tab.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Controls.Tab’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error NuGet Package restore failed for project marketezi: Unable to find version ‘2.5.2’ of package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’.
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\NuGetPackages’.
https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json: Package ‘UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base.2.5.2’ is not found on source ‘https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json’.
http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial: The V2 feed at ‘http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/Packages(Id=’UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base’,Version=’2.5.2′)’ returned an unexpected status code ‘401 Unauthorized’.
.
Error The «ResolveLibraryProjectImports» task failed unexpectedly.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Could not load assembly ‘marketezi, Version=0.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=’. Perhaps it doesn’t exist in the Mono for Android profile?
File name: ‘marketezi.dll’
at Java.Interop.Tools.Cecil.DirectoryAssemblyResolver.Resolve(AssemblyNameReference reference, ReaderParameters parameters)
at Java.Interop.Tools.Cecil.DirectoryAssemblyResolver.Resolve(String fullName)
at Xamarin.Android.Tasks.ResolveLibraryProjectImports.Extract(DirectoryAssemblyResolver res, ICollection 1 jars, ICollection 1 resolvedResourceDirectories, ICollection 1 resolvedAssetDirectories, ICollection 1 resolvedEnvironments)
at Xamarin.Android.Tasks.ResolveLibraryProjectImports.Execute()
at Microsoft.Build.BackEnd.TaskExecutionHost.Microsoft.Build.BackEnd.ITaskExecutionHost.Execute()
at Microsoft.Build.BackEnd.TaskBuilder.d__26.MoveNext() marketezi.Droid
Error CS0234 The type or namespace name ‘Artina’ does not exist in the namespace ‘UXDivers’ (are you missing an assembly reference?) marketezi E:\Grial-marketezi\Grial\starter\marketezi\App.xaml.cs 8 Active
Error CS0234 The type or namespace name ‘Artina’ does not exist in the namespace ‘UXDivers’ (are you missing an assembly reference?) marketezi E:\Grial-marketezi\Grial\starter\marketezi\Helpers\Settings.cs 6 Active
Error CS0234 The type or namespace name ‘Artina’ does not exist in the namespace ‘UXDivers’ (are you missing an assembly reference?) marketezi E:\Grial-marketezi\Grial\starter\marketezi\Properties\AssemblyInfo.cs 14 Active
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
LeoHere commented Nov 24, 2017
Looks like it failed authenticating against our nuget package source. Please double check your credentials by visiting this in your browser.
ukomiljon commented Nov 25, 2017
I can go in Grial Admin with user name and password.
But http://nuget.uxdivers.com/grial/
displays after login:
This XML file does not appear to have any style information associated with it. The document tree is shown below.
LeoHere commented Nov 27, 2017
The fact that displays the XML means you successfully authenticate, so your credentials are fine.
The problem seems to be in VS side. VS should ask you for your credentials when you try to access the Nuget package. Not sure why that is not the case in your setup.
Another option you have is to set your credentials in the NuGet.config file in the root directory (where the sln file resides).
Something like this:
Read this for more information.
ukomiljon commented Nov 28, 2017
We are using VS2017 community edition.
is it any issue with VS2017 community edition?
I checked there is no any NuGet.config file.
UXDivers.Artina.Shared,UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Base, UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Repeater and UXDivers.Artina.Shared.Tab are issue,
but UXDivers.Effects is not issue
LeoHere commented Nov 28, 2017
VS2017 Community is not an issue.
If there is no Nuget.config (which is the most common case) you will need to create it.
UXDivers.Effects is a public Nuget package, so it make sense.
ukomiljon commented Nov 29, 2017
I created Nuget.config:
But not working.
ukomiljon commented Nov 29, 2017
ukomiljon commented Nov 30, 2017
Could you give me sample Nuget.config complete package?
ukomiljon commented Nov 30, 2017
LeoHere commented Nov 30, 2017
@ukomiljon the Nuget.Config you specified looks just fine.
May be the name used in the Nuget.Config is the same as the one defined in Tools->Options->Nuget and is somehow confusing VS.
Please set the Nuget.Config to something like this.
so we are sure there is no naming conflict. Remember to set your user name and password.
HTTP Status Code: 401 in GCMDemo
Part of Google Cloud Collective
Server 401 when trying to send a message to my android device.
Could anybody tell me how to solve?Thank you!
1 Answer 1
You should take a look at the GCM docs where it explains the GCM response: http://developer.android.com/google/gcm/gcm.html#response and troubleshooting the 401 error code: http://developer.android.com/google/gcm/gcm.html#auth_error
Description from the docs:
Authentication Error The sender account that you’re trying to use to send a message couldn’t be authenticated. Possible causes are:
Authorization header missing or with invalid syntax.
Invalid project number sent as key.
Key valid but with GCM service disabled.
Request originated from a server not whitelisted in the Server Key IPs.
So I would check to make sure that you are setting you authorization header properly and that you Google Project number is properly setup with GCM and accepting your servers IP.
Postman digest Authorization request return 401 Unauthrized
I use Postman 4.4.1 in Chrome 51.0.2704.63.I have set up a web project with Tomcat6, the web.xml like:
Can someone knows the reason and how to fix it?
2 Answers 2
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
From the beginning I have used a two step process with Digest Authentication build the request build the request from Firebug and send it and get the 401 copy the nonce and sometimes the opaque into the digest fields and resend for success. Discussions on the forums lead me to believe that it is still an issue. Am using 5.1.2 Windows App. I model my initial request on what I see in Firebug when I paste the url and get back the expected response.
Late answer but posting it here as my team struggled with this as well, while it’s just a matter of carefully reading the documentation.
(..) server responds with a few details, including a number that can be used only once (nonce), a realm value, and a 401 unauthorized response. You then send back an encrypted array of data including username and password combined with the data received from the server in the first request.
As it is already visible in the output you have provided, you are indeed provided with nonce, qop and opaque values. Hence, after the initial request that gets a 401 response, you would create another one, which would be almost the same as the previous one, just with the additional nonce, qop and opaque values set.
Friendly HTTP 401 Status Code Message?
I’m a developer not a wordsmith and as such I’m stuck.
We have a subscription based site whereby users may well come across our 401 page.
We’ve decided that the IIS 401;2 page needs replacing.
Does anyone have any examples or advise about writing a good non offensive 401 page?
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Through a series of highly sophisticated and complex algorithms, this system has determined that you are not presently authorized to use this system function. It could be that you simply mistyped a password, or, it could be that you are some sort of interplanetary alien-being that has no hands and, thus, cannot type. If I were a gambler, I would bet that a cat (an orange tabby named Sierra or Harley) somehow jumped onto your keyboard and forgot some of the more important pointers from those typing lessons you paid for. Based on the actual error encountered, I would guess that the feline in question simply forgot to place one or both paws on the appropriate home keys before starting. Then again, I suppose it could have been a keyboard error caused by some form of cosmic radiation; this would fit nicely with my interplanetary alien-being theory. If you think this might be the cause, perhaps you could create some sort of underground bunker to help shield yourself from it. I don’t know that it will work, but, you will probably feel better if you try something.
And don’t get me started on all the cool 404 pages out there.
An unexpected 401.1 status is returned when you use Pre-Authentication headers with Internet Explorer and IIS
This article resolves the problem where an unexpected 401.1 status is returned with Pre-Authentication headers. It occurs when you use Internet Explorer to browser to a web application hosted on Internet Information Services (IIS).
Original product version:В IE mode for Edge, Internet Information Services, Internet Explorer 11, 10, 9
Original KB number:В 2749007
Symptoms
Consider the following scenario:
In this scenario, IIS may return an HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 401.1 response to Internet Explorer in response to the browser’s request. The web browser may prompt you to enter your username and password. Or, the HTTP 401.1 error message may be displayed in the browser window.
Cause
This behavior is by design. The 401.1 response will occur if the web browser’s first request that’s sent to the IIS application contains one of the following headers:
There are many reasons a user may be prompted for credentials in Internet Explorer that are outside the scope of this article. See the More information section below to learn how to determine if the cause of the prompt is from the issue described here.
Workaround
To work around this behavior, disable Pre-Authentication in Internet Explorer, or turn off Kernel Mode Authentication for the IIS Web application.
If you use Registry Editor incorrectly, you may cause serious problems that may require you to reinstall your operating system. Microsoft can’t guarantee that you can solve problems that result from using Registry Editor incorrectly. Use Registry Editor at your own risk.
To modify this behavior in Internet Explorer, use Registry Editor ( Regedt32.exe ) to add a value to the following registry key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER/Software/Microsoft/Windows/CurrentVersion/Internet Settings/
The above registry key is one path; it has been wrapped for readability.
Add the following registry value:
To modify this behavior in IIS, disable Kernel Mode Authentication for the IIS web application.
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager by running the following command from an administrative command prompt:
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then the site, application, or Web service for which you want to disable Kernel Mode Authentication.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Windows Authentication.
Select Advanced Settings in the Actions pane.
When the Advanced Settings dialog box appears, clear the Enable Kernel-mode authentication checkbox.
Select OK to close the Advanced Settings dialog box.
Disabling Kernel Mode Authentication may cause web applications that require Kerberos authentication and delegation to fail.
More information
To determine if the prompt is caused by the issue described in this article, use the Fiddler tool. Use the tool to view the HTTP request/response traffic for the request resulting in the prompt in Internet Explorer. You’ll also need the IIS logs from the IIS Server to confirm the HTTP status and sub status codes. The following example uses Internet Explorer 9 to illustrate this behavior:
Start the Fiddler Tool and enable traffic capture.
Browse to the IIS web application such that it will result in the prompt for credentials.
In Fiddler, look for the request that resulted in the 401. Looking at the raw request and response views, you’ll see entries similar to the following ones:
The initial request to the web application already contains the Authorization header, which then results in the 401 response. The corresponding IIS log should show an entry similar to the following one:
The HTTP status and sub status are 401.1, which maps to Access Denied due to Invalid credentials.
For more information, see the following documentation:
403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses
For a web page that exists, but for which a user does not have sufficient privileges (they are not logged in or do not belong to the proper user group), what is the proper HTTP response to serve?
What I’ve read on each so far isn’t very clear on the difference between the two. What use cases are appropriate for each response?
21 Answers 21
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
There’s a problem with 401 Unauthorized, the HTTP status code for authentication errors. And that’s just it: it’s for authentication, not authorization. Receiving a 401 response is the server telling you, “you aren’t authenticated–either not authenticated at all or authenticated incorrectly–but please reauthenticate and try again.” To help you out, it will always include a WWW-Authenticate header that describes how to authenticate.
This is a response generally returned by your web server, not your web application.
It’s also something very temporary; the server is asking you to try again.
So, for authorization I use the 403 Forbidden response. It’s permanent, it’s tied to my application logic, and it’s a more concrete response than a 401.
Receiving a 403 response is the server telling you, “I’m sorry. I know who you are–I believe who you say you are–but you just don’t have permission to access this resource. Maybe if you ask the system administrator nicely, you’ll get permission. But please don’t bother me again until your predicament changes.”
In summary, a 401 Unauthorized response should be used for missing or bad authentication, and a 403 Forbidden response should be used afterwards, when the user is authenticated but isn’t authorized to perform the requested operation on the given resource.
Another nice pictorial format of how http status codes should be used.
If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it.
From your use case, it appears that the user is not authenticated. I would return 401.
Something the other answers are missing is that it must be understood that Authentication and Authorization in the context of RFC 2616 refers ONLY to the HTTP Authentication protocol of RFC 2617. Authentication by schemes outside of RFC2617 is not supported in HTTP status codes and are not considered when deciding whether to use 401 or 403.
Brief and Terse
Unauthorized indicates that the client is not RFC2617 authenticated and the server is initiating the authentication process. Forbidden indicates either that the client is RFC2617 authenticated and does not have authorization or that the server does not support RFC2617 for the requested resource.
Meaning if you have your own roll-your-own login process and never use HTTP Authentication, 403 is always the proper response and 401 should never be used.
Detailed and In-Depth
The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8).
10.4.4 403 Forbidden The server understood the request but is refusing to fulfil it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated.
The first thing to keep in mind is that «Authentication» and «Authorization» in the context of this document refer specifically to the HTTP Authentication protocols from RFC 2617. They do not refer to any roll-your-own authentication protocols you may have created using login pages, etc. I will use «login» to refer to authentication and authorization by methods other than RFC2617
So the real difference is not what the problem is or even if there is a solution. The difference is what the server expects the client to do next.
401 indicates that the resource can not be provided, but the server is REQUESTING that the client log in through HTTP Authentication and has sent reply headers to initiate the process. Possibly there are authorizations that will permit access to the resource, possibly there are not, but let’s give it a try and see what happens.
Checks are usually done in this order:
UNAUTHORIZED: Status code (401) indicating that the request requires authentication, usually this means user needs to be logged-in (session). User/agent unknown by the server. Can repeat with other credentials. NOTE: This is confusing as this should have been named ‘unauthenticated’ instead of ‘unauthorized’. This can also happen after login if session expired. Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja)
FORBIDDEN: Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but refused to fulfill it. User/agent known by the server but has insufficient credentials. Repeating request will not work, unless credentials changed, which is very unlikely in a short time span. Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja) in the case that revealing the presence of the resource exposes sensitive data or gives an attacker useful information.
NOT FOUND: Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not available. User/agent known but server will not reveal anything about the resource, does as if it does not exist. Repeating will not work. This is a special use of 404 (github does it for example).
As mentioned by @ChrisH there are a few options for redirection 3xx (301, 302, 303, 307 or not redirecting at all and using a 401):
According to RFC 2616 (HTTP/1.1) 403 is sent when:
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead
In other words, if the client CAN get access to the resource by authenticating, 401 should be sent.
Assuming HTTP authentication (WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers) is in use, if authenticating as another user would grant access to the requested resource, then 401 Unauthorized should be returned.
403 Forbidden is used when access to the resource is forbidden to everyone or restricted to a given network or allowed only over SSL, whatever as long as it is no related to HTTP authentication.
If HTTP authentication is not in use and the service has a cookie-based authentication scheme as is the norm nowadays, then a 403 or a 404 should be returned.
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The origin server MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.4) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource. If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.1). If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
The semantics of 403 (and 404) have changed over time. This is from 1999 (RFC 2616):
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead.
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
Thus, a 403 (or a 404) might now mean about anything. Providing new credentials might help. or it might not.
I believe the reason why this has changed is RFC 2616 assumed HTTP authentication would be used when in practice today’s Web apps build custom authentication schemes using for example forms and cookies.
Pusher Logo
Show navigation menu
In this tutorial, we will explore what status code means and how to use them. We will build a simple Node.js backend to simulate all the most common status codes of all we will cover. This will help us in two ways:
HTTP status codes are the defacto language for describing results of the requests browsers (clients) make to servers. Browsers know what the status codes mean, so they know how to present information to you after you make a request.
When you think about it, it makes sense to have defined ways for the server to tell the browser the outcome of a request it made. There are different kinds of browser and different kinds of server configurations to suit specific application needs. If there was no standard communication pattern… anarchy!
Prequisites
How the browser and server talk to each other
Before you ask “Really? This? Am I three years old?”, I’d urge you to pay attention here, especially if you have not had to build APIs before. Understanding how the browser talks to the server (client-server relationship) in a network will help you make sense of why each status code is important.
Servers are like a central location for data (say a restaurant) and clients are the computers that consistently interact with that data (say hungry customers). Different clients, something in thousands or hundreds of thousands, make requests to the server for data. The server does a number of things:
The server has to do all of that in split seconds so it can respond to other users who are waiting.
The client on the other hand sends a request along with appropriate headers to properly identify who it is and how it wants to receive the information it has requested. If it is trying to request gated information, it has to present some form of access token/key or be able to show it has authorization to access the data it is requesting. The client is usually not very patient as it is pressed for time and resources. If it does not hear from the server after some time, it closes the connection (just like a hungry customer walks away when they have waited too long to be served).
However, when the server responds, it sends some code to inform the client of the status of its request. Was it successful? Should the client give it more time? Did it fail? Could it not understand the request? Did the client make a mistake in the request it sent? These are the things the server clarifies with status codes.
Of course, client server communication is a lot more complex than that, and there are different tools and protocols that come into play, but that is beyond the scope of this article. What we have looked at now is sufficient to understand the basic status codes we will encounter more frequently when we interact with public APIs.
Clients are not just web browsers. Clients can be computer terminals that make CURL requests or web/mobile applications that interact with APIs to get data or even a device like a refrigerator or TV that is connected to the internet.
The informational status codes — 1xx
What do they do? Short answer — provide information to the browser. They communicate that the request was received and understood, and in most cases, the browser should wait a little as the server processes the information.
100 Continue
101 Switching Protocols
A client can send a request to the server to switch the communication protocol using the Upgrade header. This can be say switching from HTTP/1.1 to HTTP/2 or switching to WebSocket. The server will response with a response code 101 and an Upgrade response header with information on the protocol it upgraded to.
The success status codes — 2xx
These are the status codes we encounter every single day. You load a website and it comes up? One of these status codes was used. You submit a form and get the congratulations message? One of these status codes was used. They are used to indicate that our request was successful
200 Ok
This response status code indicates that our request was successful. This is used mostly when we request for data from the server and it responds with the data. When you visit the link to a webpage, the browser sends a request to the server to give it the contents of that webpage.
Many requests for data like visiting a URL are usually GET requests. GET requests are, well, used to get data from the server.
201 Created
This is the response code the client gets after sending resource (data) to the server. This resource is stored by the server and upon successfully storing it, the 201 Created response code is returned with the newly created resource as the request body. It can be form submissions, file uploads or other related activities.
Requests that create resources on the server are usually POST requests. POST requests post resources to the server. In a situation when a PUT request (which is used to update already stored resource) creates the a resource for the first time, a 201 Created can be returned as well.
202 Accepted
This is not a very common response code sent by servers. It is used in cases where a request by the client has been received but the server has sent it in for processing. It is a non-committal response in that when the server eventually comes around to process the request, it may or may not act upon it based on if the client has the right to make that request or if the server has the means to handle it. Also, it means the server will not be sending any response afterwards.
This can be used in cases when a request is transferred to another server or when a request is batched to be proceed at another time. In such a scenario, the server ought to return an indicator of the current status of the request and a way for the client to monitor the processing of the request.
203 Non-Authoritative Information
This is also not a very common response code. It signifies that the response the client is getting is not exactly as it was when sent by the server. It can mean that the response has been modified as it passed through a proxy tunnel or some other related third party.
The data eventually returned might be a subset or superset of the data returned from the server.
204 No Content
This response code tells the client (in the case of a user agent) not to change the current document presented to the user. Header information might be updated, but no new content will be sent along.
205 Reset Content
This response status tells the client to refresh the document sample.
206 Partial Content
This response code indicates that the request has succeeded and the response body has the requested ranges of data. The server only sends ranges of data when the client sets the Range header in it’s request. Bear in mind that the client must never request a range if it cannot handle the range.
If there is only one range, the Content-Type of the whole response is set to the type of the document, and a Content-Range is provided. If several ranges are sent back, the Content-Type is set to multipart/byteranges and each fragment cover one range, with Content-Range and Content-Type describing it.
Redirections — 3xx
You see these response codes, you need to know them very well if Search Engine Optimization (SEO) means anything to you and your product. These status codes deal with redirection when a client tries to access a resource.
300 Multiple Choices
This status code means the request has more than one possible response. The client is to choose one of them. There is no standardized way of choosing so this is rarely used. In case you see it, look for the Location header which usually contains the servers preferred choice.
301 Moved Permanently
This is arguably the most important of the redirection status codes. When not used properly, it can interfere with your SEO and bury your website forever. It can also created very bad user experience and increase the churn you experience on your website.
This tells the client that the resource they seek has been moved permanently, and then presents the URL to the new location of the resource. This does two things: tells the client where to find the resource and also helps the client know where to go the next time they need the resource. The new location for the resource is specified by the Location header.
301 redirects might require the method (and the body) of the original required not to be altered when the redirection is performed. However, not all client side browsers adhere to this directive. According to Mozilla Developer Docs, it is therefore recommended to use the 301 code only as a response for GET or HEAD methods and to use the 308 Permanent Redirect for POST methods instead, as the method change is explicitly prohibited with this status
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
When you have previously fetched a cacheable content, this status code comes in handy. It tells the client that the resource they are trying to fetch has not changed, so they should retain the copy they have. This will come in handy if you are building a system like a newsfeed and you always want to check for new updates. It will prevent you fetching old data and reloading the client browser unnecessarily.
A nice option would be to use Pusher’s realtime API.
307 Temporary Redirect
We have already talked about this earlier that it will be okay to skip it right? Well, this response code is sent by the server when it intends to explicitly tell the client to maintain the method originally used for the request. It works just like 302 except it adds a very clear directive not to change anything. Best thing to use in case you have stubborn clients who always change request methods on redirect 🙄.
308 Permanent Redirect
Client Error — 4xx
These are the status codes used to inform the client that it made a mistake in the request it made. Was a required field not supplied? Did they send the wrong data format? Are they not authorized to access the resource they are looking at? Do they need to confirm their identity? All of these things are handled by these status codes.
Now, let’s dig into them.
400 Bad Request
I have to admit, this is my favorite status code 😂. Every time I get slammed with 400 Bad Request red error on my console, I first look up and ask “What kind of life did I choose?” before I proceed to investigate it.
Bad requests occur when the client sends a request with either incomplete data, badly constructed data or invalid data. Many times, it could be the fault of the developer who did not specify properly what kind of data they expect. Be that as it may, it happens because the data you sent to a request is incorrect.
401 Unauthorized
This response in simple terms means the client needs to authenticate itself before it completes the request. Authentication here could be providing access-token in the case of OAuth or Authorization token in the case of jwt based auth system or even API keys.
Anything that the server needs to identify who is making a request has to be sent for the request to be completed.
403 Forbidden
This error occurs when a client tries to access a resource it is not permitted to. This is not the same as 401 Unauthorized (just see them as fraternal twins 😃). An authenticated client can be Forbidden from accessing a resource just as an unauthenticated client can.
Many times, the client only gets 403 Forbidden after it has been authenticated, as the system will have to ensure who the client is first before forbidding or granting them access to the resources.
404 Not Found
405 Method Not Allowed
Standard practice is that when a server sends a 405 response code, it includes a list of methods supported for accessing the resource in question.
406 Not Acceptable
This is a rarely used error code. It indicates that the server cannot produce a response that matches the request the user made, and the server is not willing to send a default response. You can learn more about it on Mozilla Developer Docs.
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
This response code is sent by the server when it wants to close an idle connection opened by the client. The client may not have completed its request and may be taking so much time doing it.
The standard is that a server will send a close Connection header in the response field along with the response code.
In many cases, the server might shut down the connection without sending any response code.
409 Conflict
This response is sent by the server when a request conflicts with the servers internal operations. A good example of such conflict is trying to update a resource on the server with an older version.
410 Gone
We already mentioned that this status code shows that the resource the client wishes to access has been permanently deleted.
411 Length Required
The server returns this status code if it requires that Content-Length header is set along with the request, and the client did not set it.
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
The request data is too big for the server to handle 😃. In more technical terms, the size of the payload may have exceeded the limit specified by the server.
414 URI Too Long
Just shorten the URL and all will be fine. Realistically, this only occurs when you have a lot of things appended to a URL when constructing a GET request with a lot of parameters.
415 Unsupported Media Type
This is what it is. The server does not support the media type requested by the client.
416 Range Not Satisfiable
The server can’t fulfill the Range specified in the request header. It could mean the Range is requesting more data than the server can give. Think array index out of bounds and you will get the picture.
417 Expectation Failed
When the server cannot meet the expectation contained in the Expect request header field, it sends this response.
418 I’m a teapot
I honestly do not know why this was ever made, but it is a response code for April Fool’s day prank. It means the server refuses to brew coffee because it is a tea pot 🤣. You can read more about this prank on WikiPedia.
419 Authentication Timeout
At the moment, this is only obtainable with Laravel applications. It means the csrf token of the application has expired. The csrf token in Laravel is sent with every form submission or request to resources protected by authentication and more.
426 Upgrade Required
The server returns this response code when it is unwilling to communicate with the client via a certain protocol, but is willing to continue communication if they change protocols. Yep, I agree… These servers are just full of themselves.
The server sends an Upgrade header with this response to provide a list of protocols it is willing to use in continuing communication.
428 Precondition Required
This response is sent by the server when it requires a request to be conditional. A conditional request is a request where the result might change based on a validation of the resource requested. Conditional requests are useful in scenarios like downloads where a client can pause and resume at any time.
For such requests, a required precondition header like If-Match is required. If the precondition header does not match what the server has, then a 412 Precondition Failed is sent instead.
429 Too Many Requests
This status code is sent when a user has sent too many requests than allowed in a given period of time. It is common with APIs that limit usage by time period.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
The server is just unwilling to process the request because it feels the headers of the request are too large. That is all.
The client can reduce the headers and try the request again.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
The resource the client has requested cannot be served for some legal reasons. Serving it to that user will mean breaking the law.
In practice, you will rarely encounter most of the error codes, but it is good you know them. They become more common with increasing complexity of the applications you build.
Error — 5xx
These errors occur due to no fault of the client. The servers are to be blamed here and there is nothing the client can do to get their desired response.
500 Internal Server Error
501 Not Implemented
The server sends this code when you have made a request to it with a request method it does not know or have the capacity to resolve. Servers are required to implement only GET and HEAD methods, so you might send a PUT or PATCH request and the server will not be able to handle it.
This is not the same as 405 Method Not Allowed because with 405 the server clearly understands the request but cannot respond to it until the method is changed. With 501 the server cannot understand the method used and is therefore incapable of providing any response.
502 Bad Gateway
The server sends this code when it is acting as a proxy server and/or fetching data from an external resource and it gets an invalid response from that external source.
503 Service Unavailable
This is a common server error code that you can get. It means the server might be down and therefore, is not ready handle the request at that time. This might be a result of an ongoing maintenance or an overload on the server.
This is a temporal situation, so if you implement caching in your application, you might want to not cache this response.
504 Gateway Timeout
The direct sibling to 502 😃. The server sends this response code when it is acting as a gateway and the external resource does not provide it with a response in time.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
This status code indicates the HTTP version the client used for the request is not supported by the server. Think making a HTTP/1.1 call to a server when the server only deals in HTTP/2 😎.
511 Network Authentication Required
Where there is a difference is that 401 tells the client directory it needs to be authenticated but 511 means the proxy network cannot access the external resource because of lack of proper authorization.
Conclusion
If you followed this tutortial, then you my friend are more than ready to build very amazing web applications. A proper understanding of these status codes makes all the difference in the user experience of your application. Understanding them means you can efficiently design your application to handle errors or issues that may arise gracefully.
If you are a developer building an API, you can more easily send the appropriate responses for the scenarios your users encounter as they use your application. This is equally very important in building useful applications.
In the next tutorial, we will look it is consuming APIs and experiencing the status codes we have received.
ez code
Просто о сложном.
Описание кодов состояния HTTP
Код состояния HTTP — часть первой строки ответа сервера при запросах по протоколу HTTP. Он представляет собой целое число из трёх арабских цифр. Первая цифра указывает на класс состояния. За кодом ответа обычно следует отделённая пробелом поясняющая фраза на английском языке, которая разъясняет человеку причину именно такого ответа.
Клиент узнаёт по коду ответа о результатах его запроса и определяет какие действия ему предпринимать дальше. Набор кодов состояния является стандартом, и они описаны в соответствующих документах.
В этой статье представлен список и описание кодов состояния HTTP.
Коды 3xx (перенаправление)
Перечень кодов статуса HTTP, использующихся при перенаправлении запроса (коды 3xx).
| Код | Ошибка | Описание |
| 300 | Множественный выбор | Затребованный URL обозначает более одного ресурса (получен код 300 Multiple Choices). |
| 301 | Ресурс перемещен навсегда | Документ уже не используется сервером, а ссылка перенаправляет на другую страницу (получен код 301 Moved Permanently). |
| 302 | Ресурс временно перемещен | Запрошенный ресурс временно находится под другим адресом (получен код 302 Found). |
| 303 | Смотрите другой ресурс | Запрошенный ресурс находится под другим адресом и его следует запрашивать, используя метод GET (получен код 303 See Other). |
| 304 | Ресурс не изменялся | Получен код 304 Not Modified. |
| 305 | Следует использовать прокси | Доступ к затребованному ресурсу может осуществляться только через прокси-сервер, указанный в заголовке Location (получен код 305 Use Proxy). |
| 307 | Временное перенаправление | Затребованный ресурс был временно переведен на другой адрес, который необходимо прописать в Location (получен код 307 Temporary Redirect). |
Коды 4xx (ошибка клиента)
Содержит перечень кодов статуса HTTP, использующихся для обозначения возможных ошибок в клиентском запросе (коды 4xx).
| Код | Ошибка | Описание |
| 400 | Неверный запрос | Запрос не может быть понят сервером из-за некорректного синтаксиса (получен код 400 Bad Request). |
| 401 | Неавторизованный запрос | Для доступа к документу необходимо вводить пароль или быть зарегистрированным пользователем (получен код 401 Unauthorized). |
| 402 | Необходима оплата за запрос | Внутренняя ошибка или ошибка конфигурации сервера (получен код 402 Payment Required). |
| 403 | Доступ к ресурсу запрещен | Доступ к документу запрещен (получен код 403 Forbidden). Если вы хотите, чтобы страница индексировалась, необходимо разрешить доступ к ней. |
| 404 | Ресурс не найден | Документ не существует (получен код 404 Not Found). Если вы удалили какой-то раздел сайта, можно с помощью robots.txt запретить роботу обращаться к нему. Если такой страницы на сайте никогда не существовало, игнорируйте эту ошибку, возможно, кто-то поставил некорректную ссылку на ваш сайт. |
| 405 | Недопустимый метод | Метод, определенный в строке запроса (Request-Line), не дозволено применять для указанного ресурса (получен код 405 Method Not Allowed). |
| 406 | Неприемлемый запрос | Нужный документ существует, но не в том формате (язык или кодировка не поддерживаются). Получен код 406 Not Acceptable. |
| 407 | Требуется идентификация прокси, файервола | Необходима регистрация на прокси-сервере (получен код 407 Proxy Authentication Required). |
| 408 | Время запроса истекло | Сайт не передал полный запрос в течение установленного времени (получен код 408 Request Timeout). |
| 409 | Конфликт | Запрос конфликтует с другим запросом или с конфигурацией сервера (получен код 409 Conflict). |
| 410 | Ресурс недоступен | Затребованный ресурс был окончательно удален с сайта (получен код 410 Gone). |
| 411 | Необходимо указать длину | Сервер отказывается принимать запрос без определенного заголовка Content-Length (получен код 411 Length Required). Поправьте заголовки на своем сервере. |
| 412 | Сбой при обработке предварительного условия | При проверке на сервере одного или более полей заголовка запроса обнаружено несоответствие (сбой или ошибка при обработке предварительного условия). Получен код 412 Precondition Failed. |
| 413 | Тело запроса превышает допустимый размер | Сервер отказывается обрабатывать запрос потому, что размер запроса больше того, что может обработать сервер (получен код 413 Request Entity Too Large). |
| 414 | Недопустимая длина URI запроса | Сервер отказывается обслуживать запрос, потому что запрашиваемый URI (Request-URI) длиннее, чем сервер может интерпретировать (получен код 414 Request-URI Too Long). |
| 415 | Неподдерживаемый MIME тип | Сервер отказывается обрабатывать запрос, потому что тело запроса имеет неподдерживаемый формат (получен код 415 Unsupported Media Type). |
| 416 | Диапазон не может быть обработан | Сервер отказывается обрабатывать запрос, потому что значение поля Range в заголовке запроса указывает на недопустимый диапазон байтов (получен код 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable). |
| 417 | Сбой при ожидании | Сервер отказывается обрабатывать запрос, потому что значение поля Expect в заголовке запроса не соответствует ожиданиям (получен код 417 Expectation Failed). |
| 422 | Необрабатываемый элемент | Сервер не в состоянии обработать один (или более) элемент запроса (получен код 422 Unprocessable Entity). |
| 423 | Заблокировано | Сервер отказывается обработать запрос, так как один из требуемых ресурсов заблокирован (получен код 423 Locked). |
| 424 | Неверная зависимость | Сервер отказывается обработать запрос, так как один из зависимых ресурсов заблокирован (получен код 424 Failed Dependency). |
| 426 | Требуется обновление | Сервер запросил апгрейд соединения до SSL, но SSL не поддерживается клиентом (получен код 426 Upgrade Required). |
Коды 5xx (ошибка сервера)
Перечень кодов статуса HTTP, использующихся для обозначения возможных ошибок сервера (коды 5xx).
What’s the appropriate HTTP status code to return if a user tries logging in with an incorrect username / password, but correct format?
The answer in the thread above states that «For instance if the URI is supposed to have an ISO-8601 date and you find that it’s in the wrong format or refers to February 31st, then you would return an HTTP 400. Ditto if you expect well-formed XML in an entity body and it fails to parse.»
However, what happens if the user submitted correctly formatted data? By this I mean, the user submitted a plain alphabetical string / text for the username and password (which is perfectly valid for my application). The only issue is that the password did not match with the username. In this case, 400 will be incorrect because it is perfectly valid syntax and well-formed.
A 401 would be incorrect (as suggested here: Which HTTP status code to say username or password were incorrect?) because the user is not trying to access any page, he is simply trying to login and entered data which does not match.
If you look back at the first post I linked to, the second answer states that 422 is the correct response (and it looks correct to me), however, I am using Django Rest Framework and 422 is not part of the status codes (a list of the status codes which are part of DRF can be found here: http://www.django-rest-framework.org/api-guide/status-codes/#client-error-4xx)
404 also doesn’t look right because the data is successfully accepted and not refused.
With that said, what is the real correct response which should be used?
4 Answers 4
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
If you are strictly using the HTTP authentication framework provided by RFC 7235 for your REST API, the correct HTTP code would actually be 401. From the RFC:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The user agent MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.2).
Your REST API should employ an authentication scheme of some sort in order to return a valid 401 response to your client.
Another pertinent section from RFC 7235, page 4:
Upon receipt of a request for a protected resource that omits
credentials, contains invalid credentials (e.g., a bad password) or
partial credentials (e.g., when the authentication scheme requires
more than one round trip), an origin server SHOULD send a 401
(Unauthorized) response that contains a WWW-Authenticate header field with at least one (possibly new) challenge applicable to the
requested resource.
A higher-level response, such as a rendered login page for a visual user (redirected from a protected resource via 302), would be better served with the 200 status code (per @KernelDeimos’ answer, for example). Since login pages are typically their own resource (e.g. /login?redirect=original-resource ), the unauthenticated user is still authorized to see this page, even if they provide an incorrect username/password. Then, you redirect the authenticated user back to the resource, at which point would show 200 if allowed, or 403 if the user is forbidden to view the resource.
The area where 401 could come into play with a visual login page is a front-end library that leverages the REST API using XHR requests, then relay the 401 response from the REST API back into a meaningful format on the login page.
401 Unauthorized vs 403 Forbidden: Which is the right status code for when the user has not logged in? [duplicate]
After lots of Googling and Stackoverflowing, it still isn’t clear to me because many articles and questions/answers were too general (including 403 Forbidden vs 401 Unauthorized HTTP responses which was not specifically for my use-case).
Question: What’s the proper HTTP Status Code when the user has not logged in and requests to see some pages that should be shown only to logged-in users?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The exact satisfying one-time-for-all answer I found is:
401 Unauthorized
While we know first is authentication (has the user logged-in or not?) and then we will go into authorization (does he have the needed privilege or not?), but here’s the key that makes us mistake:
But isn’t “401 Unauthorized” about authorization, not authentication?
Back when the HTTP spec (RFC 2616) was written, the two words may not have been as widely understood to be distinct. It’s clear from the description and other supporting texts that 401 is about authentication.
So maybe, if we want to rewrite the standards! focusing enough on each words, we may refer to the following table:
It depends on the mechanism you use to perform the login.
The spec for 403 Forbidden says:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
While 401 Unauthorized is not defined in the main HTTP status codes spec but is in the HTTP Authentication spec and says:
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource.
So if you are using WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers as your authentication mechanism, use 401. If you are using any other method, then use 403.
Angular 2 REST request HTTP status code 401 changes to 0
I’m developing an Angular2 application. It seems when my access-token expires the 401 HTTP Status code gets changed to a value of 0 in the Response object. I’m receiving 401 Unauthorized yet the ERROR Response object has a status of 0. This is preventing me from trapping a 401 error and attempting to refresh the token. What’s causing the 401 HTTP status code to be changed into HTTP status code of 0?
Here’s screenshot from Firefox’s console:
This code resides in a custom http service that extends Angular2’s HTTP so I can intercept errors in a single location.
In Google Chrome, I get this error message:
XMLHttpRequest cannot load https://api.cloudcms.com/repositories/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX/branches/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX/nodesXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX. No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource. Origin ‘http://screwtopmedia.local.solutiaconsulting.com’ is therefore not allowed access. The response had HTTP status code 401.
This is confusing because I am including ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header in request.
Here’s a picture of results received in Google Chrome:
I’ve tried accessing ‘WWW-Authenticate’ Response Header as a means to trap for 401. However, the following code returns a NULL:
It’s puzzling that I’m getting a CORS issue because I’m not getting any CORS errors when a valid access token is provided.
How do I trap for 401 HTTP status code? Why is 401 HTTP status code being changed to 0?
Thanks for your help.
7 Answers 7
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
The issue is related to CORS requests, see this github issue
No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource
means that ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ is required in the response headers.
If cloudcms.com do to not set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin in 401 response, then nothing much you can do. You properly have to open support ticket with them to confirm if that is normal behavior.
javascript in browsers(FF, Chrome & Safari) I tested won’t receive any info if CORS error occur, other than status 0. Angular2 has no control of it.
I created a simple test and get the same result as yours:
lucassp commented on Aug 19, 2013
I found the issue for a while now but I forgot post here a reply. EVERY response, even Error 500, must have the CORS headers attached. If the server doesn’t attach the CORS headers to the Error 500 response then the XHR Object won’t parse it, thus the XHR Object won’t have any response body, status, or any other response data inside.
Result from Firefox network monitor seems supporting the above reason.
Javascript request will receive empty response.
Plain url request(copy&paste the link in the address bar) will get response body
Javascript use XHRHttpRequest for http communication.
When a XHR reply arrive, the browser will process the header, that’s why you will see those 401 network messages. However, if the XHR reply is from a different host then the javascript AND the response header contain no CORS header(eg Access-Control-Allow-Origin: * ), the browser will not pass any info back to the XHR layer. As a result, the reply body will be completely empty with no status(0).
I tested with FF 48.0.1, Chrome 52.0.2743.116 and Safari 9.1.2, and they all have the same behavior.
Use browser network monitor to check response header for those 401 Unauthorized entries, it is very likely that there is no Access-Control-Allow-Origin header and causing the issue you are facing. This can be a bug or by design on the service provider side.
everyone. I’m new to Angular 2 and Spring Framework. I’m trying a simple get request with an authorization header (basic auth).
I’m using Spring Boot (1.2.6.RELEASE), which can also be relevant. My CORS configuration looks like this.
And here’s what it looks like from the client side
XMLHttpRequest cannot load http://localhost:8080/api/login?username=user. Response for preflight has invalid HTTP status code 401
Please help, i don’t know what i’m missing. I checked around a lot of posts already but couldn’t get there.
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
This could be very late but this could solve some ones problem, after long hours i found the answer
avoid filtering and set status 200 when http method is OPTIONS
If there is anyone getting into the similar situation working around with Spring Boot, Spring Security and clients like angular 2/4, I’ve posted the findings here.
For those who are looking for a short answer, you have to configure two things:
With Spring Boot, the recommended way to enable global CORS is to declare within Spring MVC and combined with fine-grained @CrossOrigin configuration as:
Then, while working with Spring Security, you have to enable CORS at Spring Security level as well to allow it to leverage the configuration defined at Spring MVC level as:
Why my httpwebrequest post to myhandler.ashx is rejected with status code 401
Application Trace (trace.axd) shows the following as my last 3 entries:
Here is a snippet of code from the UploadHandler.ashx file (but this doesn’t appear to be reached):
Both default.aspx and UploadHandler.ashx are in the root of a virtual directory on my localhost; the directory security is currently set to «Anonymous access» CHECKED and «Integrated Windows authentication» CHECKED.
When I click the «View Details» link on the trace.axd display, I see all the data in the Forms collection that I expect to see and hope to process but this 401 seems to be stopping everything. I could post the code for my little function called BuildFormData() if useful.
EDIT: Revised handler as follows (has had no effect; same error occurs):
2 Answers 2
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Have you tried turning off Integrated Windows Auth and just leaving anonymous checked? Does it make a difference?
My response: This is actually a good thing. This means we’re getting closer to what is going on. If you’re getting that error message and the only thing you have enabled is anonymous authentication via IIS, that means that the ASP.NET impersonation user doesn’t have NTFS permissions on the files in question.
I’m not sure if you are on XP or Win 2k3, but now you want to check and make sure that either the ASPNET (XP) or Network Service (Win 2k3) users have at least read access on the files in question. Make sure that user has at least that level of access and then let me know how it goes.
Update: I don’t know why I didn’t think of this before. You may need to set credentials on your HttpWebRequest. To use the credentials of the current user, try adding this to your request.
If you need to add different credentials you can try Network Credentials
What do the HTTP status codes, such as 403, 404, 500, mean?
For every request from a webbrowser the server responds with a status code. If there was a error, you can get additional information about the error. You can find the most frequent error codes and a brief description in the list below.
The server can’t process the request due to clientside errors.
The 401 status code indicates that the HTTP request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials (usually username and password) for the target resource.
If the request included authentication credentials, the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. Please check if your username and password are correct.
Sometimes user authentication was provided, but the authenticated user is not permitted to view the content of the folder or file. Other times the operation is forbidden to all users. Sometimes this error occurs if there are too many connections at the same time. The easyname support team can explain you this issue in depth.
This error message is shown when a site or folder on a server are requested but cannot be found at the given URL. Please check your input.
Please note that this error can also appear if there is no start file (index.php or index.html).
The IP address is automatically unblocked after some time and access to the web application is then possible again. The time period depends on the severity of the violation.
Another possibility to make it accessible again is to deactivate the application firewall. It can be deactivated either for the entire web hosting or only for individual subdomains.
For the entire web hosting: Go to the menu item [Web Hosting] then to [Web Server Settings]. In the left-hand panel General, switch off «Mod Security» and click on the «Save» button.
This option causes new subdomains to be created without protection by the application firewall. For already existing subdomains, the protection must be removed manually.
For individual subdomains: Go to the menu item [Web Hosting] then [Subdomains]. Click on the blue pen symbol (Edit) next to the corresponding subdomain. Then click on the link Advanced Options. A menu will open in which you will see a tick next to «Activate application firewall». Click on the tick to deactivate the application firewall. Save your settings by clicking on the «Save» button.
Disabling the Application Firewall will make your web application or website more vulnerable to attackers. It is therefore not recommended to disable it.
The server took longer than it’s allocated timeout window. In this case the server terminates the connection.
The HTTP 429 Too Many Requests response status code indicates the user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time.
A Retry-After header might be included to this response indicating how long to wait before making a new request. For example if more than 50 requests are received from the same IP address (cumulative hits) within the same second, our server will block that IP for the next 10 minutes as a security measure.
This HTTP status code indicates, that under the specified URL there’s no content to be displayed.
This means, that the server is currently unavailable or the server is overallocated. You can check the file php_error.log as described for the status code 500.
Should you not find helpful error messages in the logfile, please try changing the session_cache to the option filesystem, you can do this in the easyname control panel if you navigate to [Web Hosting] → [PHP settings] and click the link «Settings».
Please note that this change will take up to 15 minutes to take effect, so please try waiting 15 minutes before trying to call up your site and refresh it.
This means, that the server has not responded within the specified time period.
Is it OK to return a HTTP 401 for a non existent resource instead of 404 to prevent information disclosure?
Inspired by a thought while looking at the question «Correct HTTP status code when resource is available but not accessible because of permissions», I will use the same scenario to illustrate my hypothetical question.
Imagine I am building a a carpooling web service.
Suppose the following
retrieves the current position of user «angela». Only angela herself and a possible driver that is going to pick her should be able to know her location, so if the request is not authenticated to an appropriate user, a 401 Unauthorized response is returned.
Also consider the request
when no user called john has registered with the system. There is no john resource let alone a resource for john’s location, so this obviously returns a 404 Not Found. Or does it?
What if I don’t want to reveal whether or not john is registered with the system?
(Perhaps the usernames are drawn from a small pool of university logins, and there is a very militant cycling group on campus that takes a very dim view of car usage, even if you are pooling? They could make requests to the URL for every user, and if they receive a 401 instead of 404, infer that the user is a car pooler)
Does it make sense to return a 401 Unauthorized for this request, even though the resource does not exist and there is no possible set of credentials that could be supplied in a request to have the server return a 200?
Axios post request failed with status code 401
Hi so Im trying to pull data from https://opentimetable.dcu.ie/ based on the course code so like CASE3, so im trying to pull the weeks timetable, but im new to axios and my post request is failing because of the headers i believe and im not sure why I thought i was doing it correct? im basically trying to get the course identity in the api in the post request below
1 Answer 1
401 error status response code indicates that the request lacks valid authentication credentials. So I was doubtful about your authorization token. However, using postman, I got 200 ok. So the token is fine. So my guess is authorization was failing because of the way you are passing headers. Anyways, Here the code, let me know if it works.
I’m trying to return 401 response status in my AngularJS app. But in console that I see, it returns -1
What I use in php:
Also in codeigniter:
1 Answer 1
You are making a cross origin request from XMLHttpRequest.
In a simple case, this means that the server has to grant permissions to the JavaScript before the browser will give the data to the JavaScript.
This is not a simple case. You are making a complex request which requires preflight authorisation.
Before making the POST request you want to make, the browser is making an OPTIONS request asking for permission.
The server is responding to the OPTIONS request with a 401 response. The error message tells you this explicitly:
Response for preflight has invalid HTTP status code 401
The browser is then refusing to make the POST request at all.
You need to respond to the OPTIONS request with a 200 status (and appropriate CORS permissions headers). Then the browser will make a POST request (which you can reject with a 401 if you like).
403 Forbidden и 401 Unauthorized HTTP-ответы
Для веб-страницы, которая существует, но для которой пользователь не имеет достаточных прав (они не вошли в систему или не принадлежат к надлежащей группе пользователей), какой ответ HTTP следует обслуживать?
То, что я читал по каждому из них, пока не очень ясно показывает разницу между ними. Какие варианты использования подходят для каждого ответа?
задан 21 июля ’10, 04:07
17 ответы
Четкое объяснение от Дэниел Ирвин:
Это ответ, обычно возвращаемый вашим веб-сервером, а не вашим веб-приложением.
Это тоже что-то очень временное; сервер просит вас повторить попытку.
Итак, для авторизации я использую 403 Запрещено отклик. Он постоянный, он привязан к логике моего приложения, и это более конкретный ответ, чем 401.
При получении ответа 403 сервер говорит вам: «Мне очень жаль. Я знаю, кто вы, я верю в то, кем вы себя называете, но у вас просто нет разрешения на доступ к этому ресурсу. Может быть, если вы вежливо спросите системного администратора, вы получите разрешение. Но, пожалуйста, не беспокой меня больше, пока твое затруднительное положение не изменится ».
Таким образом, 401 Несанкционированный ответ должен использоваться для отсутствующей или неправильной аутентификации, а 403 Запрещено ответ следует использовать позже, когда пользователь аутентифицирован, но не авторизован для выполнения запрошенной операции с данным ресурсом.
Другой красивый графический формат о том, как следует использовать коды состояния http.
401 не авторизован:
Если запрос уже включал учетные данные авторизации, то ответ 401 указывает, что в авторизации для этих учетных данных было отказано.
Сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его выполнить.
Из вашего варианта использования кажется, что пользователь не аутентифицирован. Я бы вернул 401.
ответ дан 17 мар ’21, в 22:03
Что-то отсутствует в других ответах, так это то, что необходимо понимать, что аутентификация и авторизация в контексте RFC 2616 относятся ТОЛЬКО к протоколу HTTP-аутентификации RFC 2617. Аутентификация по схемам за пределами RFC2617 не поддерживается в кодах состояния HTTP и не считается при принятии решения, использовать ли 401 или 403.
Кратко и лаконично
Неавторизованный означает, что клиент не прошел проверку подлинности RFC2617 и сервер инициирует процесс проверки подлинности. Запрещено означает, что либо клиент аутентифицирован по RFC2617 и не имеет авторизации, либо сервер не поддерживает RFC2617 для запрошенного ресурса.
Это означает, что если у вас есть собственный процесс входа в систему и вы никогда не используете HTTP-аутентификацию, 403 всегда будет правильным ответом, а 401 никогда не следует использовать.
Подробно и подробно
Запрос требует аутентификации пользователя. Ответ ДОЛЖЕН включать поле заголовка WWW-Authenticate (раздел 14.47), содержащее запрос, применимый к запрошенному ресурсу. Клиент МОЖЕТ повторить запрос с подходящим полем заголовка авторизации (раздел 14.8).
10.4.4 403 Запрещено Сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его выполнить. Авторизация не поможет и запрос НЕ ДОЛЖЕН повторяться.
Первое, что следует иметь в виду, это то, что «Аутентификация» и «Авторизация» в контексте этого документа относятся конкретно к протоколам HTTP-аутентификации из RFC 2617. Они не относятся к каким-либо протоколам собственной аутентификации, которые вы, возможно, создали. с использованием страниц входа в систему и т. д. Я буду использовать слово «вход» для обозначения аутентификации и авторизации другими методами, кроме RFC2617.
Таким образом, реальная разница не в том, в чем проблема, и даже не в том, есть ли решение. Разница в том, что сервер ожидает от клиента следующих действий.
401 указывает, что ресурс не может быть предоставлен, но сервер ТРЕБУЕТ, чтобы клиент вошел в систему через HTTP-аутентификацию и отправил заголовки ответа для запуска процесса. Возможно, есть авторизации, которые разрешают доступ к ресурсу, возможно, нет, но давайте попробуем и посмотрим, что произойдет.
Проверки обычно выполняются в таком порядке:
НЕСАНКЦИОНИРОВАНО: Код состояния (401), указывающий, что запрос требует идентификация, обычно это означает, что пользователю необходимо войти в систему (сеанс). Пользователь / агент неизвестен серверу. Можно повторить с другими учетными данными. ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ. Это сбивает с толку, так как это должно было быть названо «неавторизованным», а не «неавторизованным». Это также может произойти после входа в систему, если срок сеанса истек. Особый случай: Можно использовать вместо 404 чтобы избежать выявления наличия или отсутствия ресурса (кредиты @gingerCodeNinja)
ЗАПРЕЩЕНО: Код состояния (403), указывающий, что сервер понял запрос, но отказался его выполнить. Пользователь / агент известен серверу, но имеет недостаточные полномочия. Повторный запрос не будет работать, если не будут изменены учетные данные, что очень маловероятно за короткий промежуток времени. Особый случай: Можно использовать вместо 404 чтобы избежать раскрытия наличия или отсутствия ресурса (кредиты @gingerCodeNinja) в случае, если раскрытие наличия ресурса раскрывает конфиденциальные данные или дает злоумышленнику полезную информацию.
НЕ НАЙДЕНО: Код состояния (404), указывающий, что запрошенный ресурс недоступен. Пользователь / агент известен, но сервер ничего не раскрывает о ресурсе, как будто он не существует. Повторить не получится. Это специальное использование 404 (например, github).
Как упоминал @ChrisH, есть несколько вариантов для перенаправление 3xx (301, 302, 303, 307 или вообще без перенаправления и с использованием 401):
ответ дан 01 апр.
Согласно информации RFC 2616 (HTTP / 1.1) 403 отправляется, когда:
Сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его выполнить. Авторизация не поможет и запрос НЕ ДОЛЖЕН повторяться. Если метод запроса не был HEAD и сервер желает обнародовать причину невыполнения запроса, он ДОЛЖЕН описать причину отказа в объекте. Если сервер не желает предоставлять эту информацию клиенту, вместо этого можно использовать код состояния 404 (Not Found).
Другими словами, если клиент МОЖЕТ получить доступ к ресурсу путем аутентификации, необходимо отправить 401.
Создан 21 июля ’10, 08:07
Предполагая HTTP-аутентификацию (WWW-Authenticate и Авторизация заголовки) используется, если аутентификация от имени другого пользователя предоставит доступ к запрошенному ресурсу, то следует вернуть 401 Unauthorized.
403 Forbidden используется, когда доступ к ресурсу запрещен для всех, ограничен определенной сетью или разрешен только через SSL, если это не связано с HTTP-аутентификацией.
Если HTTP-аутентификация не используется и служба имеет схему аутентификации на основе файлов cookie, что является нормой в настоящее время, тогда следует возвращать 403 или 404.
Код состояния 401 (неавторизован) указывает, что запрос не был применен, поскольку ему не хватает действительных учетных данных для аутентификации для целевого ресурса. Исходный сервер ДОЛЖЕН отправить поле заголовка WWW-Authenticate. (Раздел 4.4), содержащий как минимум одну проблему, применимую к целевому ресурсу. Если запрос включал учетные данные аутентификации, то ответ 401 указывает, что в авторизации для этих учетных данных было отказано.. Клиент МОЖЕТ повторить запрос с новым или замененным полем заголовка авторизации (раздел 4.1). Если ответ 401 содержит тот же вызов, что и предыдущий ответ, и пользовательский агент уже пытался аутентифицироваться хотя бы один раз, то пользовательский агент ДОЛЖЕН предоставить пользователю вложенное представление, поскольку оно обычно содержит релевантную диагностическую информацию.
Семантика 403 (и 404) со временем изменилась. Это с 1999 года (RFC 2616):
Сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его выполнить. Авторизация не поможет и запрос НЕ ДОЛЖЕН повторяться. Если метод запроса не был HEAD и сервер желает обнародовать причину невыполнения запроса, он ДОЛЖЕН описать причину отказа в объекте. Если сервер не желает предоставлять эту информацию клиенту, вместо этого можно использовать код состояния 404 (Not Found).
Код состояния 403 (Запрещено) указывает, что сервер понял запрос, но отказывается его авторизовать. Сервер, который желает сделать общедоступным, почему запрос был запрещен, может описать эту причину в полезных данных ответа (если таковые имеются).
Если в запросе были указаны учетные данные для аутентификации, сервер считает их недостаточными для предоставления доступа. Клиенту НЕ СЛЕДУЕТ автоматически повторять запрос с теми же учетными данными. Клиент МОЖЕТ повторить запрос с новыми или другими учетными данными. Однако запрос может быть запрещен по причинам, не связанным с учетными данными.
Исходный сервер, который желает «скрыть» текущее существование запрещенного целевого ресурса, МОЖЕТ вместо этого ответить кодом состояния 404 (Not Found).
Я считаю, что причина, по которой это изменилось, заключается в том, что RFC 2616 предполагает, что HTTP-аутентификация будет использоваться, когда на практике сегодняшние веб-приложения создают собственные схемы аутентификации, используя, например, формы и файлы cookie.
What HTTP status code for unactivated account?
Which HTTP status code should I respond with after authenticating the user and then finding out that they have not activated their account after registration?
3 Answers 3
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
401 means that the user is unknown (not authenticated at all or authenticated incorrectly, e.g. the credentials are invalid).
403 means that the user is known but not authorized (i.e. doesn’t have the proper role/group).
You could also interpret a registered but inactivated account as an user having a specific role like «INACTIVE» and/or lacking the proper role. 403 is more appropriate in your particular case.
If you deem that an account that has not been activated should not be authorised, then the response should surely have a 401 Unauthorized status code.
I think a 403 Forbidden would also be appropriate, yes. However in your case I think 401 Unauthorized is more appropriate.
This answer summarises the two quite well, quoting this for 401 Unauthorized:
If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.
That certainly applies, as your case suggests they have provided credentials but those credentials aren’t valid as the account has not been activated (which you deem as unauthorized).
@Josh Davenport: You described authorization and authentication in each other’s place: authentication is credential checking, authorization is role/group assignment.
On the other hand, as you stated in comment to yourself, 401 assumes both failed authentication and authorization in one go. User needs to fail both to get 401. 403 is used in cases where data is completely Forbidden and authentication is not performed/necessary at all.
As an analogy: 401 = checkpoint where credentials are checked. 403 = STOP sign, can’t enter.
To answer the question of OP: 401 is logically the status code for unactivated account, BUT since it requires HTTP-Auth implementation, 403 might be used instead of it, if you are authenticating and authorizing by other means. I personally would still stick to 401, since standards don’t necessarily cover all real-life situations. Nowadays almost noone use HTTP-Auth for authentication purposes.
Let’s learn HTTP Status Codes
HTTP status codes are a set of standard responses sent by a web server to a client (such as a web browser) indicating whether a specific HTTP request was completed successfully or not.
We have 5 categories under which these responses are classified:
There are quite a number of HTTP status codes available but I’m not going to cover all in this article. I’ll only go over the ones that frequently occur in the course of web application development.
To follow along, all you need is a working internet connection and your web browser. I also make use of a command line utility known as curl to display response headers for various requests in the terminal. If you want to try that as well, find out how to install curl on your favourite operating system.
200 OK
This status code indicates that the request made was successful. The HTTP request method used is what decides when a request should be considered successful. For example, a GET request will return 200 OK if the requested resource was retrieved successfully and transmitted in the response body.
301 Moved permanently
A 301 status code is sent to the client when the requested resource has been moved permanently to a new location. This location can be found in the response headers.
The browser will automatically redirect to the new location and search engines will update their links to point to the new URL. A 301 redirect instructs the browser to use the new location for subsequent requests until the cache is cleared.
To see this in action, open a new tab in your browser, fire up the developer tools, and click the network tab. Then load freecodecamp.com again into your address bar.
302 Found
This status code is also used for redirection, but the HTTP 1.1 spec states that it should only be used for temporary redirects. This means that the resource is only temporarily moved and the client should continue using the original URL for future requests. In addition, search engines will not update indexed links to the entity.
304 Not Modified
The 304 Not Modified response is essentially a caching mechanism implemented to prevent unnecessary server requests and improve performance. When the browser stores something in its cache, it also stores a Last-Modified or ETag header gotten from the server.
When making requests to the server for a cached asset, the browser will send request headers which may contain a If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match field which the server uses to determine if a 304 response is appropriate or not.
The Last-Modified and ETag response headers are what the browser uses to set the values of If-Modified-Since and If-None-Match request headers respectively.
A 304 response is triggered if the requested resource has not been modified on the server according to the values of If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match (whichever is present in the request headers). The resource content is not included with this response; it is the responsibility of the browser to load the content from its cache.
If the resource has been modified, or if neither field is present in the request headers, such as when the request is being performed for the first time, a 200 OK response is sent and the content is included in the response body.
You can observe this by opening a website you frequently visit or reloading an already loaded page. If you check the network tab in the developer tools, you will probably notice a few 304 Not Modified responses for certain assets.
400 Bad request
This status code indicates that the request made by the client is invalid and should not be made again without modification. This error is usually thrown in API requests where the query parameters are absent or have invalid values.
Here’s an example using the OpenWeatherMap API:
We get a 400 error because we passed invalid values to the lat and lon parameters.
If you get this error, you have to double check to confirm that the parameters of your request are in order before making the request again.
You should be able find helpful information on how to fix this error in the response body.
401 Unauthorized
A 401 Unauthorized response indicates that a request was rejected because the client lacks the necessary authorisation credentials to access that resource.
The HTTP 1.1 spec specifies that servers generating a 401 error should include a WWW-Authenticate header field that contains information on how to obtain authorisation.
You can get this error if you make an API request without specifying an API key or token for endpoints that require one.
403 Forbidden
A 403 error can occur if the server refuses to honor your request even if it is understood. This can happen if your credentials, while valid, is not sufficient to access the requested resource. In this case, repeating the request will make no difference until you get sufficient permissions to access the requested entity.
404 Not Found
404 Not Found is probably the most popular browser error on the Internet. It is triggered when the server cannot find the requested resource at a specified URL. This can happen if the page or resource that is requested never existed on the server or was moved to a new location without a 301 or 302 redirect.
Most websites make a custom 404 page to provide guidance to users when they see this error.
410 Gone
A 410 Gone response is sometimes returned instead of a 404 error when the requested resource is not present anymore at the specified location, but it used to be there in the past.
The requested resource is no longer available at the server and no forwarding address is known. This condition is expected to be considered permanent. The 410 response is primarily intended to assist the task of web maintenance by notifying the recipient that the resource is intentionally unavailable and that the server owners desire that remote links to that resource be removed.
A 410 error can indicate that an entity was intentionally removed or an API endpoint has been turned off.
500 Internal Server Error
The HTTP 500 Internal Server Error is a generic error response code that is used when no specific message is suitable. It is a server error and cannot be fixed from the client side. Unless you control your server environment, you cannot do anything about this error.
Conclusion
There are many more HTTP status codes out there, but I believe these are the ones you should pay most attention to since they occur more frequently than the others.
As always, leave your thoughts or questions in the comments below or on Twitter.
About the Author
Ayo is a Software Developer by trade. He enjoys writing about diverse technologies in web development, mainly in Go and JavaScript/TypeScript.
Learn more.
Ошибка 401 Несанкционированный доступ: что это такое, почему возникает и как ее исправить
Первое, что мы собираемся сделать, это выяснить, почему происходит этот сбой и какие сообщения об ошибках могут возникнуть. Затем мы представим серию решений для устранения этой ошибки.
Что такое ошибка 401 и почему она возникает
Игровой автомат 401 Несанкционированная ошибка означает, что у пользователя нет разрешения на доступ к веб-сайту без предварительного входа в систему с соответствующими учетными данными. Это пример сообщения об ошибке, которое мы могли найти в нашем браузере:
Хотя это может показаться ошибкой, связанной с серверами хостинга веб-сайта, на самом деле у нас есть проблема с разрешениями доступа к веб-сайту, и что они связаны с аутентификацией для этой веб-службы.
Решения ошибки 401 Несанкционированный доступ
Чтобы решить эту ошибку 401 Unauthorized, которая может возникнуть в любой момент при доступе к веб-странице, абсолютно необходимо просмотреть некоторые параметры и узнать, требует ли клиент аутентификации для доступа к определенному URL-адресу. В случае необходимости аутентификации нам нужно будет знать как имя пользователя, так и пароль.
Просмотрите URL-адрес и обновите веб-сайт
Мы также можем перезагрузить веб-сайт, нажав клавишу F5 и нажав клавишу ВВОД. Если с этим мы не сможем это исправить, мы попробуем другие решения, такие как те, которые вы увидите ниже.
Внимательно проверьте свои учетные данные
Как мы уже упоминали, ошибка 401 Unauthorized возникает во многих случаях, потому что мы неправильно вводим свое имя пользователя и пароль. Мы собираемся не торопиться и делать все правильно, правильно вводя учетные данные. Для этого оставим поля имени пользователя и пароля пустыми.
Затем мы вводим свое имя пользователя или адрес электронной почты, а затем пароль. Когда мы это делаем, мы должны быть очень осторожны при вводе прописных и строчных букв или соответствующих символов.
Очистите кеш вашего браузера
В этом случае мы кратко объясним, как это делается для браузеров, которые наиболее часто используются в Windows, которые Google Chrome и Mozilla FireFox. В Google Chrome мы переходим в правый верхний угол, где находятся три точки выбора. Затем мы должны выполнить следующие шаги:
Затем мы выбираем те же параметры, которые мы установили на этом экране, и нажимаем на OK кнопку.
Затем мы проверяем, была ли устранена ошибка 401, в противном случае мы пробуем следующий вариант.
Очистка кеша DNS в Windows
In Microsoft операционных систем мы можем выполнить очистку с Командная строка окно. Для этого из Windows Start Menu мы пишем команду » CMD ”И нажмите ввод. Когда мы находимся в окне командной строки, мы должны ввести следующую команду и нажать Enter:
Это будет пример после введения этой команды, которая может исправить ошибку 401.
Если это была проблема, мы можем снова зайти на этот веб-сайт, в противном случае мы можем попробовать следующие решения.
Другие решения, которые мы можем использовать
Нам также придется протестировать эти ресурсы, если все вышеперечисленное не помогло:
HTTP Status Codes: A Complete Guide to the Most Common Error Codes
Every time we want to visit a website, whether it is an online store to buy the latest mobile phone or check the movement of our bank account, you should enter the URL in the browser, or do a Google search. Once you click on the appropriate page, a request is made to the server to return the appropriate content and always returns the HTTP three-digit code.
Thanks to this HTTP status code, we can know whether our request has been completed correctly, or if there is an error that prevents the server from the back of content users or visitors trying to access.
If you have a web page is very important that you know and understand all of the different HTTP status codes that exist. These messages returned by the server is the best tool you can have to diagnose and solve certain problems or errors that may arise on your website.
For the avoidance of doubt, we will look forward to what is HTTP code, type of HTTP status codes that exist and most importantly HTTP code.
What is the HTTP status code?
HTTP status code is a message returned by the server each time the browser requests the server. If the server can restore the content requested by the browser, and no mistake, this HTTP code is not visible to users. Conversely, if something goes wrong, you will notice that the server returns an HTTP status code that indicates that something is not working as expected.
Depending on the status code returned by the server, we can get an idea of the type of error that has occurred. That is why we say that when you have a web page is very important that you know the types of HTTP code so you can see what a mistake it was and quickly fix it.
Samples of HTTP codes
If the HTTP status code that is new to you, you will find that you are more used to seeing them when you try to access a web page than you think.
Do a 404 ring a bell? a very common mistake is still an HTTP status code that tells the user that the content they are trying to access is either not on the server or not available.
Response Types of HTTP Status Codes
HTTP status codes are standardized and listed in the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) HTTP status code registry.
HTTP code is divided into five different categories and the first digit of the code allows you to identify what kind of response we are dealing with: informative responses, a successful response, redirects, error browser, and server errors.
1xx Status Code: This is an informative response and indicates that the browser can continue to make your request.
2xx status code: Association of 2xx code represents a satisfactory response, they merely indicate that the request is processed correctly, so ideally, all websites have returned HTTP code. Generally, as the request was successful, the status code is not displayed, the browser simply returns the user requested content.
3xx status code: HTTP Code refers to when the browser should perform additional actions, such as redirect.
4xx Codes Status: The status code beginning with a 4 refers to the errors generated by the web browser. In this case, users typically receive an HTML page in which they were told about the error.
5xx status code: HTTP Code also indicates an error, but on the webserver.
List of the Most Important HTTP codes
In each group the HTTP status code that we have seen before, various codes can be returned by the server.
1xx Status Codes
2xx Status Codes
3xx Status Codes
4xx Status Codes:
5xx Status Codes
Summing Up
Knowing and understanding the different HTTP code that the server can back it is important to detect and troubleshoot possible errors on your website. Furthermore, this status code plays a fundamental role in the position of your website SEO.
Как исправить ошибку HTTP 401 Unauthorized Request?
Вся сеть работает на основе протокола связи между браузером и веб-сервером. Когда что-то пойдет не так, вы можете увидеть в браузере различные типы кодов ошибок HTTP. 4xx Ошибка HTTP или код состояния указывает на то, что браузер послал неправильный деталь к серверу. Веб-серверы вернут код 401, если они не могут обработать запрос из-за неправильной аутентификации.
Эта проблема чаще встречается на веб-сайтах, которые предлагают вход в систему и специальный контент по подписке. Хотя в большинстве случаев причиной является неправильный вход в систему, в некоторых случаях может произойти ошибка 401 Несанкционированный запрос, даже если у вас есть действительные учетные данные для входа. В этом случае веб-сервер мог не получить ваши данные для входа из-за проблемы на стороне браузера и вернуть ошибку 401.
Если вы видите ошибку 401, выполните следующие действия, чтобы устранить ошибку. Большинство решений довольно легко исправить. Мы также отдельно сгруппировали возможные исправления для обычных пользователей и владельцев веб-сайтов. Вы можете попробовать подходящий случай.
Для обычных пользователей
1 Проверить URL
Это наиболее частая причина ошибки 401 несанкционированный запрос. Это могло произойти, если вы вводите URL вручную. В противном случае вы можете щелкнуть устаревший URL-адрес, отмеченный закладкой в вашем браузере. Ошибка может появиться, если страница больше не существует. Итак, проверьте URL-адрес и убедитесь, что нет орфографических ошибок и веб-страница все еще доступна.
2 Очистить DNS
В некоторых случаях ошибки DNS также могут вызывать ошибку 401 неавторизованный запрос. Вы можете исправить ошибку, очистив DNS.
Следуйте инструкциям в Windows:
Если вы используете macOS, очистка DNS немного отличается.
3 Очистить файлы cookie браузера
Файлы cookie – это фрагменты информации, которые используются веб-сайтами для запоминания вашей уникальной личной информации. Во многих случаях файлы cookie также хранят информацию об аутентификации пользователя и напоминают веб-серверу об уровне авторизации, который может быть предоставлен пользователю. К сожалению, это не всегда работает гладко, и может произойти неправильная аутентификация сервера. Ошибка 401 может произойти, если веб-сервер не может распознать токен сеанса, отправленный вашим веб-браузером. Когда сервер считает, что ваш токен недействителен, вы можете получить ошибку 401 Unauthorized Request.
Гораздо проще удалить все файлы cookie полностью или только для определенных веб-сайтов. Когда вы очищаете файлы cookie, вам придется повторно ввести данные для входа в электронную почту, социальные сети и другие веб-сайты, требующие входа в систему. После очистки кеша попробуйте войти на веб-сайт и проверьте, можете ли вы получить полный доступ. на этот раз без проблем.
4 Проверьте свои права доступа
Ошибка 401 может произойти из-за неправильного входа в систему или разрешения. Например, ссылка может быть зарезервирована только для участников, и при нажатии на нее вы получите ошибку 401 неавторизованный запрос. В этом случае вам может потребоваться связаться с владельцем сайта, чтобы получить надлежащий доступ.
В других случаях вы могли вводить неверные учетные данные для входа на веб-сайт. Если вы знаете, что учетные данные верны, очистите файлы cookie и очистите DNS, как описано в предыдущих разделах. Теперь попробуйте еще раз войти на сайт.
Если вы действительно забыли пароль, найдите на сайте ссылку для сброса пароля. Как правило, веб-сайт запрашивает у вас адрес электронной почты, который вы использовали для создания учетной записи в прошлом. В некоторых случаях ошибочно включается неправильное требование аутентификации, и веб-сайт становится недоступным для пользователей, вошедших в систему. Эту проблему может решить только администратор веб-сайта.
5 Выйдите из системы и войдите снова
Большинству веб-сайтов требуются регулярные простои для обслуживания. Также есть вероятность, что владелец веб-сайта может вносить некоторые изменения в серверную часть, вызывая временные проблемы. Если вы столкнулись с проблемами со статусом входа в систему, выйдите из системы и войдите снова. Во многих случаях веб-сайт может снова работать нормально.
Владельцам веб-сайтов
6 Откат к предыдущей версии CMS
Большинство систем управления контентом обновляется довольно регулярно. Иногда при незначительном обновлении случайно появляются новые ошибки, в том числе необъяснимое появление ошибки 401 Unauthorized Request. Если ваши пользователи сообщают об этой проблеме после недавнего обновления CMS, вам следует рассмотреть возможность отката к предыдущей версии.
К сожалению, некоторые CMS не позволяют откатиться. В таком случае вам может потребоваться официальная поддержка поставщика услуг.
7 Удалите ваши изменения
Некоторые системы управления контентом, такие как WordPress, предлагают плагины, темы, модули, виджеты и расширения. Вы можете использовать эти функции для добавления новых функций и изменения внешнего вида очень универсально. К сожалению, некоторые плагины, темы, модули, виджеты и расширения находятся в плохом состоянии. Некоторые расширения могут также привести к внесению большего количества изменений, чем необходимо.
Когда вы видите ошибку 401 после любого обновления, первое, что вы можете сделать, это удалить последний обновленный плагин и проверить результат. Следует отметить, что проблема может быть решена не сразу после удаления или понижения версии плагина. Это могло произойти, если плагин изменил данные в серверной базе данных или файлах PHP. Таким образом, после удаления плагина любые изменения в базе данных или файлах PHP не могут быть отменены. В таком случае вам может потребоваться вернуть содержимое к ранее работающей версии из резервной копии.
Заключение
Во многих случаях ошибка 401 Unauthorized Request возникает, когда вы пытаетесь войти в систему с неправильными учетными данными. Некоторые веб-сайты, такие как банковские сайты, могут заблокировать вашу учетную запись, если вы несколько раз попытаетесь ввести неправильный пароль. Поэтому убедитесь, что вы указали правильные данные для входа, в противном случае обратитесь в службу поддержки веб-сайта, чтобы решить вашу проблему. С другой стороны, если вы являетесь владельцем веб-сайта, попробуйте вернуться к своим предыдущим действиям, чтобы восстановить доступ к сайту.
Источники:
- http://auth0.com/blog/forbidden-unauthorized-http-status-codes/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3297048/403-forbidden-vs-401-unauthorized-http-responses
- http://oddstyle.ru/wordpress-2/stati-wordpress/kak-bystro-ispravit-oshibku-401-5-metodov.html
- http://www.lifewire.com/401-unauthorized-error-what-it-is-and-how-to-fix-it-2622934
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/211747/friendly-http-401-status-code-message
- http://kinsta.com/knowledgebase/401-error/
- http://www.ionos.com/digitalguide/hosting/technical-matters/401-error-what-can-you-do-about-it/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/50143518/401-unauthorized-vs-403-forbidden-which-is-the-right-status-code-for-when-the-u
- http://www.clickminded.com/status-code-401/
- http://hostingpill.com/ru/401-%D0%BD%D0%B5%D1%81%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%BA%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%BE%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%B0%D1%8F-%D0%BE%D1%88%D0%B8%D0%B1%D0%BA%D0%B0/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/50143518/401-unauthorized-vs-403-forbidden-which-is-the-right-status-code-for-when-the-u?rq=1
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7297707/what-causes-http-status-401-ok
- http://ru.stackoverflow.com/questions/1171513/%D0%A0%D0%B0%D0%B7%D0%BD%D0%B8%D1%86%D0%B0-%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%B6%D0%B4%D1%83-%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B0%D0%BC%D0%B8-%D0%BE%D1%82%D0%B2%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B2-403-%D0%B8-401
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/outlook/troubleshoot/authentication/repeated-status-codes-401-200-mapi-over-http
- http://hostingpill.com/401-unauthorized-error/
- http://www.freecodecamp.org/news/http-401-error-vs-http-403-error-status-code-responses-explained/
- http://stackoverflow.com/tags/http-status-code-401/info
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/50143518/401-unauthorized-vs-403-forbidden-which-is-the-right-status-code-for-when-the-u?lq=1
- http://jeka.by/ask/214/401-vs-403-http-responses/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/50143518/401-unauthorized-vs-403-forbidden-which-is-the-right-status-code-for-when-the-u/50143750
- http://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/partner/develop/error-codes
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6110672/correct-http-status-code-for-login-form
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/45123075/how-to-deal-with-401-unauthorized-response-i-jmeter-v3-0-or-lower
- http://witt-magazine.ru/oshibka-servera-401-chto-eto-za-oshibka-i-kak-ee-ispravit
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1901701/how-to-check-for-an-http-status-code-of-401
- http://devqa.io/http-status-codes/
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/troubleshoot/azure/general/unauthorized-errors-invoke-apis
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10479434/server-returned-http-response-code-401-for-url-https
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2057014/customerrors-for-401-2-in-asp-net
- http://apihandyman.io/hands-off-that-resource-http-status-code-401-vs-403-vs-404/
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/troubleshoot/developer/webapps/iis/www-authentication-authorization/401-error-preauthentication-header
- http://developer.mozilla.org/ru/docs/Web/HTTP/Authentication
- http://myroad.club/kak-ispravit-oshibku-http-401-neavtorizovannogo-zaprosa-webnots/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/55280429/axios-login-request-unauthorized-request-status-code-401
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3282780/the-request-failed-with-http-status-401-unauthorized
- http://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/-http-401-error-message-when-you-try-to-access-web-resources-that-require-kerberos-authentication-on-a-computer-that-is-running-windows-7-or-windows-server-2008-r2-b7785b46-e59d-0025-dc55-0684de45d96b
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/211747/friendly-http-401-status-code-message?rq=1
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/45153773/correct-http-code-for-authentication-token-expiry-401-or-403
- http://qainsights.com/solving-error-26630-http-status-code401-unauthorized/
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/45405983/http-status-code-401-even-though-i-m-sending-credentials-in-the-request
- http://github.com/UXDivers/Grial-UI-Kit-Support/issues/318
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13984888/http-status-code-401-in-gcmdemo
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/38656778/postman-digest-authorization-request-return-401-unauthrized
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/211747/friendly-http-401-status-code-message/211817
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/developer/webapps/iis/www-authentication-authorization/401-error-preauthentication-header
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3297048/403-forbidden-vs-401-unauthorized-http-responses/23804835
- http://pusher.com/tutorials/http-response-codes-part-1/
- http://easy-code.ru/lesson/http-code-status
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/32752578/whats-the-appropriate-http-status-code-to-return-if-a-user-tries-logging-in-wit
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/50143518/401-unauthorized-vs-403-forbidden-which-is-the-right-status-code-for-when-the-u/50143519
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/38999235/angular-2-rest-request-http-status-code-401-changes-to-0
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/40370022/response-for-preflight-has-invalid-http-status-code-401-spring
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1279416/why-my-httpwebrequest-post-to-myhandler-ashx-is-rejected-with-status-code-401
- http://www.easyname.com/en/support/hosting/158-what-do-the-http-status-codes-such-as-403-404-500-mean
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4038981/is-it-ok-to-return-a-http-401-for-a-non-existent-resource-instead-of-404-to-prev
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/66212891/axios-post-request-failed-with-status-code-401
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/39567558/php-401-status-returns-1
- http://stackovergo.com/ru/q/732491/403-forbidden-vs-401-unauthorized-http-responses
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/15620746/what-http-status-code-for-unactivated-account
- http://freshman.tech/http-status-codes/
- http://itigic.com/ru/error-401-unauthorized-what-it-is-why-it-happens/
- http://dev.to/aanchalrathor/http-status-codes-a-complete-guide-to-the-most-common-error-codes-4n5n
- http://techblog.sdstudio.top/kak-ispravit-oshibku-http-401-unauthorized-request/




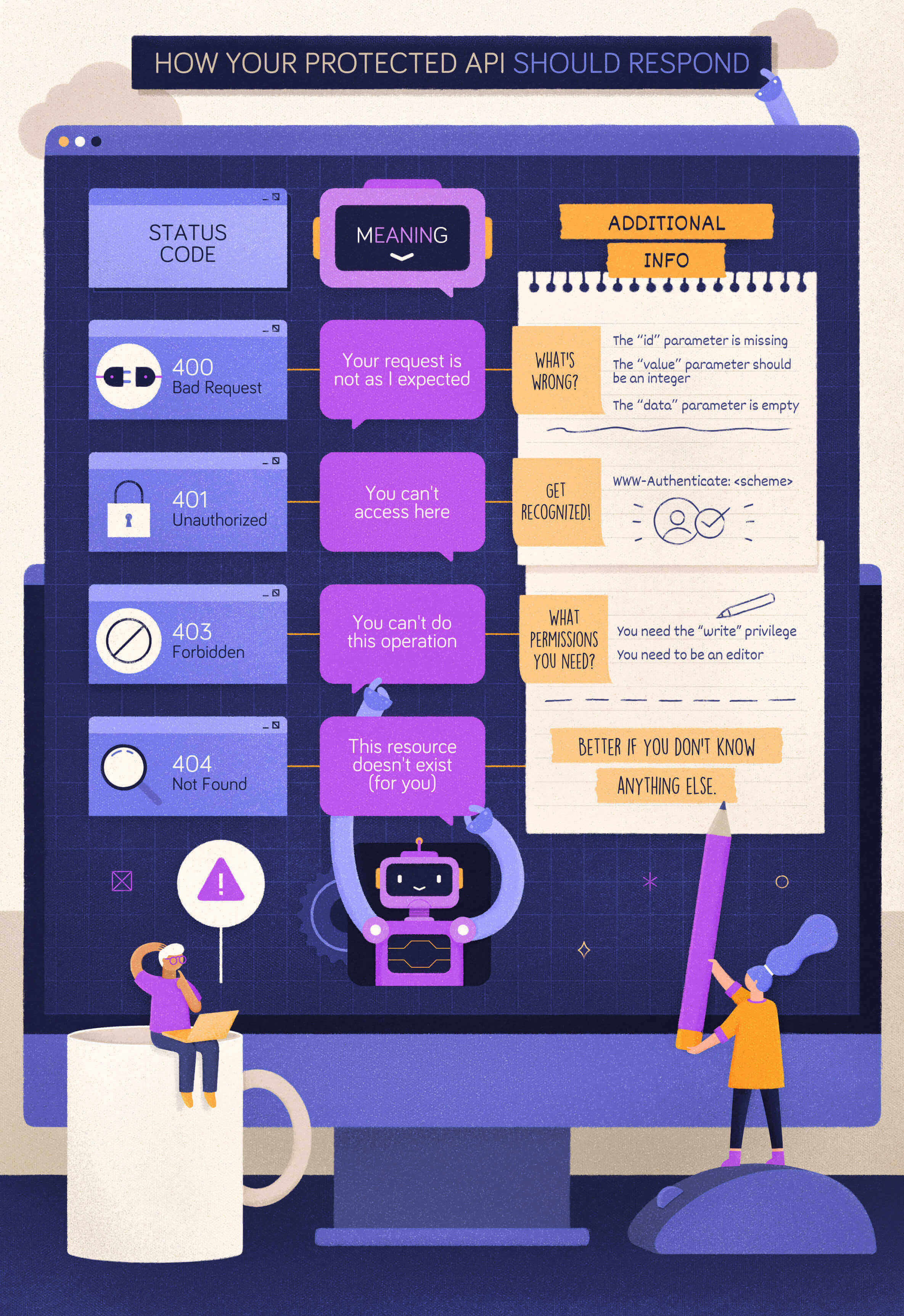




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/401-unauthorized-error-what-it-is-and-how-to-fix-it-2622934-e98cc16b41504abdbc47fb6cbaeebcfa.png)