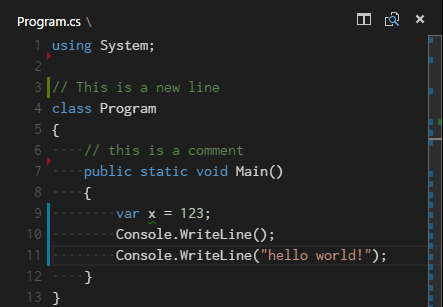
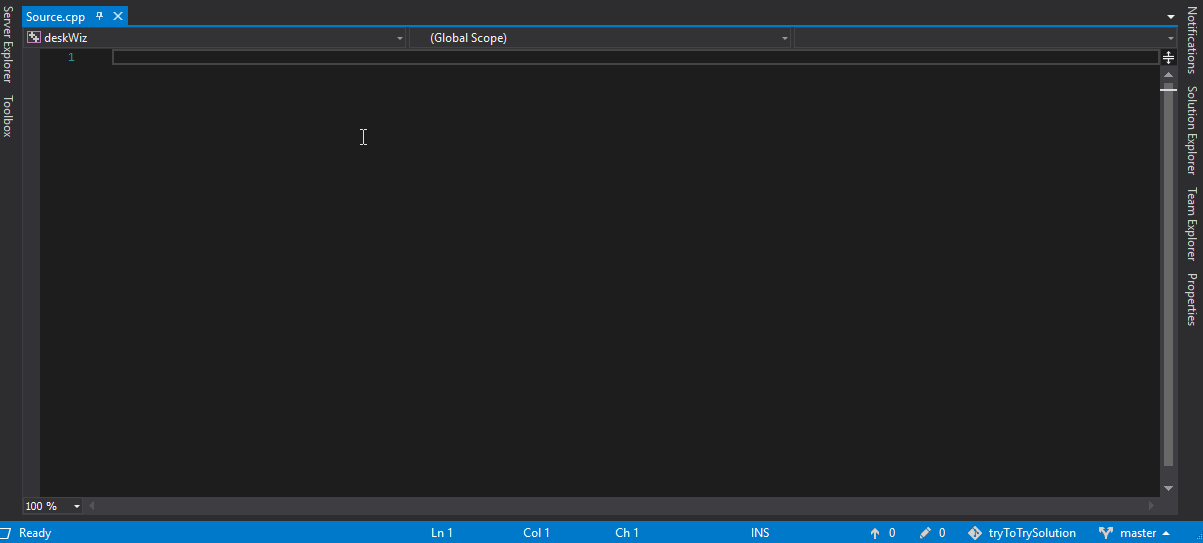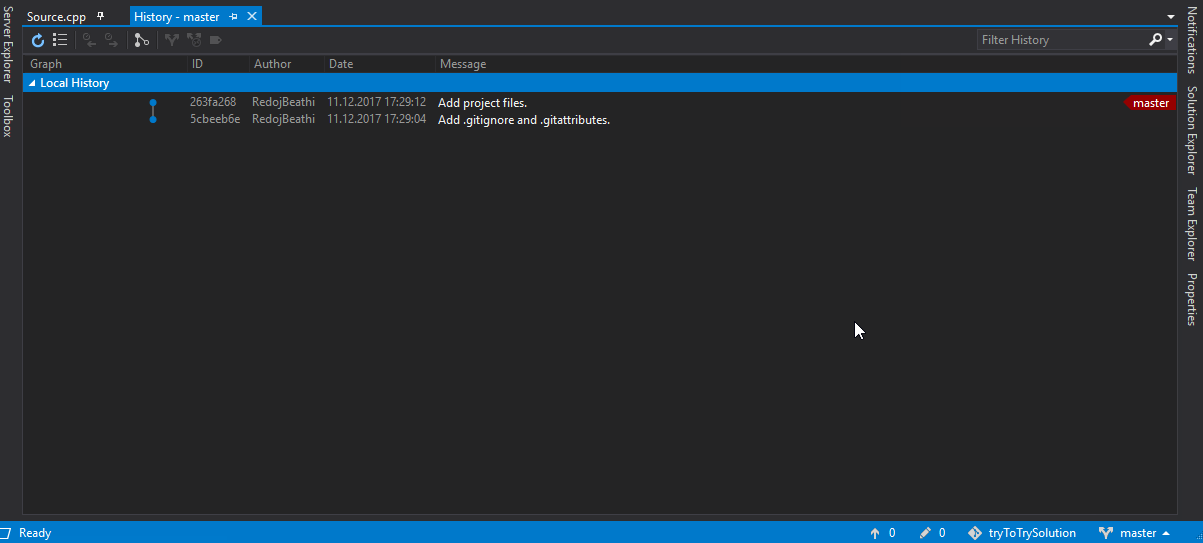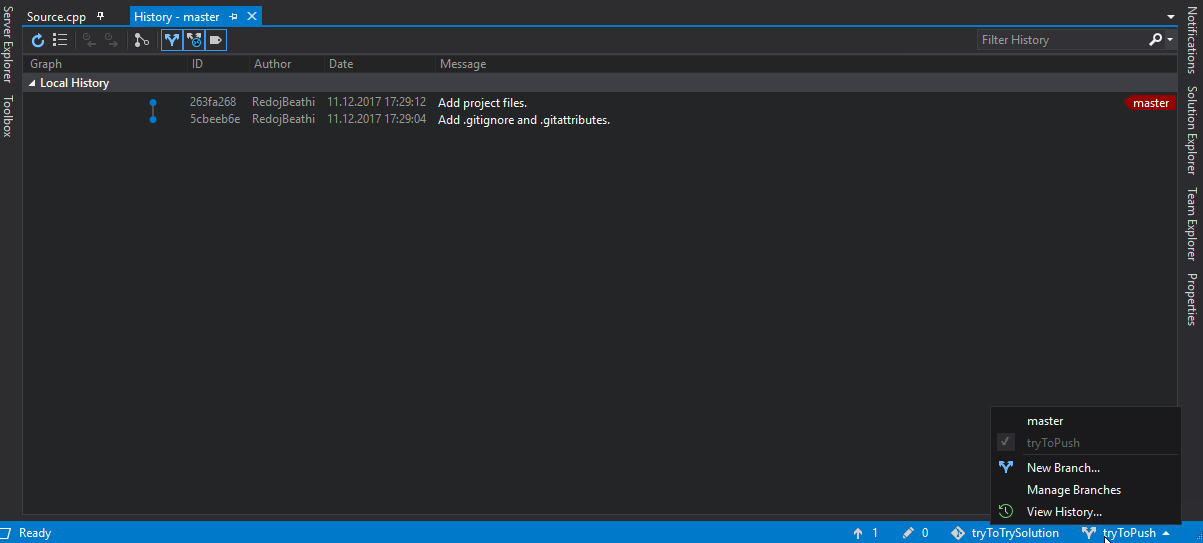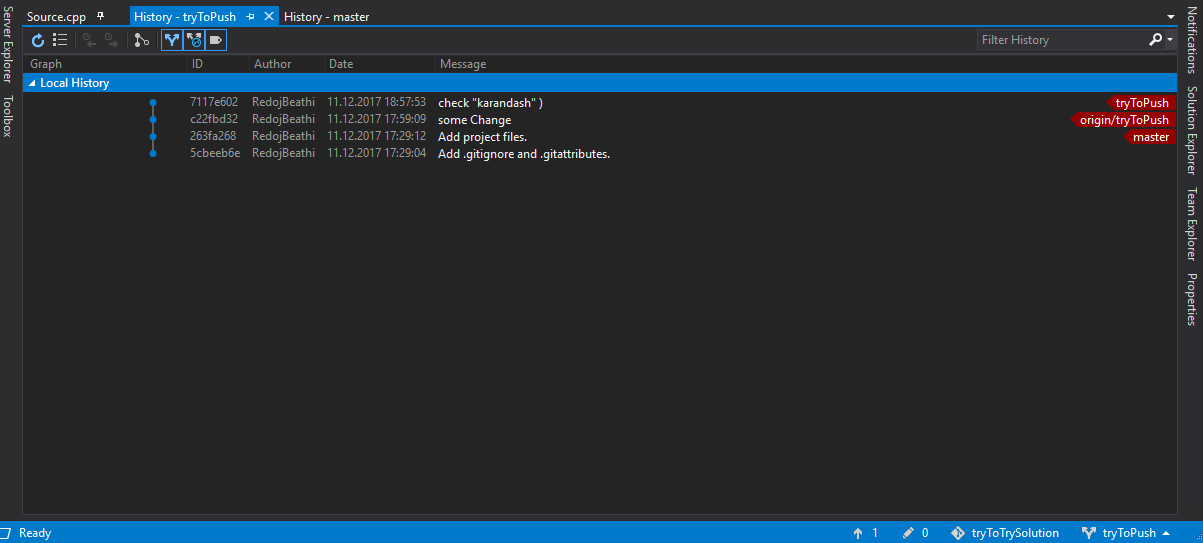
Visual studio code github
Visual studio code github
GitHub Student Developer Pack
Welcome to Visual Studio Code! VS Code is a free coding editor that helps you start coding quickly. Use it to code in any programming language, without switching editors. VS Code comes with built-in source control, so you can compare versions of your code side-by-side and save your work over time by backing it up on GitHub. We have resources specifically created for students and educators, including our Python and Java Coding Packs, programming lessons built in partnership with NASA and Netflix, and videos to quickly get up to speed.
To get started with VS Code and learn how to best use GitHub, check out the resources below:
Lessons
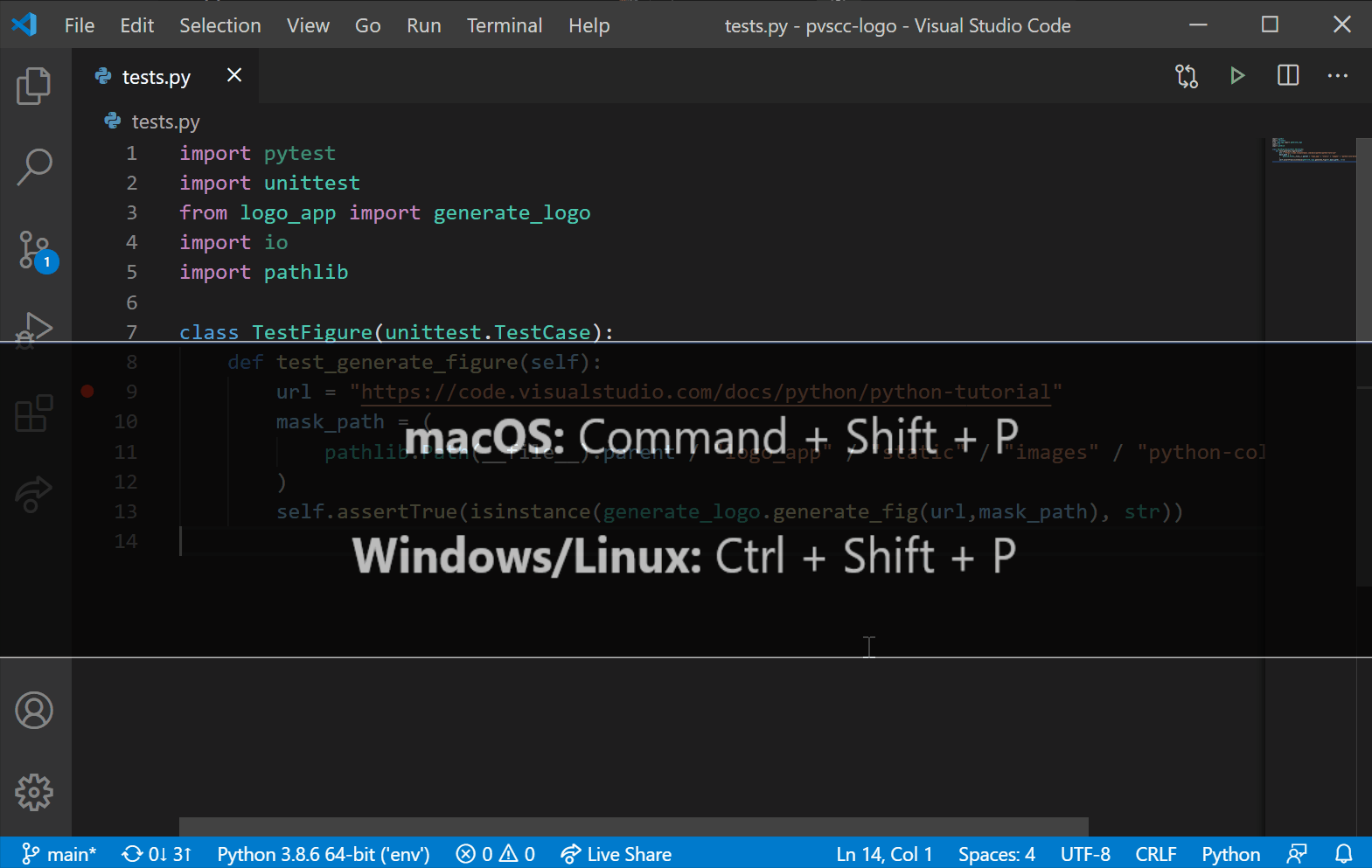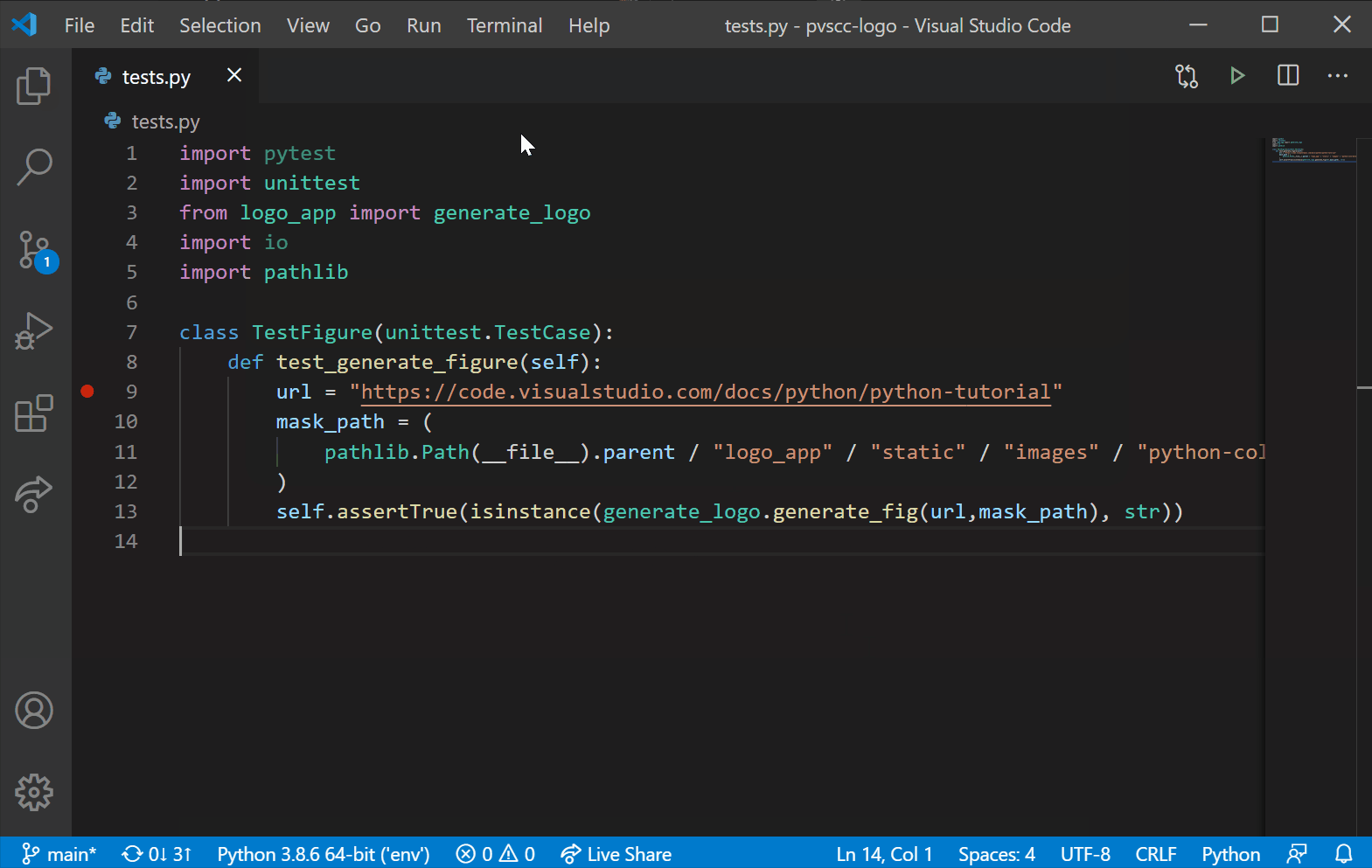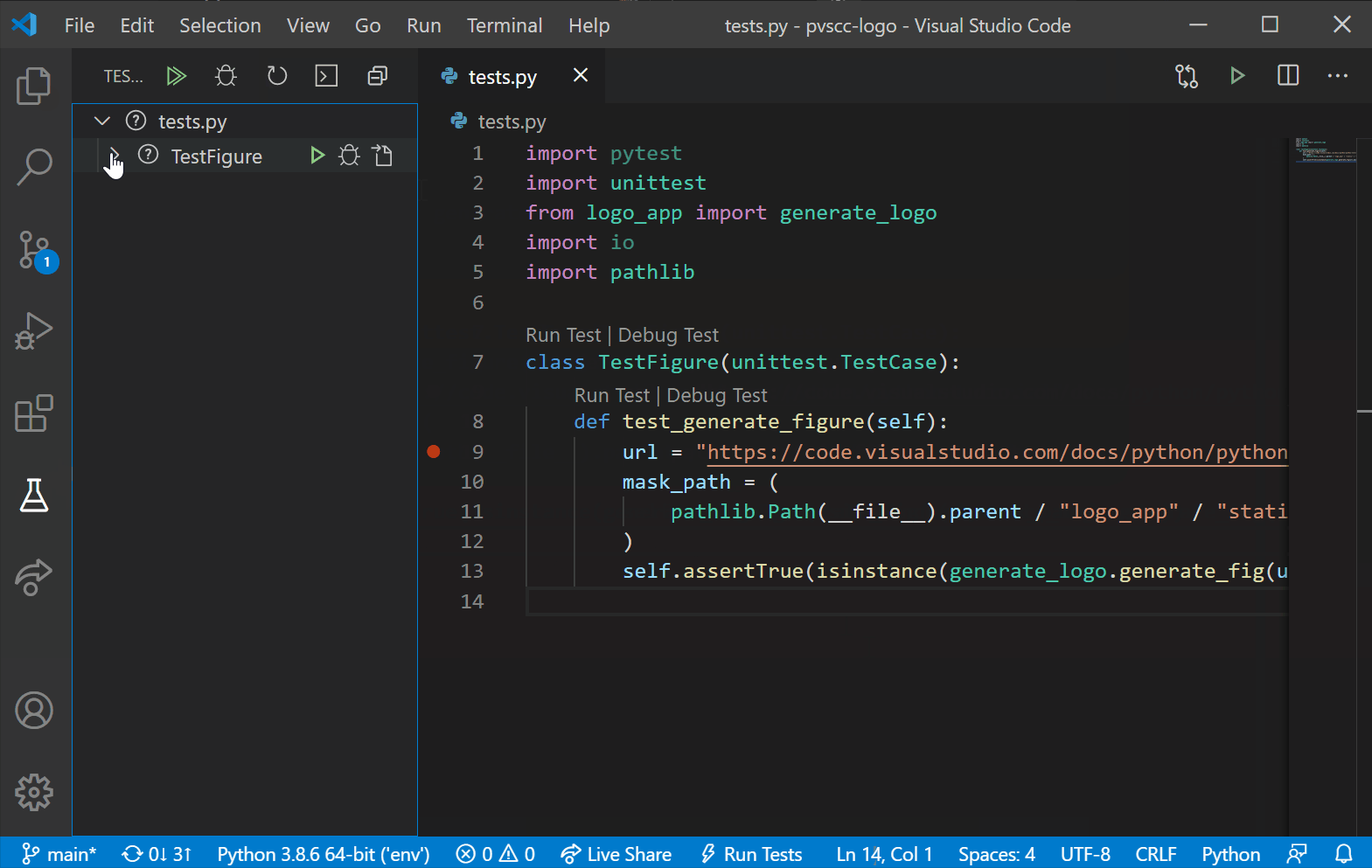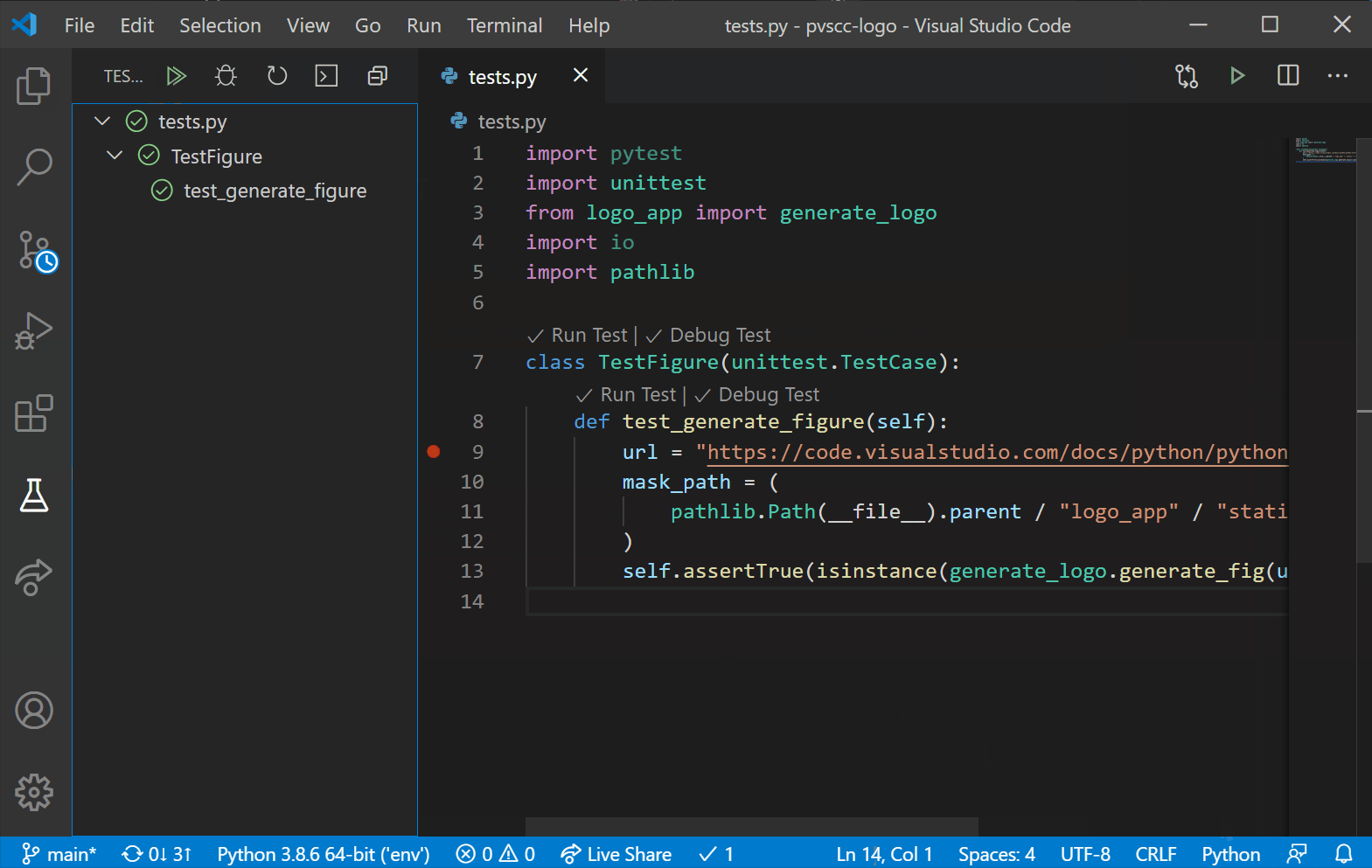
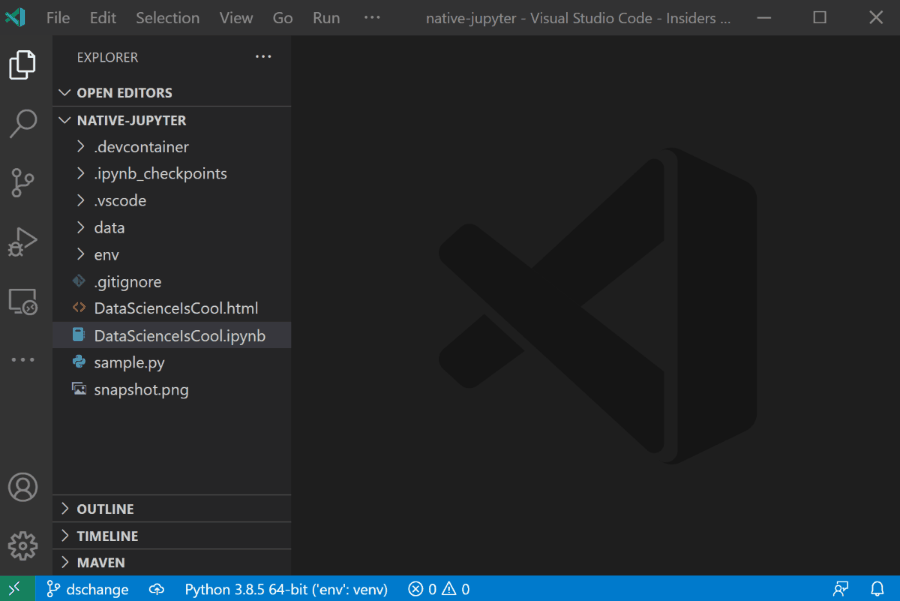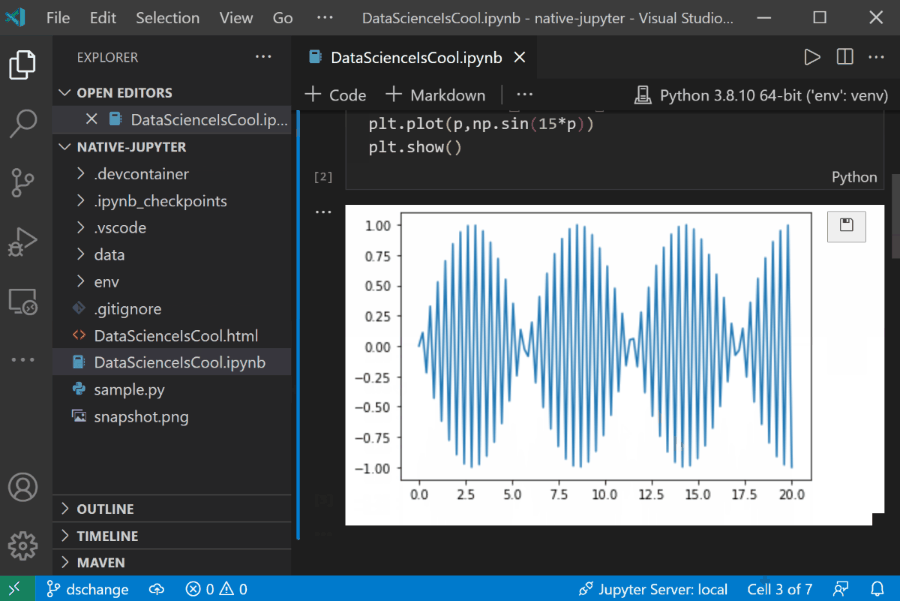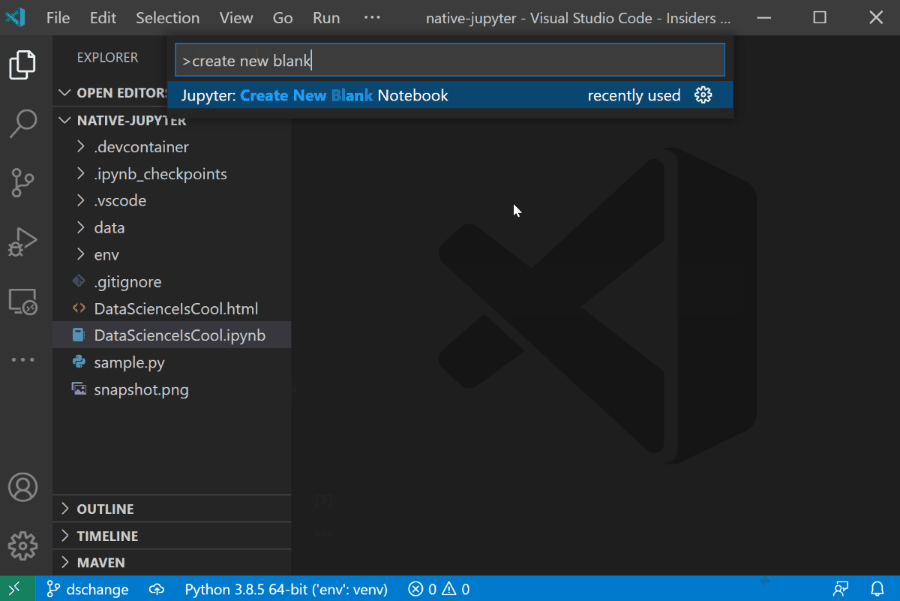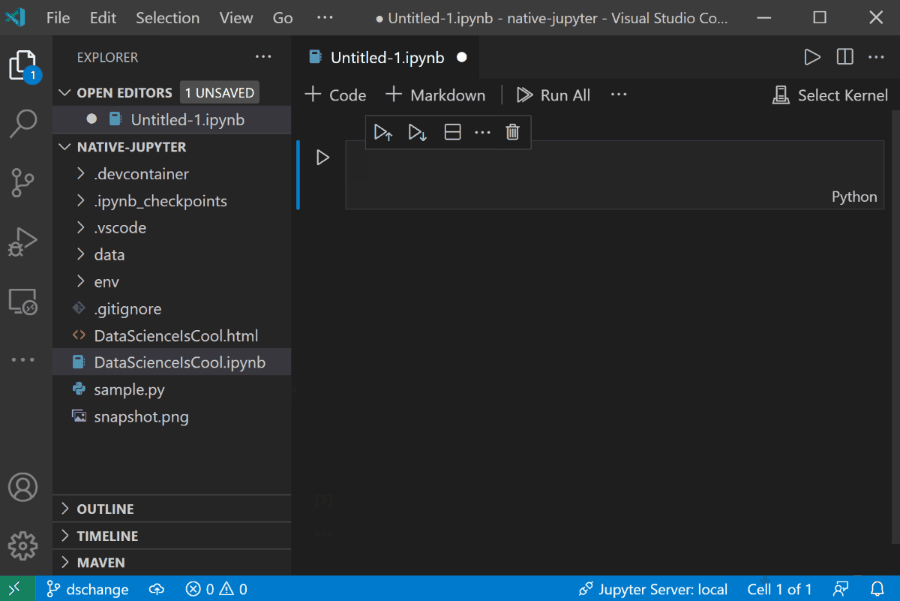
In this 20-minute tutorial, you’ll learn how to search GitHub for repositories, clone them, and publish your own projects onto GitHub right from VS Code.
In this module, learn the fundamentals of version control systems like Git.
Tutorials
In this video, you’ll see how GitHub is used when building a project. After completing this one hour tutorial and you’ll end up creating a Node.js app, hosting it on GitHub, and deploying it to the cloud.
Helpful extensions
With this extension, you can quickly create pull requests and review other pull requests or issues, right from VS Code. To learn more about using this extension, check out the video below or read about the features.
The GitLens extension enhances the built-in Git features in VS Code, like showing you when lines of code were written, by whom, and in what commit. To learn more, check out this helpful video.
GitHub and Visual Studio Code
Bring your workflows closer to your code. Learn how Visual Studio Code and GitHub are better together.
Get started with GitHub in Visual Studio Code
Check out our 20-minute tutorial to get the best of GitHub in the editor.
Our top 20 tips and tricks
Codespaces
No editor, no problem. Code in a browser with a real VS Code experience, powered by GitHub Codespaces.
Clone And Code
You can directly clone a repo from Visual Studio Code. Authenticate with your GitHub account and clone any repo you want. VS Code takes care of setting your remote so you can clone, code and push in no time flat.
Publish Your Project
Publish any project directly to GitHub without having to create a repo first. VS Code will create the repo for you and give you control over whether or not it should be public or private.
Integrated Source Control View
The source control view tracks your file changes and makes it easy to commit and push those changes. Add a commit message, mention another user in the repo, and click on ‘sync changes’ in the status bar. This will pull any remote changes down, and push your commits upstream.
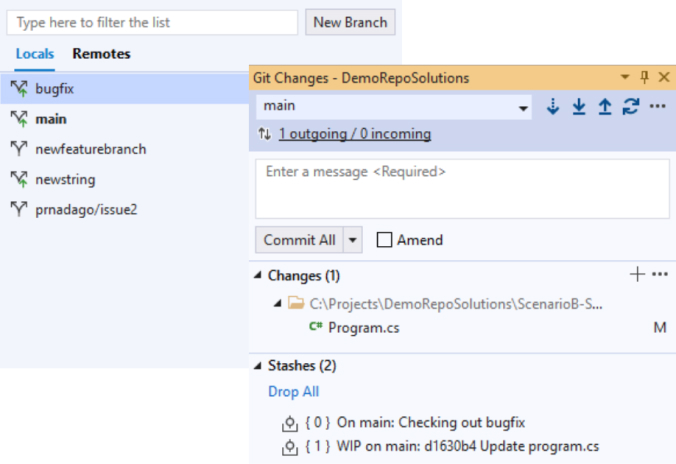
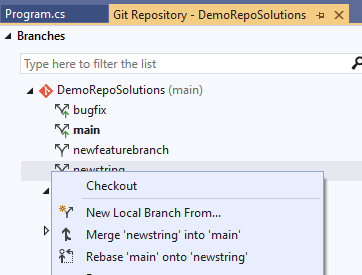
Branching
From the status bar, you can view all branches and easily switch to another one. From the command palette, you can also checkout another branch, create a new one, or rename a branch. Branch away!
Stashing
Temporarily set aside the code changes you already made with a Git stash then get back to them later!
Stage Commits
The Source Control view in VS Code lets you stage specific changes only, so you can control what’s part of your commit and what’s still a WIP (Work In Progress) Then click on ✔️ to make a commit.
Merge Your Way
Do you most commonly merge, squash/merge, or rebase/merge? Well, from the GitHub Pull Request and Issues extension, you can choose either merge option.
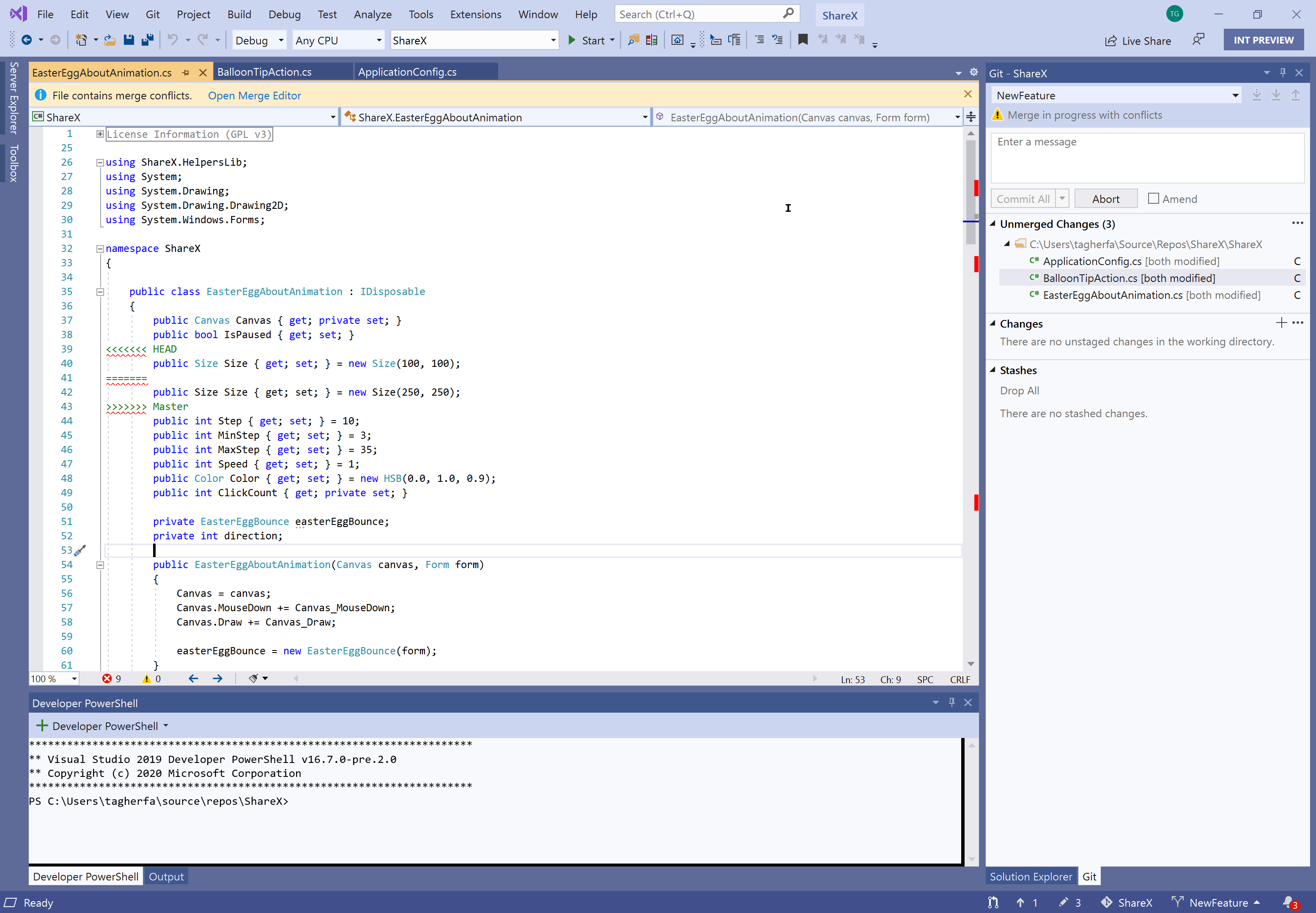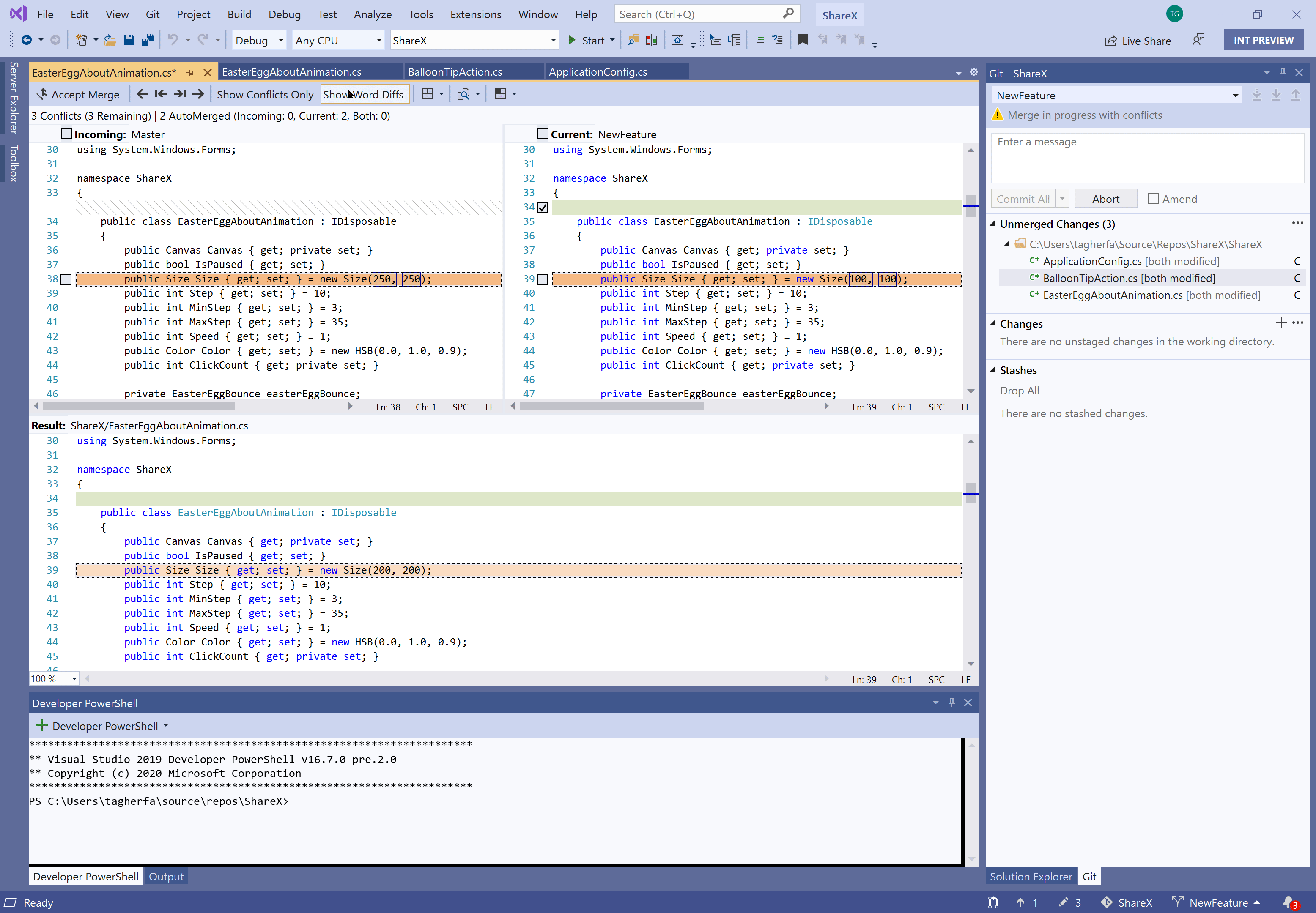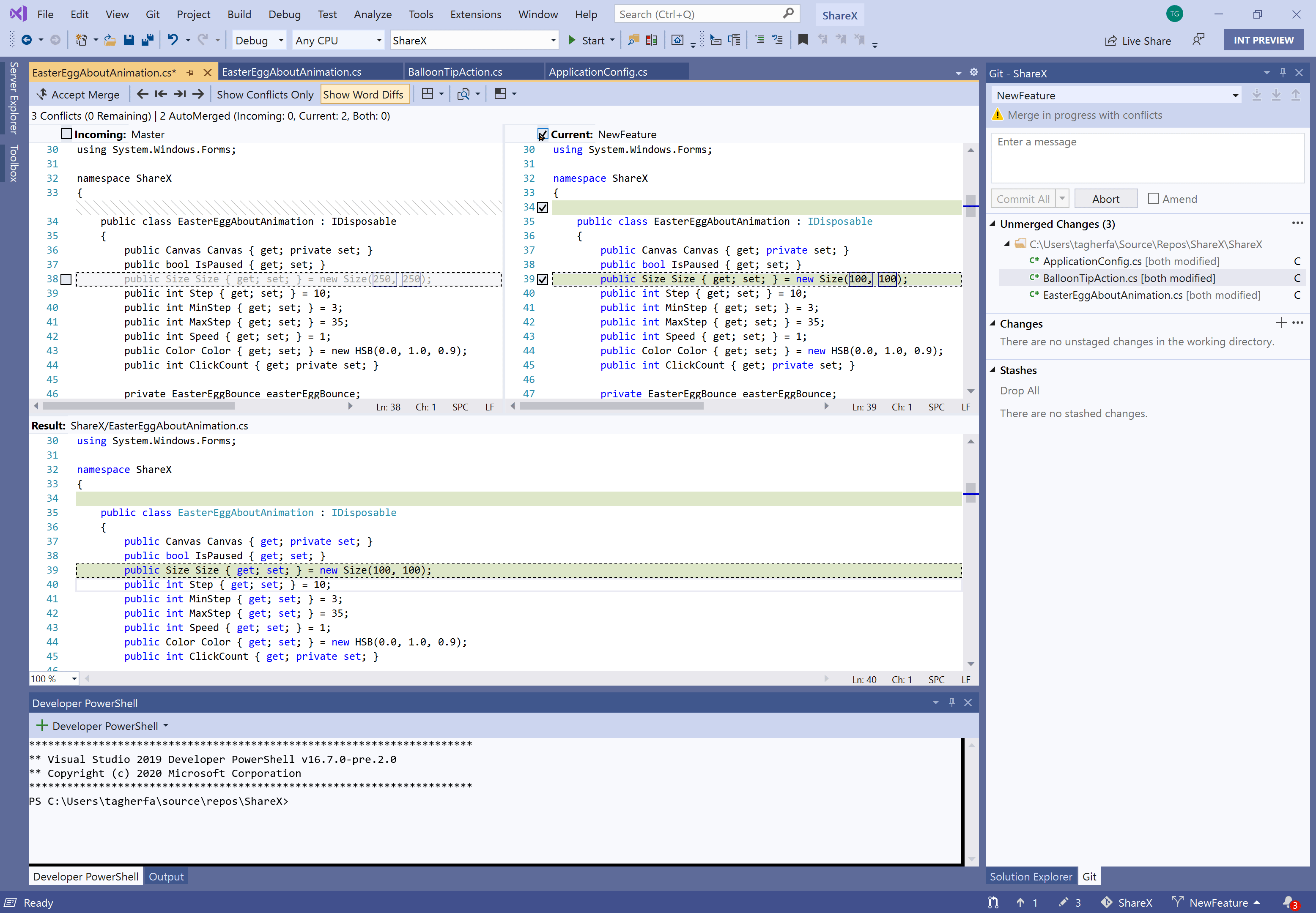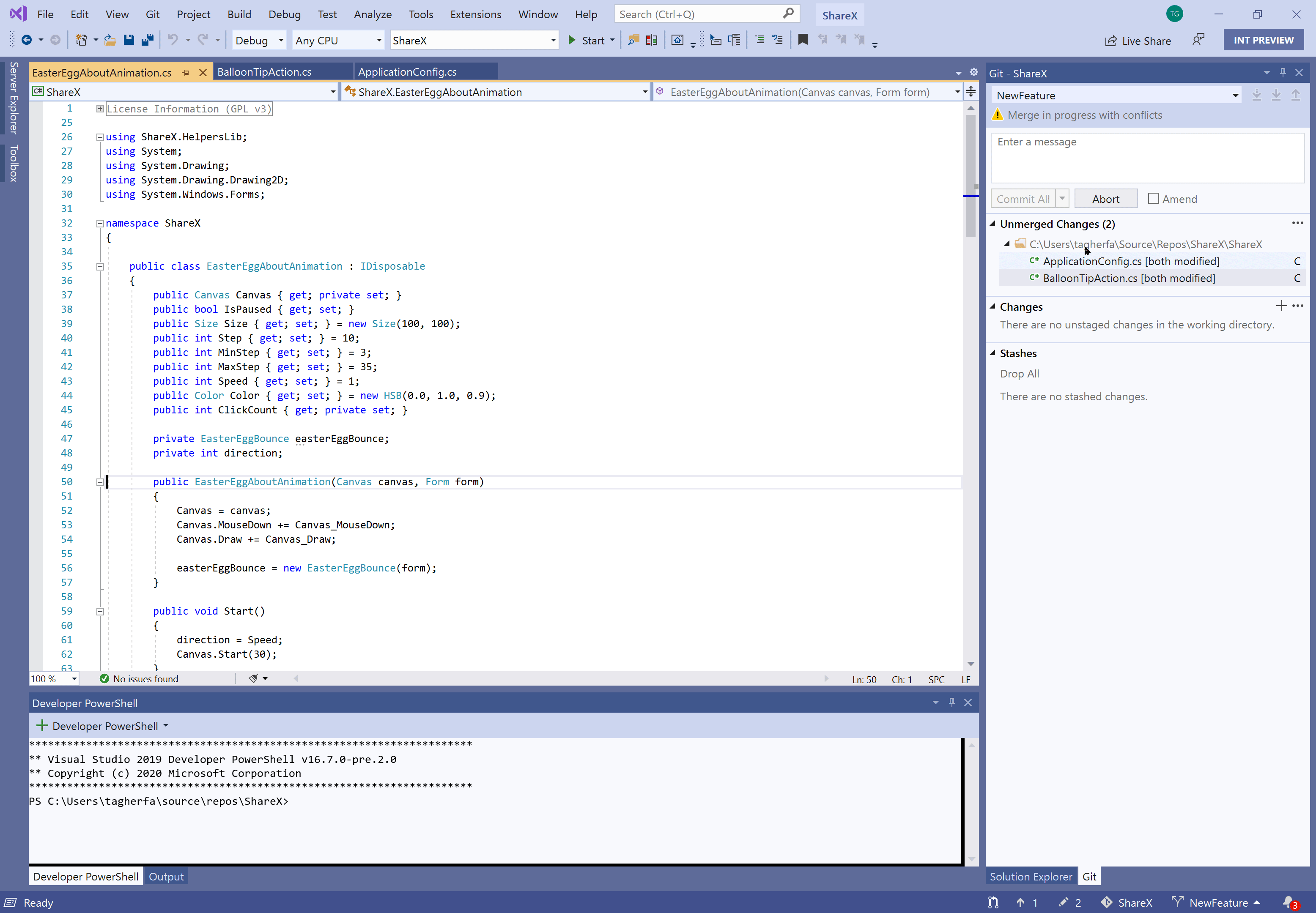
Handle Merge Conflicts
VS Code will recognize merge conflicts, highlight the differences, and make it easy to choose the current change or the incoming change. If you have multiple changes, you can search for ‘Merge Conflict’ in the command palette and take action on all conflicts.
Change Your Diff View
Some people prefer a to see their diff’s side-by-side and some prefer an inline view. Get both in VS Code. This setting persists when it’s changed so you can set it and forget it.
Jump Directly To GitHub
Sometimes you’re just knee deep in source code and need to switch over to GitHub. With the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension, you can copy a permalink or directly open a permalink in GitHub so you don’t lose your place.
Create Issues
Do you find yourself putting //TODO comments throughout your code and then forgetting to. do them? With the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension, you can make those comments actionable and create GH issues directly from code comments.
Manage Issues
View issues from GitHub directly from VS Code. Create custom queries using the same GitHub filter syntax you already know. Your issues organized your way.
Request A Review
You can request a review on your PR right from VS Code using the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension. Open the PR from the Github Pull Requests explorer and assign away.
Keep Track of PRs
Choose the categories you see in the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues tree view. Customize it and make sure you never lose track of PRs again.
Code Reviews
View PRs. Check out branches. Add comments. Merge and delete branches from the editor.
Time Travel
You can see the Git commit history of a specific file in the Timeline view. Choosing a commit opens up the diff view of the changes from that commit. Easily copy the commit Id or commit message to help you go to important points in your code’s
GitLens
Get in-line blame annotations and hover information for recent commits, search through commits, visualize and compare commits across branches, and so much more. GitLens is a must-have extension if you’re using version control in VS Code.
Sign Commits
Use the integrated terminal in VS Code for advanced actions like GPG signing your commits so you can get that big green «verified» badge.
Check Under The Hood
Curious to see the Git commands VS Code is doing? You can always peek under the hood. The full output of what VS Code is doing with Git is always available for you in case you need it.
Первые шаги в GIT + GITHUB + VS CODE 👶
Рано или поздно у разработчика наступает момент, когда разработка вида «хренак, хренак и в продакшен» уже не устраивает и требуются системы, которые бы работали как сохранения в игре, и в любой момент можно вернуться к определенному шагу разработки. Такие системы называют системами контроля версий, их очень много, но речь сегодня пойдет именно про GIT.
Что такое GIT
GIT является одной из самых популярных систем. Её отличие от других программ — отсутствие графической версии. Поэтому работа с Git ведётся через командную строку. В разных операционных системах свои программы для взаимодействия с Git.
В Windows их две: PowerShell и cmd.exe. В Ubuntu это Terminal. Самая популярная программа на macOS тоже называется Terminal. Если вам не подходит встроенная в систему программа для работы с командной строкой, вы можете поставить свою. Например, написанную на JavaScript программу Hyper, которая работает на любой операционной системе. На Windows популярны программы Cmder и Git Bash, а на macOS — iTerm.
В мире разработки такие программы называют «терминал» или «консоль». А работает это так: мы вводим команду и получаем реакцию машины: сообщение об ошибке, запрос на подтверждение информации, результат выполненных действий.
Установка GIT
Если вы ранее не работали с GIT, то для начала его нужно установить. В зависимости от системы нужно выбрать свой вариант
Установка GIT в Linux (Ubuntu)
В зависимости от вашего дистрибутива Linux требуется установить через консоль, например в убунту эта команда будет иметь следующий вид:
Команды для других дистрибутивов можно посмотреть здесь.
Установка на macOS
Установка в Windows
Скачайте exe-файл инсталлятора с сайта Git и запустите его. Это Git для Windows, он называется msysGit. Установщик спросит добавлять ли в меню проводника возможность запуска файлов с помощью Git Bash (консольная версия) и GUI (графическая версия). Подтвердите действие, чтобы далее вести работу через консоль в Git Bash. Остальные пункты можно оставить по умолчанию.
Проверим, что Git установлен.
Настройка Git
После установки производим настройку своего профиля вводя в терминал поочереди команды:
Заменив значения ВАШЕ_ИМЯ и АДРЕС вашими значениями.
После указания своих данных, можно их просмотреть:
GITHUB
GitHub — веб-сервис, который основан на системе Git. Это такая социальная сеть для разработчиков, которая помогает удобно вести коллективную разработку IT-проектов. Здесь можно публиковать и редактировать свой код, комментировать чужие наработки, следить за новостями других пользователей. Именно в GitHub работаем мы, команда Академии, и студенты интенсивов.
Чтобы начать работу с GitHub, нужно зарегистрироваться на сайте, если вы ещё этого не сделали.
После того как у вас будет создан аккаунт в Github можно будет начать полноценно работать с ним.
Копирование репозитория Git в локальную папку
Для начала определим, что такое репозиторий. Это рабочая директория с вашим проектом. По сути, это та же папка с HTML, CSS, JavaScript и прочими файлами, что хранится у вас на компьютере, но находится на сервере GitHub. Поэтому вы можете работать с проектом удалённо на любой машине, не переживая, что какие-то из ваших файлов потеряются — все данные будут в репозитории при условии, что вы их туда отправите. Но об этом позже.
Копировать или клонировать репу c GitHub можно по HTTPS или SSH.
Команда для копирования репозитория:
После клонирования переходим в папку репозитория:
Working with GitHub in VS Code
GitHub is a cloud-based service for storing and sharing source code. Using GitHub with Visual Studio Code lets you share your source code and collaborate with others right within your editor. There are many ways to interact with GitHub, for example, via their website at https://github.com or the Git command-line interface (CLI), but in VS Code, the rich GitHub integration is provided by the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension.
To get started with the GitHub in VS Code, you’ll need to install Git, create a GitHub account and install the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension. In this topic, we’ll demonstrate how you can use some of your favorite parts of GitHub without leaving VS Code.
If you’re new to source control or want to learn more about VS Code’s basic Git support, you can start with the Version Control topic.
Getting started with GitHub Pull Requests and Issues
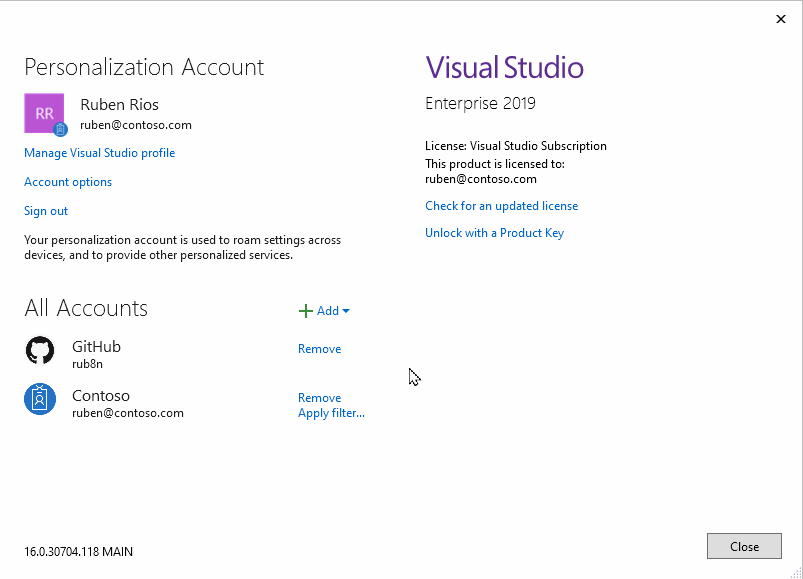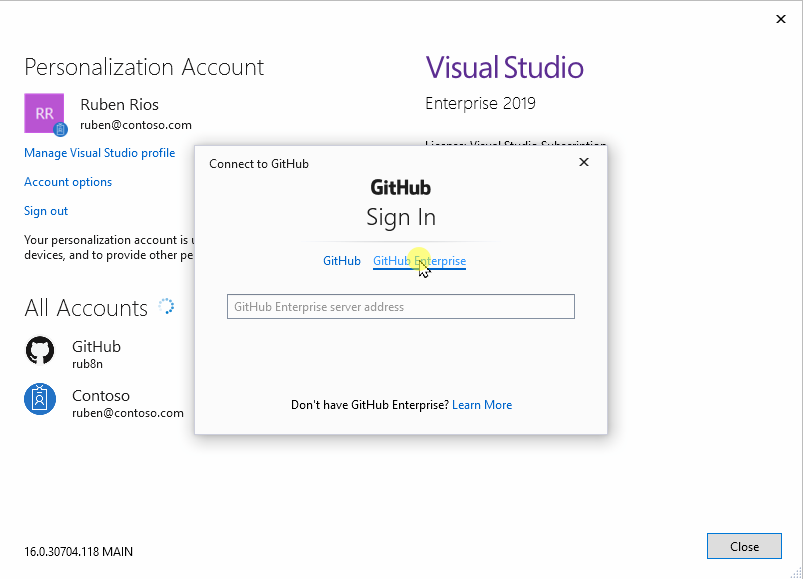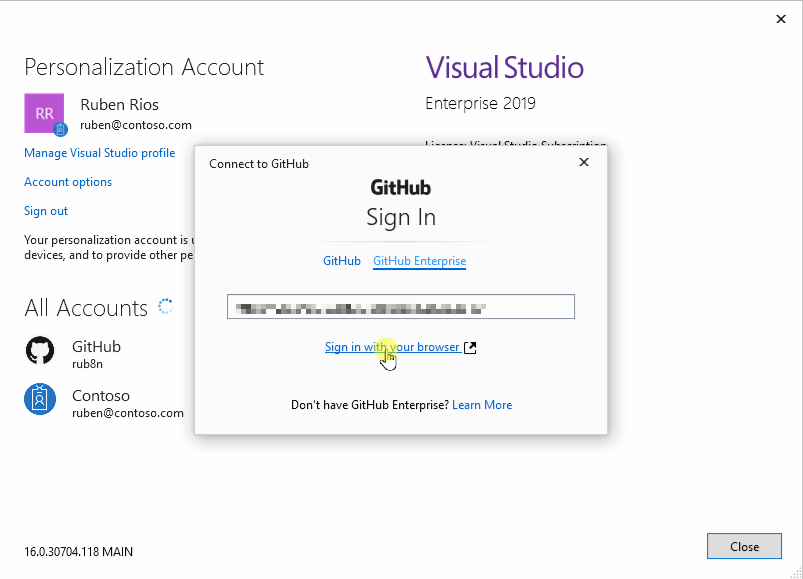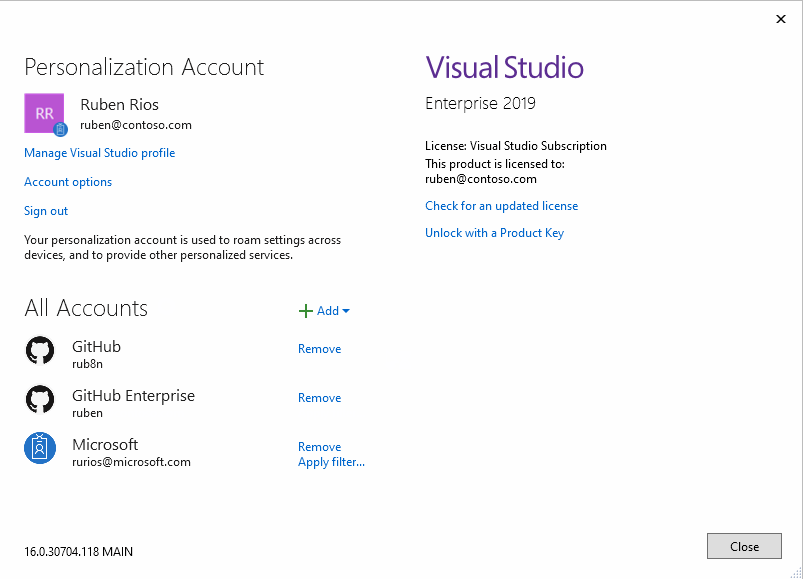
Once you’ve installed the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension, you’ll need to sign in. Follow the prompts to authenticate with GitHub in the browser and return to VS Code.
Setting up a repository
Cloning a repository
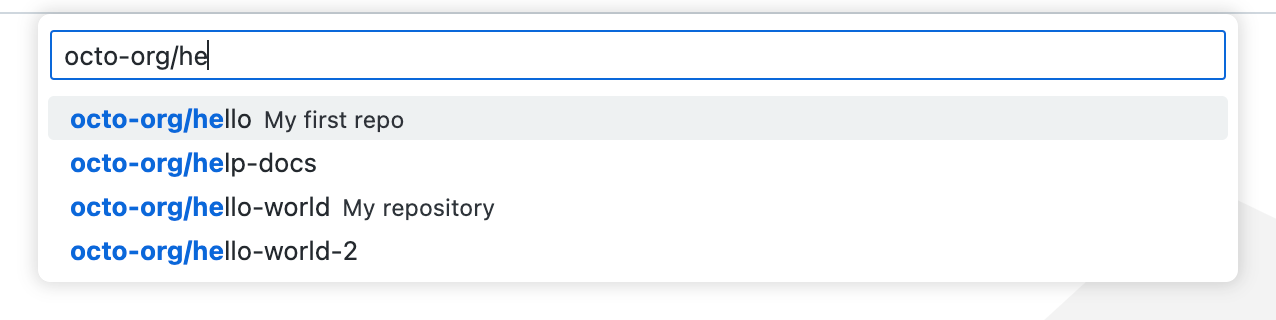
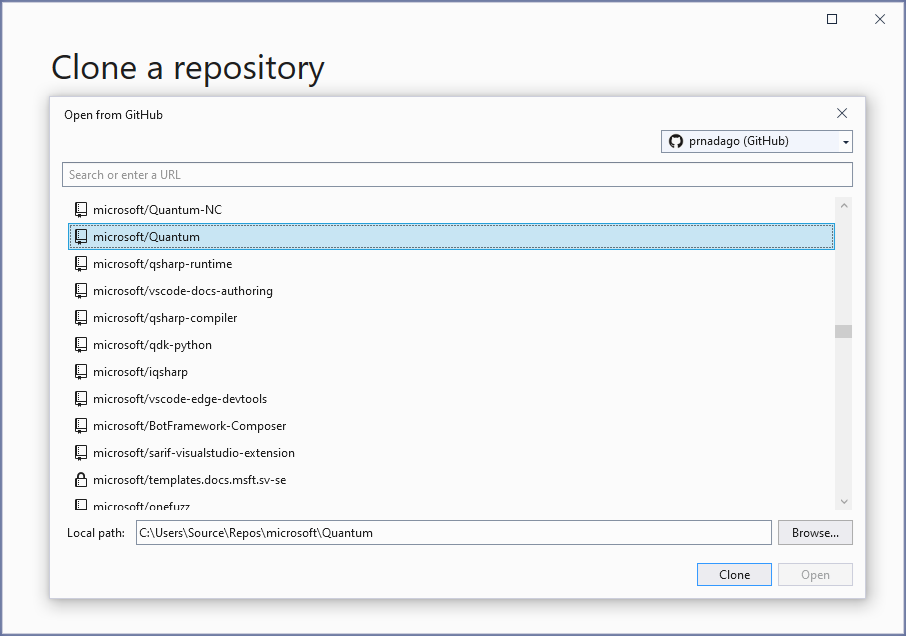
You can search for and clone a repository from GitHub using the Git: Clone command in the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) or by using the Clone Repository button in the Source Control view (available when you have no folder open).
From the GitHub repository dropdown you can filter and pick the repository you want to clone locally.
Authenticating with an existing repository
Enabling authentication through GitHub happens when you run any Git action in VS Code that requires GitHub authentication, such as pushing to a repository that you’re a member of or cloning a private repository. You don’t need to have any special extensions installed for authentication; it is built into VS Code so that you can efficiently manage your repository.
When you do something that requires GitHub authentication, you’ll see a prompt to sign in:
Follow the steps to sign into GitHub and return to VS Code. If authenticating with an existing repository doesn’t work automatically, you may need to manually provide a personal access token. See Personal Access Token authentication for more information.
Note that there are several ways to authenticate to GitHub, including using your username and password with two-factor authentication (2FA), a personal access token, or an SSH key. See About authentication to GitHub for more information and details about each option.
Note: If you’d like to work on a repository without cloning the contents to your local machine, you can install the GitHub Repositories extension to browse and edit directly on GitHub. You can learn more below in the GitHub Repositories extension section.
Editor integration
Hovers
When you have a repository open and a user is @-mentioned, you can hover over that username and see a GitHub-style hover.
There is a similar hover for #-mentioned issue numbers, full GitHub issue URLs, and repository specified issues.
Suggestions
User suggestions are triggered by the «@» character and issue suggestions are triggered by the «#» character. Suggestions are available in the editor and in the Source Control view’s input box.
The issues that appear in the suggestion can be configured with the GitHub Issues: Queries ( githubIssues.queries ) setting. The queries use the GitHub search syntax.
You can also configure which files show these suggestions using the settings GitHub Issues: Ignore Completion Trigger ( githubIssues.ignoreCompletionTrigger ) and GitHub Issues: Ignore User Completion Trigger ( githubIssues.ignoreUserCompletionTrigger ). These settings take an array of language identifiers to specify the file types.
Pull requests
From the Pull Requests view you can view, manage, and create pull requests.
The queries used to display pull requests can be configured with the GitHub Pull Requests: Queries ( githubPullRequests.queries ) setting and use the GitHub search syntax.
Creating Pull Requests
Once you have committed changes to your fork or branch, you can use the GitHub Pull Requests: Create Pull Request command or the Create Pull Request button in the Pull Requests view to create a pull request.
A new Create Pull Request view will be displayed where you can select the repository and branch you’d like your pull request to target as well as fill in details such as the title, description, and whether it is a draft PR. If your repository has a pull request template, this will automatically be used for the description.
Once you select Create, if you have not already pushed your branch to a GitHub remote, the extension will ask if you’d like to publish the branch and provides a dropdown to select the specific remote.
The Create Pull Request view now enters Review Mode, where you can review the details of the PR, add comments, reviewers, and labels, and merge the PR once it’s ready.
After the PR is merged, you’ll have the option to delete both the remote and local branch.
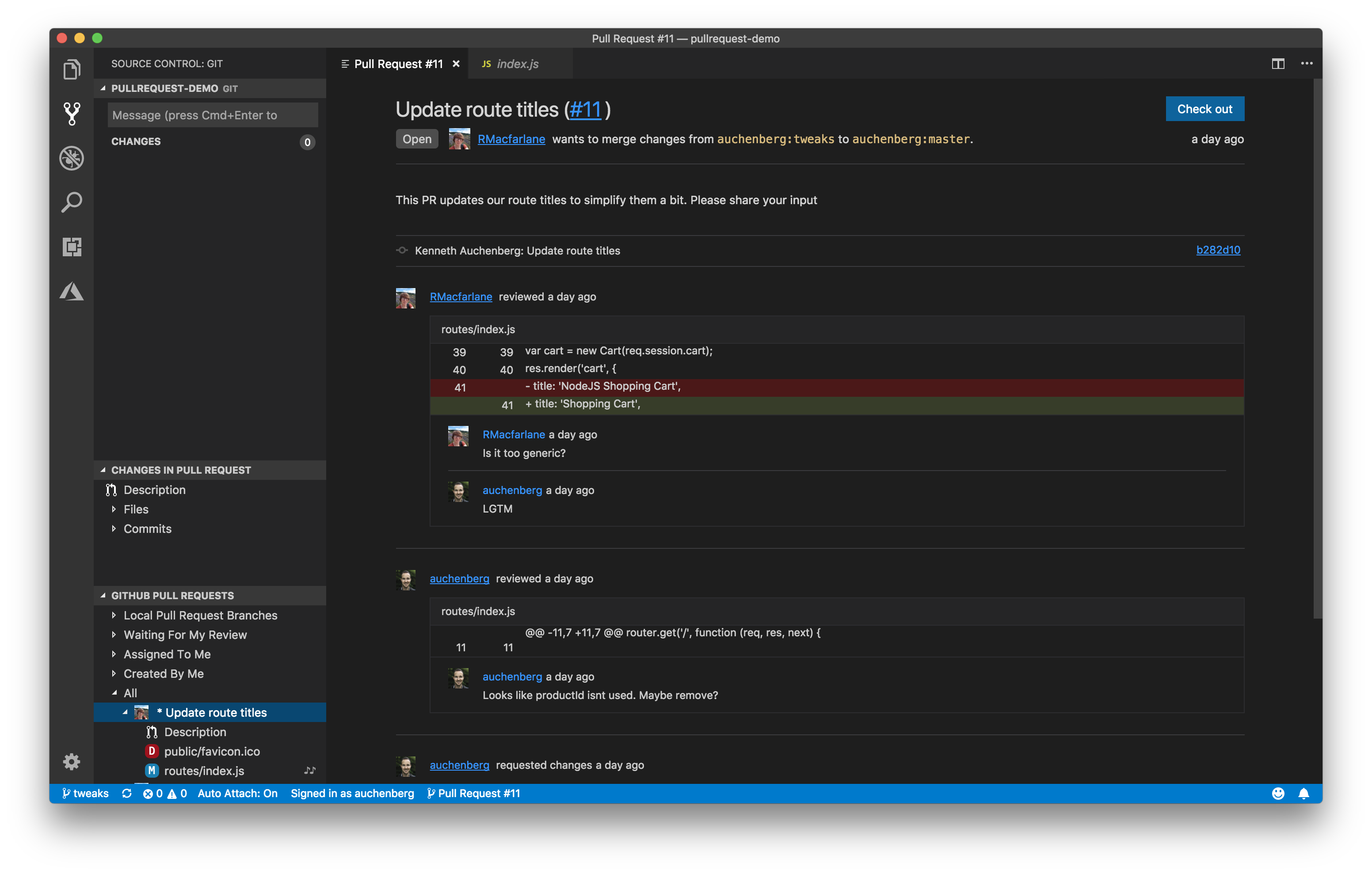
Reviewing
Pull requests can be reviewed from the Pull Requests view. You can assign reviewers and labels, add comments, approve, close, and merge all from the pull request Description.
From the Description page, you can also easily checkout the pull request locally using the Checkout button. This will switch VS Code to open the fork and branch of the pull request (visible in the Status bar) in Review Mode and add a new Changes in Pull Request view from which you can view diffs of the current changes as well as all commits and the changes within these commits. Files that have been commented on are decorated with a diamond icon. To view the file on disk, you can use the Open File inline action.
The diff editors from this view use the local file, so file navigation, IntelliSense, and editing work as normal. You can add comments within the editor on these diffs. Both adding single comments and creating a whole review is supported.
When you are done reviewing the pull request changes you can merge the PR or select Exit Review Mode to go back to the previous branch you were working on.
Issues
Creating issues
Issues can be created from the + button in the Issues view and by using the GitHub Issues: Create Issue from Selection and GitHub Issues: Create Issue from Clipboard commands. They can also be created using a Code Action for «TODO» comments. When creating issues, you can take the default description or select the Edit Description pencil icon in the upper right to bring up an editor for the issue body.
You can configure the trigger for the Code Action using the GitHub Issues: Create Issue Triggers ( githubIssues.createIssueTriggers ) setting.
The default issue triggers are:
Working on issues
From the Issues view, you can see your issues and work on them.
By default, when you start working on an issue (Start Working on Issue context menu item), a branch will be created for you, as shown in the Status bar in the image below.
The Status bar also shows the active issue and if you select that item, a list of issue actions are available such as opening the issue on the GitHub website or creating a pull request.
You can configure the name of the branch using the GitHub Issues: Issue Branch Title ( githubIssues.issueBranchTitle ) setting. If your workflow doesn’t involve creating a branch, or if you want to be prompted to enter a branch name every time, you can skip that step by turning off the GitHub Issues: Use Branch For Issues ( githubIssues.useBranchForIssues ) setting.
Once you are done working on the issue and want to commit a change, the commit message input box in the Source Control view will be populated with a message, which can be configured with GitHub Issues: Working Issue Format SCM ( githubIssues.workingIssueFormatScm ).
GitHub Repositories extension
The GitHub Repositories extension lets you quickly browse, search, edit, and commit to any remote GitHub repository directly from within Visual Studio Code, without needing to clone the repository locally. This can be fast and convenient for many scenarios, where you just need to review source code or make a small change to a file or asset.
Opening a repository
Once you have installed the GitHub Repositories extension, you can open a repository with the GitHub Repositories: Open Repository. command from the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) or by clicking the Remote indicator in the lower left of the Status bar.
When you run the Open Repository command, you then choose whether to open a repository from GitHub, open a Pull Request from GitHub, or reopen a repository that you had previously connected to.
If you haven’t logged into GitHub from VS Code before, you’ll be prompted to authenticate with your GitHub account.
You can provide the repository URL directly or search GitHub for the repository you want by typing in the text box.
Once you have selected a repository or Pull Request, the VS Code window will reload and you will see the repository contents in the File Explorer. You can then open files (with full syntax highlighting and bracket matching), make edits, and commit changes, just like you would working on a local clone of a repository.
One difference from working with a local repository is that when you commit a change with the GitHub Repository extension, the changes are pushed directly to the remote repository, similar to if you were working in the GitHub web interface.
Another feature of the GitHub Repositories extension is that every time you open a repository or branch, you get the up-to-date sources available from GitHub. You don’t need to remember to pull to refresh as you would with a local repository.
Switching branches
You can easily switch between branches by clicking on the branch indicator in the Status bar. One great feature of the GitHub Repositories extension is that you can switch branches without needing to stash uncommitted changes. The extension remembers your changes and reapplies them when you switch branches.
Remote Explorer
You can quickly reopen remote repositories with the Remote Explorer available on the Activity bar. This view shows you the previously opened repositories and branches.
Create Pull Requests
If your workflow uses Pull Requests, rather than direct commits to a repository, you can create a new PR from the Source Control view. You’ll be prompted to provide a title and create a new branch.
Once you have created a Pull Request, you can use the GitHub Pull Request and Issues extension to review, edit, and merge your PR as described earlier in this topic.
Virtual file system
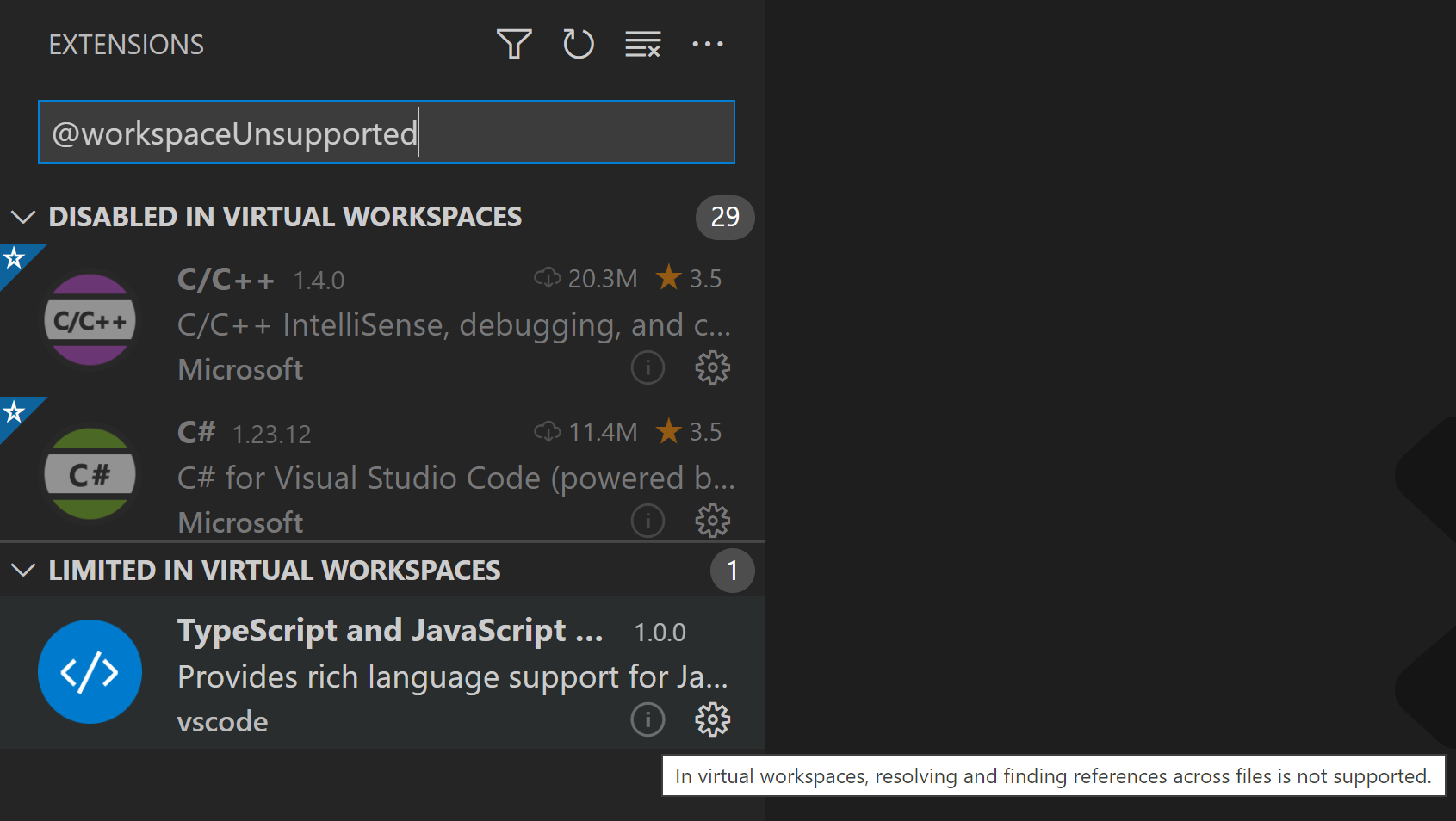
Without a repository’s files on your local machine, the GitHub Repositories extension creates a virtual file system in memory so you can view file contents and make edits. Using a virtual file system means that some operations and extensions which assume local files are not enabled or have limited functionality. Features such as tasks, debugging, and integrated terminals are not enabled and you can learn about the level of support for the virtual file system via the features are not available link in the Remote indicator hover.
Extension authors can learn more about running in a virtual file system and workspace in the Virtual Workspaces extension author’s guide.
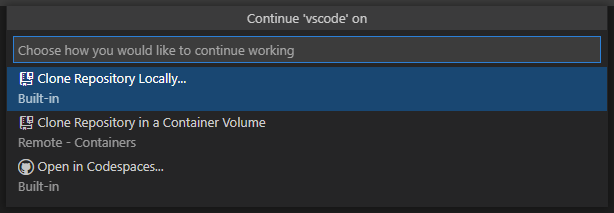
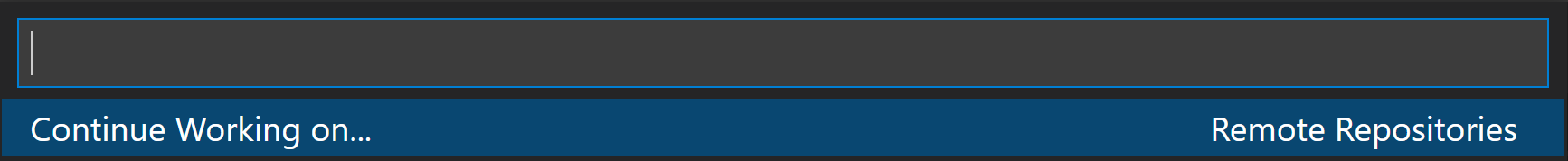
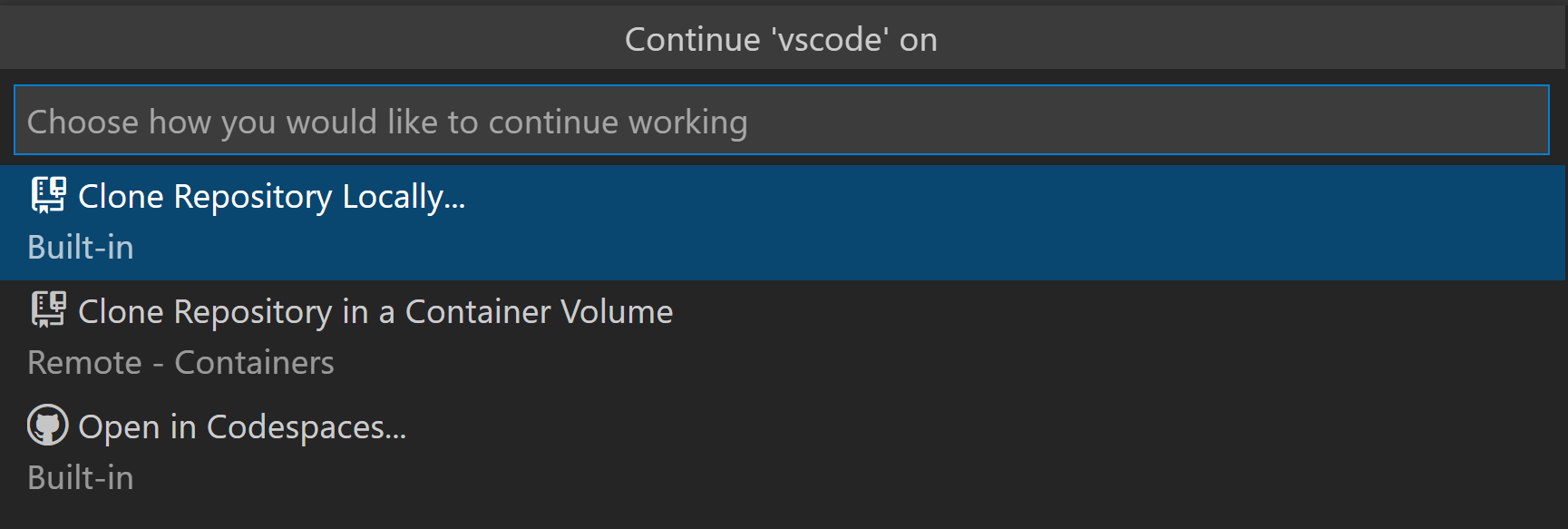
Continue Working on.
Sometimes you’ll want to switch to working on a repository in a development environment with support for a local file system and full language and development tooling. The GitHub Repositories extension makes it easy for you to clone the repository locally or into a Docker container (if you have Docker and the Microsoft Docker extension installed) with the GitHub Repositories: Continue Working on. command available from the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ) or by clicking on the Remote indicator in the Status bar.
If you are using the browser-based editor, the «Continue Working On. « command has the options to open the repository locally or within a cloud-hosted environment in GitHub Codespaces.
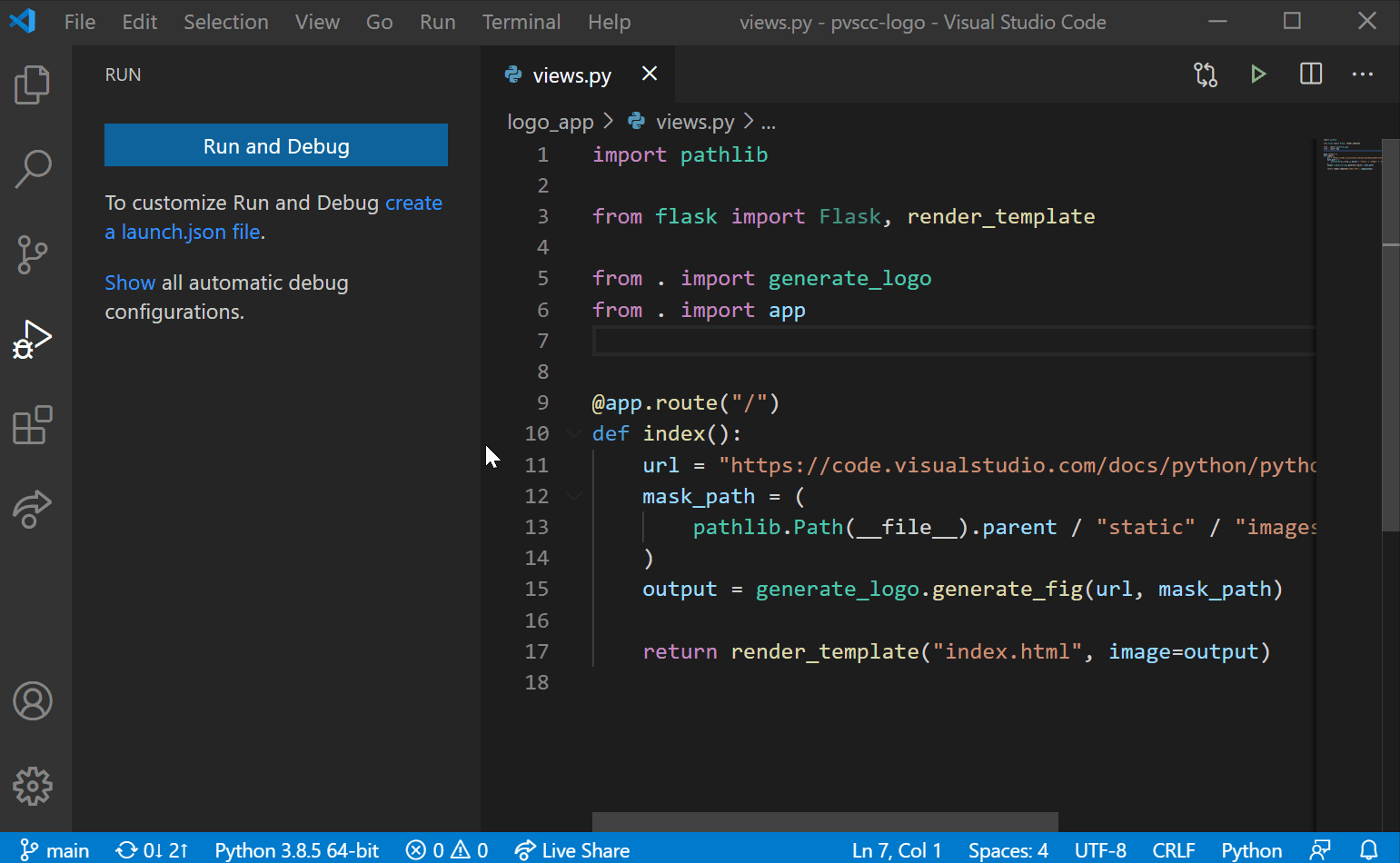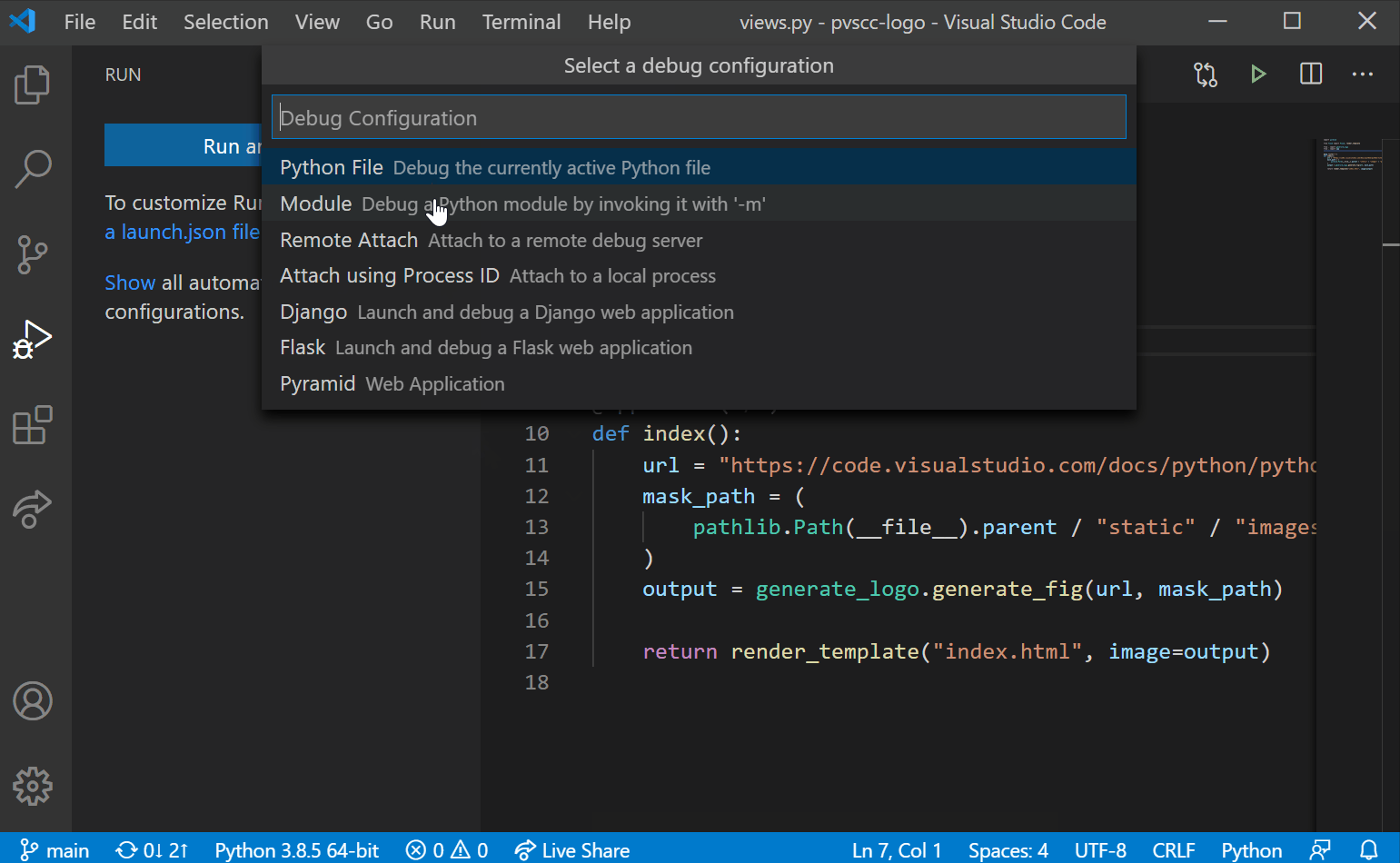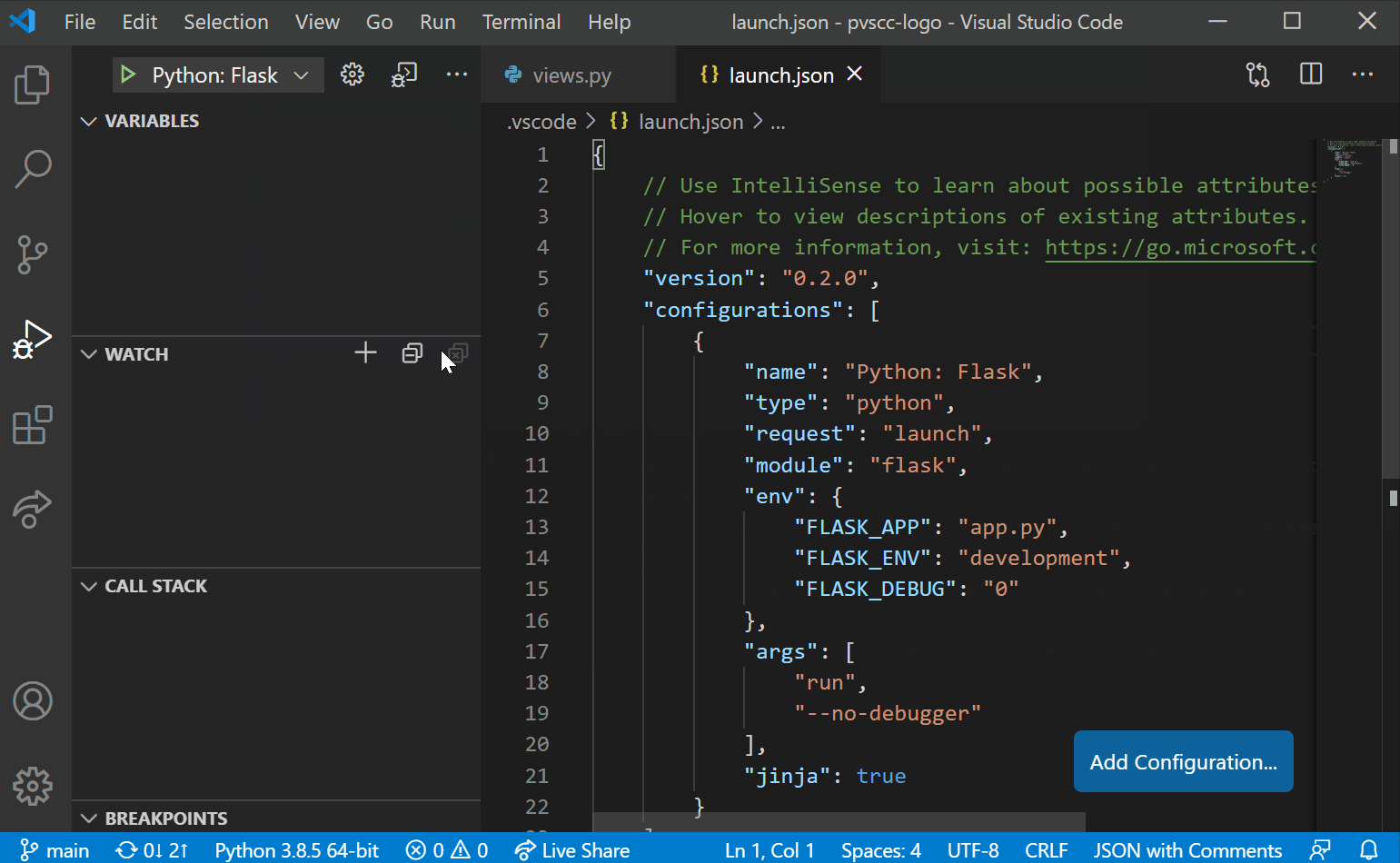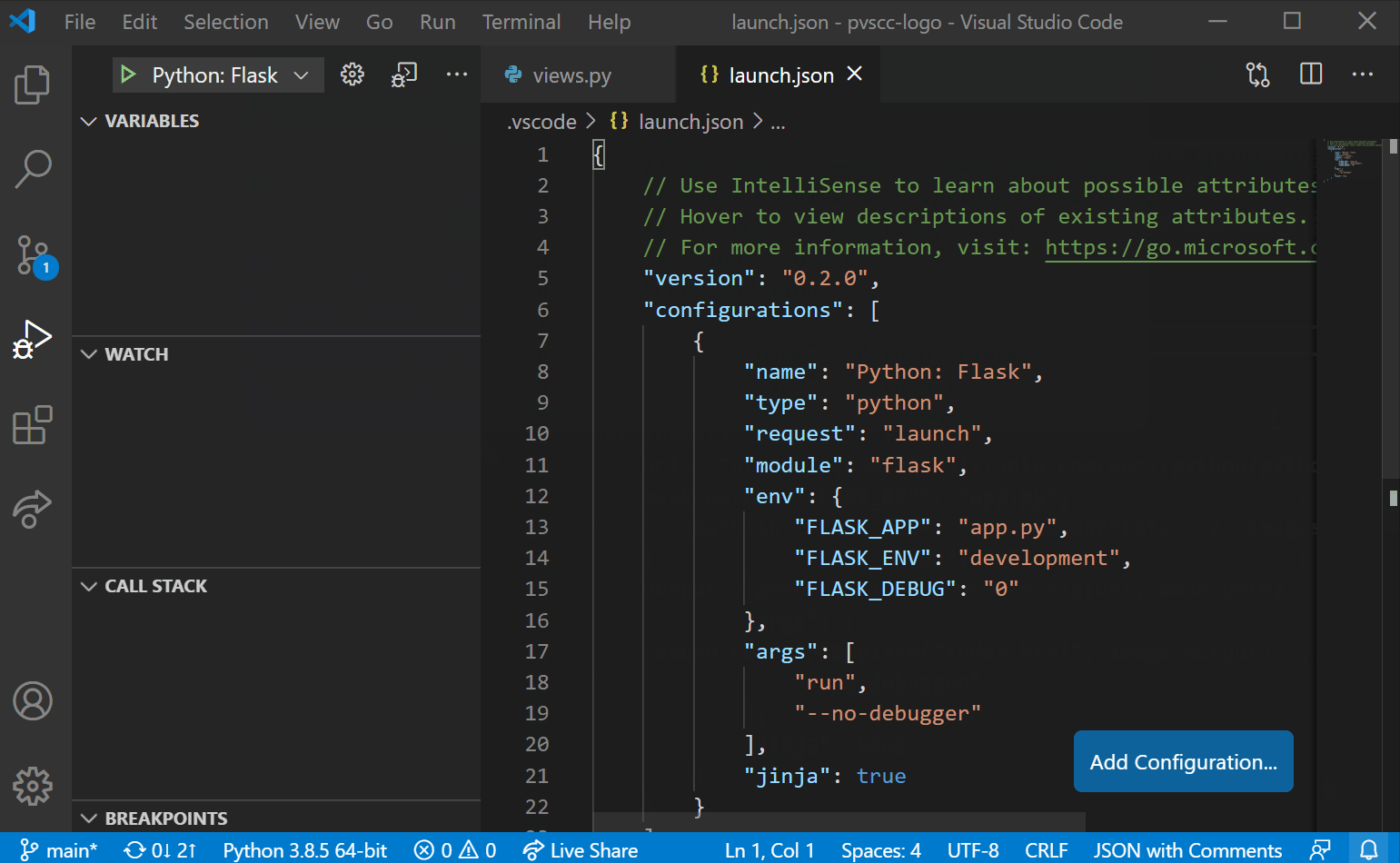
How to Get Visual Studio Code GitHub Setup Going!
Read more tutorials by June Castillote!
Table of Contents
There’s nothing wrong with using separate tools to perform those related activities. But, wouldn’t it be efficient if all your needed actions can be performed without leaving your IDE?
Not a reader? Watch this related video.
In this article, you will learn the basic Visual Studio Code GitHub setup. Then, you will be able to perform the typical Git actions like clone, stage, commit, and push, all while staying inside the Visual Studio Code application.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
If you plan to follow along with this walkthrough, you need to meet some requirements as follows.
The Git Extension
To get your Visual Studio Code GitHub setup working, you’ll need to work with Git. Visual Studio Code comes installed with a built-in extension for source control using Git. There are many configurations available with the Git extension. Still, the default settings are already right as they are out of the box.
Nevertheless, there are some configuration changes with the Git extension that you may want to change as a matter of preference. But before you do, you’ll need to know where to find the Git extension settings. Can’t change something when you can’t find it, yeah?
To open the settings using the menu, click on File —> Preferences —> Settings. Or you can also press CTRL+, shortcut.
Then, in the Settings tab, click Extensions —> Git. You should then see the list of configuration items for the Git extension, as shown below.
Now, this article does not cover every configuration item for Git. Still, they are mostly self-explanatory, especially if you’re already familiar with working with source control.
Making Sure Git Is Installed
“What? I thought Git is already built-in?”.
Well, the Git extension is built-in, but the Git program is not. The extension, as the name implies, is only meant to “extend” VS Code to integrate with Git. It can be confusing, and if it is for you, you may want to read up on What is Git first to have a better understanding.
To determine if GIt is installed and detected by the Git extension, click on the Source Control button or press CTRL+SHIFT+G while inside the VS Code window. If Git is not installed or detected, you would see a message, similar to the one below.
As you can see from the image above, in the Output pane, there are standard paths where VS Code tries to look for a valid Git binary installation. This situation means that you either have to install Git first or maybe Git is installed but in a path that is not recognized by VS Code.
If Git is Installed But in a Non-Standard Path
If Git is installed in a non-standard path, you can fix that by changing the Path value in the Git extension setting, as you can refer to below.
When you click on the Edit in settings.json link, the file will be opened in VS Code. See the screenshot below for reference. The value of the git.path must be changed to point to the correct path where the Git binary is installed. Then, save the settings after modification.
If Git is Not Installed
Needless to say, if Git is not installed, you need to install it. You can do so by downloading the installation file from this link —> https://git-scm.com/.
Once you’ve downloaded the file, follow the demonstration below on how to install Git with default options. The installation is straightforward, and there is no need to change the default options for this article. You’ll be well on your way to finishing your Visual Studio Code GitHub setup.
After you’re done installing Git, restart Visual Studio Code and confirm that the Git is now detected. The screenshot below shows what you’d expect to see if Git is detected.
Cloning a GitHub Repository
Now that you’ve completed the initial steps to ensure that VS Code works with GitHub, it is time to put it into action and confirm that you’ve done so far is correct. The fastest way to test is by cloning an existing repository in your GitHub account.
In this example, a private repository named junecastillote/demo will be used. You can use your repository for this instead. On the off chance that you do not have a repository yet, please refer to the Creating a new repository doc in GitHub to learn how to create one.
Follow the procedure below on how to clone a GitHub repository in VS Code.
The authorization page will automatically launch in your default web browser. Click on the Continue button.
The next page shows you the permission request details. To proceed in giving VS Code the required permissions, click on the Authorize GitHub button.
When authorization is done, you will get a status page similar to the one shown below. If prompted that the site is trying to open Visual Studio Code, click Open.
Once you’re back in the VS Code window, you can either search of the repository name or select the repository name that you intend to clone. In the example below, the repository name junecastillote/demo was searched and then selected.
After selecting the repository to clone, you will be asked to provide the folder where the repository will be saved locally on your computer. Specify the destination folder and click on Select Repository Location.
Note: GitHub log in will be triggered when performing actions that require authentication. Such actions include cloning from a private repository or pushing to a repository
The GitHub Login window will pop up, and you need to enter your GitHub credentials to log in.
After completing the login, VS Code will proceed to clone the remote repository to your computer. Once the cloning is done, you would get a notification at the bottom right of the VS Code window, as you can see from the screenshot below. Now, you can click either Open or Open in New Window depending on your preference.
As you can see from the screenshot below, the contents of the cloned GitHub repository is now loaded in VS Code. At this point, you can start making changes to your repository.
Staging, Committing and Pushing Changes to GitHub
Continuing on with your Visual Studio Code GitHub setup, at this point, VS Code is already setup to use Git and work with your GitHub repository. Also, a repository has been cloned in the previous section, which indicates all is working. However, you’re not done yet.
Next is to determine whether your changes to your cloned repository can be successfully pushed to your remote GitHub repository.
Adding and Modifying Files
Using the cloned repository in the previous section, the file README.MD is edited, as you can see below, to add a new line.
Next, to add a new file to the workspace, press CTRL+N or go to File —> New File. In this example, the new file is named demo.ps1. Edit the file to add content to it and then save it.
You would see that the new file you created will be marked with a U, which means untracked. Refer to the example screenshot below.
Untracked files are any files in your working directory that were not in your last snapshot and are not in your staging area. Reference: 2.2 Git Basics – Recording Changes to the Repository
Reviewing and Staging Changes
To look at and review the changes, go to the Source Control view. You should see that the two changes are needed to be reviewed. As you can see from the image below, clicking on each of the changes will open comparison of the original contents of the file and the proposed changes in it.
After reviewing, you are expected to either discard or stage the changes to the files.
You have the option to discard or stage the changes of each file. By clicking on the discard (↶) or the stage (+) sign next to the filename.
You can also stage or discard all changes at once by clicking on the More actions (…) button and selecting either the Stage All Changes or Discard All Changes menu items. In this example, all changes will be staged.
Committing Changes
Now that the changes have been staged, the next action is to commit the changes to the local repository. This step comes before pushing the changes to the remote GitHub repository.
To commit the changes, you must include a meaningful message to the commit. Like the example below, type in the message that you want to include in the commit. Once you’re satisfied with your message, press CTRL+ENTER or click the commit (✓) button to finish saving the changed to the local repository.
Pushing Changes to GitHub
After the changes are saved to the local repository, the Source Control view should reflect that the number of changes has reset to zero (0).
To finally push the changes in the local repository to remote repository in GitHub, click on the More actions (…) button and then click on Push.
Lastly, if you wish to confirm that the changes were pushed to GitHub, you can visit your GitHub repository and look for the last update details. As you can see below, the message or description of the files is the same as the message that was added to the commit before pushing the repository back to GitHub.
Extending VS Code Git with the GitHub Extension
If you’ve completed all the previous steps, then VS Code can already be used to work on your GitHub repositories. But GitHub integration can be further expanded by installing the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension. The said extension will add features such as the ability to review and manage pull requests and issues directly in VS Code, among others.
To install the extension, go to the Extensions view. Then in the search box, enter the search term “GitHub Pull Requests and Issues“. When the extension page is displayed, click on the Install button to install it. Refer to the demonstration below.
Another way you can install the extension is by command line. First, copy the command below and run in the VS Code terminal to install the extension.
Once the command above has completed, you may need to reload your VS Code window for the extension to be activated.
To reload the VS Code window, press CTRL+SHIFT+P to bring up the command palette. Then type in reload window and press enter, and the VS Code window will be reloaded. You can refer to the install process demo below.
Summary
Visual Studio Code is a feature-rich application where different functionalities converge and integrate with the use of various extensions. The Git extension that comes with VS Code allows developers to use a single interface to perform code editing, staging, committing and pushing changes to a remote repository such as GitHub.
In this example, you learned how to set up VS Code and Git to work with GitHub. You’ve learned how to perform various Git actions inside VS Code such as clone, stage, commit and push.
The knowledge covered in this article only pertains to the basics of using VS Code with GitHub. As you’re already aware, VS Code’s GitHub integration can be further expanded by installing extensions.
Where you’re ready to learn more, one of the things you can test is using VS Code to review and manage issues or even merge pull requests in GitHub all within the VS Code application.
Thank you for reading!
Further Reading
Hate ads? Want to support the writer? Get many of our tutorials packaged as an ATA Guidebook.
More from ATA Learning & Partners
Recommended Resources!
Recommended Resources for Training, Information Security, Automation, and more!
Get Paid to Write!
ATA Learning is always seeking instructors of all experience levels. Regardless if you’re a junior admin or system architect, you have something to share. Why not write on a platform with an existing audience and share your knowledge with the world?
ATA Learning Guidebooks
ATA Learning is known for its high-quality written tutorials in the form of blog posts. Support ATA Learning with ATA Guidebook PDF eBooks available offline and with no ads!
How to Contribute
Project Management
Contributing
Documentation
Clone this wiki locally
Contributing to Visual Studio Code
There are many ways to contribute to the Visual Studio Code project: logging bugs, submitting pull requests, reporting issues, and creating suggestions.
After cloning and building the repo, check out the issues list. Issues labeled help wanted are good issues to submit a PR for. Issues labeled good first issue are great candidates to pick up if you are in the code for the first time. If you are contributing significant changes, or if the issue is already assigned to a specific month milestone, please discuss with the assignee of the issue first before starting to work on the issue.
You’ll need the following tools:
In case of issues, try deleting the contents of
/.cache/node-gyp for Linux,
/Library/Caches/node-gyp/ for macOS, or %USERPROFILE%\AppData\Local\node-gyp for Windows) first and then run yarn cache clean and then try again.
If you have Visual Studio 2019 installed, you may face issues when using the default version of node-gyp. If you have Visual Studio 2019 installed, you may need to follow the solutions here.
Docker / the Codespace should have at least 4 Cores and 6 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended) to run the full build. See the development container README for more information.
Enable Commit Signing
If you’re a community member, feel free to jump over this step.
Otherwise, if you’re a member of the VS Code team, follow the Commit Signing guide.
If you want to understand how VS Code works or want to debug an issue, you’ll want to get the source, build it, and run the tool locally.
NOTE: If you need to debug the 32bit version of VS Code on 64bit Windows, follow the guide on how to do that.
Getting the sources
First, fork the VS Code repository so that you can make a pull request. Then, clone your fork locally:
Occasionally you will want to merge changes in the upstream repository (the official code repo) with your fork.
Manage any merge conflicts, commit them, and then push them to your fork.
Install and build all of the dependencies using Yarn :
Then you have two options:
The incremental builder will do an initial full build and will display a message that includes the phrase «Finished compilation» once the initial build is complete. The builder will watch for file changes and compile those changes incrementally, giving you a fast, iterative coding experience.
Troubleshooting:
Errors and Warnings
👉 Tip! You don’t need to stop and restart the development version of VS Code after each change. You can just execute Reload Window from the command palette. We like to assign the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + R ( CMD + R on macOS) to this command.
Running on Electron with extensions run in NodeJS:
macOS and Linux
Windows
👉 Tip! If you receive an error stating that the app is not a valid Electron app, it probably means you didn’t run yarn watch first.
VS Code for the Web
Extensions and UI run in the browser.
👉 Besides yarn watch also run yarn watch-web to build the web bits for the built-in extensions.
macOS and Linux
Windows
Code Server Web
UI in the browser, extensions run in code server (NodeJS):
macOS and Linux
Windows
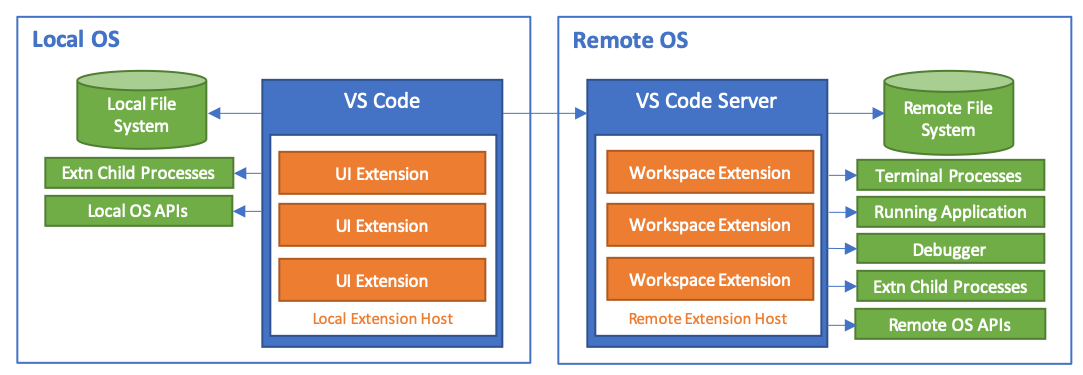
VS Code has a multi-process architecture and your code is executed in different processes.
The render process runs the UI code inside the Shell window. To debug code running in the render you can either use VS Code or the Chrome Developer Tools.
Using the Chrome Developer Tools
The search process can be debugged, but must first be started. Before attempting to attach, start a search by pressing Ctrl + P ( CMD + P on macOS), otherwise, attaching will fail and time out.
We also have automated UI tests. The smoke test README has all the details.
To lint the source as you make changes you can install the eslint extension.
Even if you have push rights on the Microsoft/vscode repository, you should create a personal fork and create feature branches there when you need them. This keeps the main repository clean and your personal workflow cruft out of sight.
Before we can accept a pull request from you, you’ll need to sign a Contributor License Agreement (CLA). It is an automated process and you only need to do it once.
To enable us to quickly review and accept your pull requests, always create one pull request per issue and link the issue in the pull request. Never merge multiple requests in one unless they have the same root cause. Be sure to follow our Coding Guidelines and keep code changes as small as possible. Avoid pure formatting changes to code that has not been modified otherwise. Pull requests should contain tests whenever possible.
Introducing usage of new Electron API with a PR
A pull request that depends on Electron API that VS Code is currently not using comes with a certain risk and may be rejected. Whenever we update Electron, there is a chance that less popular Electron APIs break and it is very hard to find out upfront. Once a PR lands in VS Code, the role of maintaining the feature moves to the team and as such we have to follow up with upstream components to ensure the feature is still supported. As such, as a rule of thumb:
Where to Contribute
Check out the full issues list for a list of all potential areas for contributions. Note that just because an issue exists in the repository does not mean we will accept a contribution to the core editor for it. There are several reasons we may not accept a pull request like:
To avoid multiple pull requests resolving the same issue, let others know you are working on it by saying so in a comment.
Spell check errors
Pull requests that fix spell check errors in translatable strings (strings in nls.localize(. ) calls) are welcomed but please make sure it doesn’t touch multiple feature areas, otherwise it will be difficult to review. Pull requests only fixing spell check errors in source code are not recommended.
VS Code can be packaged for the following platforms: win32-ia32 | win32-x64 | darwin-x64 | darwin-arm64 | linux-ia32 | linux-x64 | linux-arm
These gulp tasks are available:
👉 Tip! Run gulp via yarn to avoid potential out of memory issues, for example yarn gulp vscode-linux-x64
We’re also interested in your feedback for the future of VS Code. You can submit a suggestion or feature request through the issue tracker. To make this process more effective, we’re asking that these include more information to help define them more clearly.
We accept feedback on translations in language packs via GitHub issues in our localization repo that contains our currently supported language packs.
In order to keep the conversation clear and transparent, please limit discussion to English and keep things on topic with the issue. Be considerate to others and try to be courteous and professional at all times.
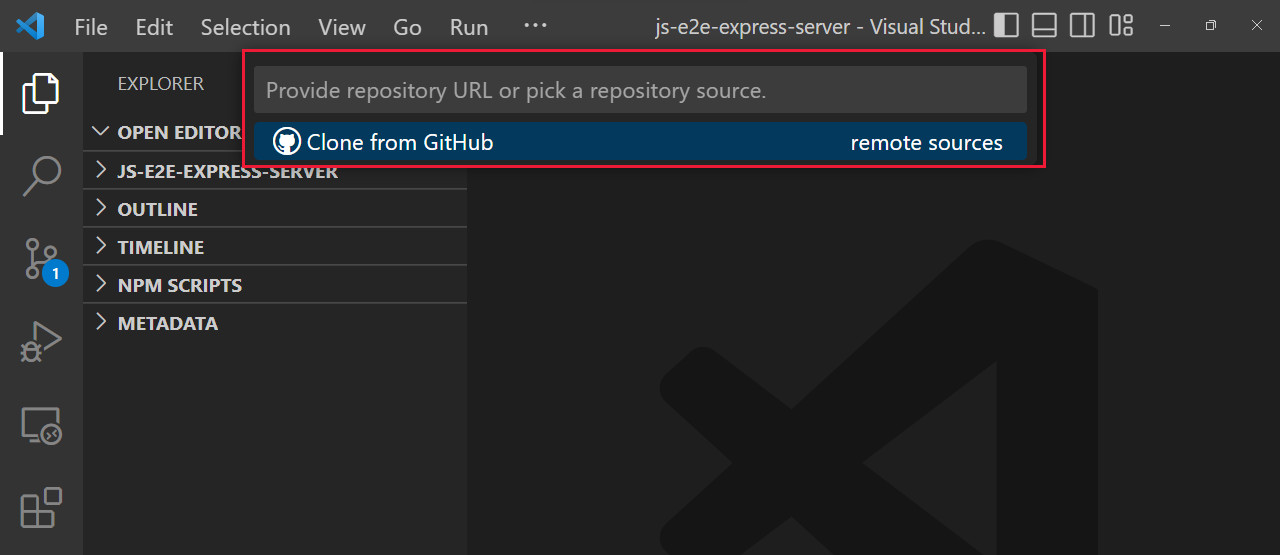
Clone and use a GitHub repository in Visual Studio Code
Learn the steps to clone a public repository from GitHub to your local computer using Visual Studio Code.
Clone repository
To get started, download the sample project using the following steps:
When prompted for the Repository URL, select clone from GitHub, then press Enter.
If you are asked to sign into GitHub, complete the sign-in process.
Enter azure-samples/js-e2e-express-server in the Repository URL field.
Select (or create) the local directory into which you want to clone the project.
When you receive the notification asking if you want to open the cloned repository, select Open.
Clone your repo with the following git command:
Change your terminal into that new subdirectory:
Then open in Visual Studio Code:
Initialize new repository
If you don’t have a GitHub repository yet, but would like to start your project locally, initialize your folder with git.
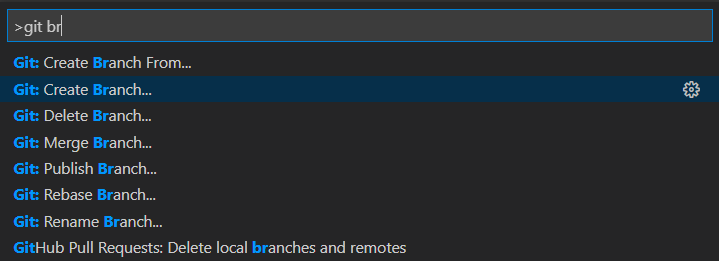
Create a branch for changes
Enter a new branch name. The branch name is visible in the status bar.
Select the branch name in the status bar. This opens the command palette.
The status bar is usually found at the bottom of Visual Studio code.
In the command palette, select +Create a new branch.
Enter your new branch name.
Enter a new branch name. The branch name is visible in the status bar.
Create a new branch named MY-BRANCH with the following git command:
Commit changes locally
Once you have made changes on your branch, commit the changes.
Push a local branch to GitHub
On the Visual Studio Code status bar, select the push icon to the right of the branch name.
Select the remote name from the pop-up box. If you have just one remote, you won’t be asked to select the remote name.
Select the Source Control icon from the activity bar.
Select the remote name from the pop-up box. If you have just one remote, you won’t be asked to select the remote name.
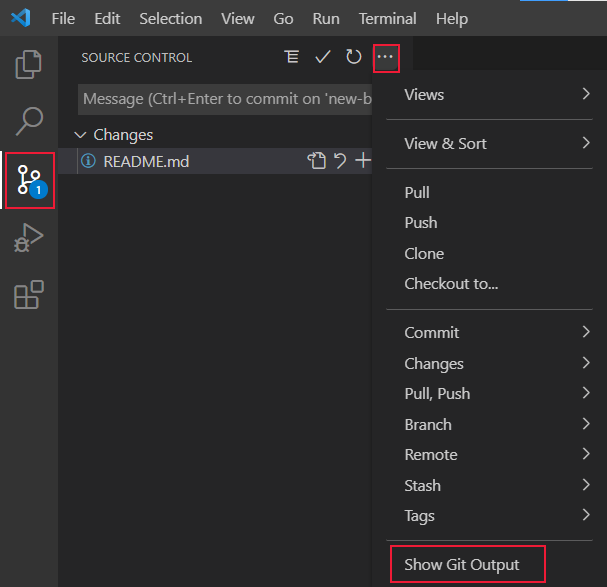
View Git output
You can view the Git commands run when you use the Source control extension. This helps debug when a command fails.
Select the Source Control icon from the activity bar.
Select the ellipsis (. ) then select Show Git Output.
Visual Studio Code tools to work with Git and GitHub
Working in Visual Studio Code with a repository uses separate tools.
Клонирование и использование репозитория GitHub в Visual Studio Code
Сведения о клонировании общедоступного репозитория из GitHub на локальный компьютер с помощью Visual Studio Code.
Клонирование репозитория
Чтобы приступить к работе, скачайте пример проекта, как описано ниже.
Если появится запрос на ввод URL-адреса репозитория, выберите параметр клонирования из GitHub и нажмите клавишу ВВОД.
Если поступает запрос на вход в GitHub, завершите процедуру входа.
Введите azure-samples/js-e2e-express-server в поле URL-адрес репозитория.
Выберите (или создайте) локальный каталог, в который нужно клонировать проект.
Когда появится уведомление с вопросом, нужно ли открыть клонированный репозиторий, выберите вариант Открыть.
Откройте интегрированный терминал из терминала —> новый терминал.
Клонируйте репозиторий с помощью следующей команды Git:
Измените терминал на новый подкаталог:
Затем откройте Visual Studio Code:
Инициализация нового репозитория
Если у вас еще нет репозитория GitHub, но вы хотите запустить проект локально, инициализируйте папку с помощью Git.
Создание ветви для изменений
Введите имя для новой ветви. Имя ветви будет отображатся в строке состояния.
Выберите имя ветви в строке состояния. Откроется палитра команд.
Строка состояния обычно находится в нижней части Visual Studio code.
Выберите в палитре команд элемент Создание ветви.
Введите имя для новой ветви.
Введите имя для новой ветви. Имя ветви будет отображатся в строке состояния.
Откройте интегрированный терминал из терминала —> новый терминал.
Создайте новую ветвь с именем MY-BRANCH с помощью следующей команды Git:
Фиксация изменений в локальной среде
После внесения изменений в ветвь зафиксируйте изменения.
Отправка локальной ветви в GitHub
В строке состояния Visual Studio Code выберите значок отправки справа от имени ветви.
Выберите имя удаленного расположения во всплывающем окне. Если вы имеете только одно удаленное расположение, вам не будет предложено выбрать имя такого расположения.
Щелкните значок «Система управления версиями» на панели действий.
Выберите имя удаленного расположения во всплывающем окне. Если вы имеете только одно удаленное расположение, вам не будет предложено выбрать имя такого расположения.
Просмотр выходных данных Git
Вы можете просмотреть команды Git, выполняемые при использовании расширения системы управления версиями. Это помогает выполнить отладку при сбое команды.
Щелкните значок «Система управления версиями» на панели действий.
Щелкните многоточие (. ) и выберите элемент Показать выходные данные Git.
средства Visual Studio Code для работы с Git и GitHub
При работе в Visual Studio Code с репозиторием необходимо использовать отдельные средства.
Deploy your projects on Github using Visual Studio Code and Git
Visual Studio Code is the new black. Everywhere I go, whether it’s youtube or one of the popular social media sites, Visual Studio is being held in high esteem. I wondered why? So I checked out what it had to offer and what converted me to become a regular user is the way VSC approached version control.
What’s not to love? It has an integrated terminal. It presents version control in a visually appealing manner, making it easy to track file changes, and not to mention the plethora of commands organized in a drop-down menu.
In this article, I will hold your hand from beginning to end and show you how you can start using Visual Studio Code and Git to deploy your projects on Github.
( If you haven’t done so yet, check out my previous article, “ How to understand Git and GitHub for beginners” in which I light-heartedly explain the what and the why to version control and its fundamental importance for anyone aspiring to be a web developer. )
What you need:
Installing them is pretty straightforward, but if you like reading manuals then docs are provided within the links I provided.
Once everything is installed, we begin with the first step.
1. Open the Gitbash terminal and configure git settings
Run these four commands:
git config — global user.name “type your name here”
git config — global user.email typeyour@email.com
git config — global push.default matching
git config — global alias.co checkout
To see if you did this right, you can type:
git config — global user.name and git config — global user.email
2. Create a folder for your project
3. Open your folder project in Visual Studio Code
Click file → Click open folder → Highlight your folder →Click Select Folder
You can just drag your folder and drop it inside VSC
At this point, it should look like this:
4. Create a new file
Click file → Click new file → Click file again → Click save → Name your file index.html
5. Set up your index.html
Make sure you’re on the index.html — Click on the blank canvas → Type doc then press Tab immediately after
This will automatically create a simple HTML template for your index file, one of the many built-in functions that make VSC awesome.
Установка средств для создания содержимого
В этой статье объясняется, как установить клиентские средства Git и Visual Studio Code в интерактивном режиме.
Если вы вносите в статью лишь небольшие изменения, вам не нужно выполнять описанные здесь шаги. Вы можете сразу перейти к рабочему процессу по внесению быстрых изменений.
Участникам, которые будут вносить значительные изменения, рекомендуется выполнить эти шаги. Это позволит им применить рабочий процесс по внесению значительных изменений или изменений, требующих длительного времени. Даже если у вас есть разрешения на запись в основном репозитории, настоятельно рекомендуется (и в этом руководстве предполагается, что вы это сделаете) создать вилку и клон репозитория, чтобы у вас были права на чтение и запись для хранения в этой вилке предлагаемых вами изменений.
Установка клиентских средств для Git
Пакет установки включает систему управления версиями Git и приложение командной строки Git Bash, используемое для взаимодействия с локальным репозиторием Git.
Установка клиентских средств Git для Windows
Запустите скачанный исполняемый файл (.EXE) и следуйте инструкциям по установке. Щелкните Далее в каждом запросе, чтобы принять все параметры по умолчанию.
Щелкните Готово, чтобы завершить установку.
После установки Git для Windows вам нужно будет настроить свое имя и адрес электронной почты Git перед установкой Visual Studio Code.
Установка клиентских средств Git для Mac и Linux
Следуйте инструкциям по установке и настройке для выбранного клиента.
Установка Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (также называется VS Code) — это простой редактор, который работает в Windows, Linux и Mac. Он включает интеграцию с Git и поддержку расширений.
Установка Visual Studio Code для Windows, Mac и Linux
Установка расширений Visual Studio Code
Чтобы установить расширения:
Запустите Visual Studio Code.
Щелкните квадратный значок Расширения на панели навигации слева. Откроется область Расширения: Marketplace.
В поле Поиск расширений в Marketplace введите имя расширения, которое нужно найти.
В появившихся результатах выберите нужное расширение и щелкните Установить.
Установка пакета создания документации.
Расширение Docs Authoring Pack для Visual Studio Code обеспечивает базовую помощь в разработке Markdown, а также поддержку шаблонов Markdown, markdownlint и средства проверки орфографии кода, а также позволяет выполнять предварительный просмотр страниц. Эти функции упрощают и ускоряют процесс публикации. Поэтому мы рассмотрим расширение Docs Authoring Pack, которое является обязательным для участников.
Чтобы установить Docs Authoring Pack, щелкните Install (Установить) на странице Docs Authoring Pack в VS Code Marketplace.
Сведения о редакторах Markdown
Markdown — это упрощенный язык разметки, используемый для создания содержимого. Visual Studio Code — предпочтительное средство для редактирования разметки Markdown в Майкрософт. Atom — еще одно популярное средство для редактирования разметки Markdown. Основные сведения о Markdown и функциях, которые поддерживаются настраиваемыми расширениями OPS для Markdown, см. в статье Справочник по Markdown.
Using GitHub Codespaces in Visual Studio Code
In this article
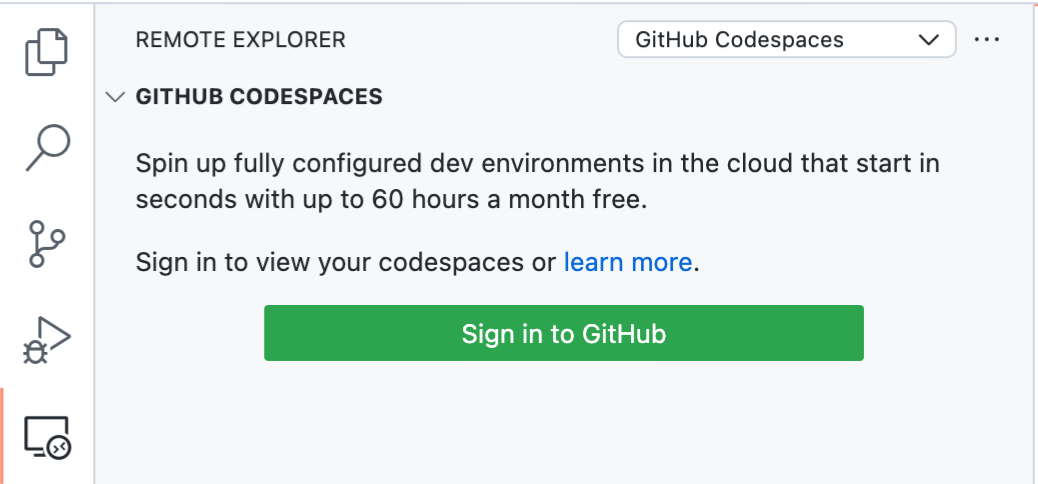
You can develop in your codespace directly in Visual Studio Code by connecting the GitHub Codespaces extension with your account on GitHub.
GitHub Codespaces is available for organizations using GitHub Team or GitHub Enterprise Cloud. GitHub Codespaces is also available as a limited beta release for individual users on GitHub Free and GitHub Pro plans. For more information, see «GitHub’s products.»
About GitHub Codespaces in Visual Studio Code
You can use your local install of Visual Studio Code to create, manage, work in, and delete codespaces. To use GitHub Codespaces in VS Code, you need to install the Codespaces extension. For more information on setting up Codespaces in VS Code, see «Prerequisites.»
By default, if you create a new codespace on GitHub.com, it will open in the browser. If you would prefer to open any new codespaces in VS Code automatically, you can set your default editor to be VS Code. For more information, see «Setting your default editor for GitHub Codespaces.»
If you prefer to work in the browser, but want to continue using your existing VS Code extensions, themes, and shortcuts, you can turn on Settings Sync. For more information, see «Personalizing GitHub Codespaces for your account.»
To develop in a codespace directly in VS Code, you must install and sign into the Codespaces extension with your GitHub credentials. The Codespaces extension requires VS Code October 2020 Release 1.51 or later.
Use the Visual Studio Code Marketplace to install the Codespaces extension. For more information, see Extension Marketplace in the VS Code documentation.
In VS Code, in the left sidebar, click the Remote Explorer icon.
Note: If the Remote Explorer is not displayed in the Activity Bar:
To authorize VS Code to access your account on GitHub, click Allow.
Sign in to GitHub to approve the extension.
In VS Code, in the left sidebar, click the Remote Explorer icon.
Note: If the Remote Explorer is not displayed in the Activity Bar:
Use the «REMOTE EXPLORER» drop-down, then click GitHub Codespaces.
To authorize VS Code to access your account on GitHub, click Allow.
Sign in to GitHub to approve the extension.
Creating a codespace in VS Code
After you connect your account on GitHub.com to the GitHub Codespaces extension, you can create a new codespace. For more information about the GitHub Codespaces extension, see the VS Code Marketplace marketplace.
Note: Currently, VS Code doesn’t allow you to choose a dev container configuration when you create a codespace. If you want to choose a specific dev container configuration, use the GitHub web interface to create your codespace. For more information, click the Web browser tab at the top of this page.
In VS Code, in the left sidebar, click the Remote Explorer icon.
Note: If the Remote Explorer is not displayed in the Activity Bar:
Click the Add icon:
Type the name of the repository you want to develop in, then select it.
Click the branch you want to develop on.
If prompted to choose a dev container configuration file, choose a file from the list.
Click the machine type you want to use.
Note: Your choice of available machine types may be limited by a policy configured for your organization, or by a minimum machine type specification for your repository. For more information, see «Restricting access to machine types» and «Setting a minimum specification for codespace machines.»
Opening a codespace in VS Code
In VS Code, in the left sidebar, click the Remote Explorer icon.
Note: If the Remote Explorer is not displayed in the Activity Bar:
Under «Codespaces», click the codespace you want to develop in.
Click the Connect to Codespace icon.
Changing the machine type in VS Code
Typically, you can run your codespace on a choice of remote machine, from 2 cores to 32 cores. Each of these has a different level of resources and a different billing tier. For information, see «About billing for GitHub Codespaces.»
By default the machine type with the lowest valid resources is used when you create a codespace. You can change the machine type of your codespace at any time.
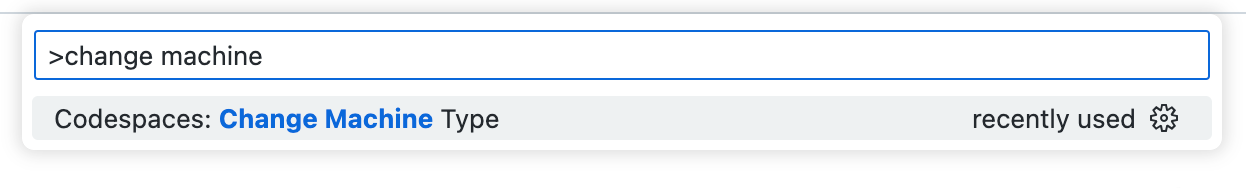
In VS Code, open the Command Palette ( shift command P / shift control P ).
Search for and select «Codespaces: Change Machine Type.»
Click the codespace that you want to change.
Choose the machine type you want to use.
Note: Your choice of available machine types may be limited by a policy configured for your organization, or by a minimum machine type specification for your repository. For more information, see «Restricting access to machine types» and «Setting a minimum specification for codespace machines.»
If the codespace is currently running, a message is displayed asking if you would like to restart and reconnect to your codespace now.
Click Yes if you want to change the machine type used for this codespace immediately.
If you click No, or if the codespace is not currently running, the change will take effect the next time the codespace restarts.
Deleting a codespace in VS Code
You can delete codespaces from within VS Code when you are not currently working in a codespace.
In VS Code, in the left sidebar, click the Remote Explorer icon.
Note: If the Remote Explorer is not displayed in the Activity Bar:
Under «GITHUB CODESPACES», right-click the codespace you want to delete.
Click Delete Codespace.
Switching to the Insiders build of VS Code
You can use the Insiders Build of VS Code within Codespaces.
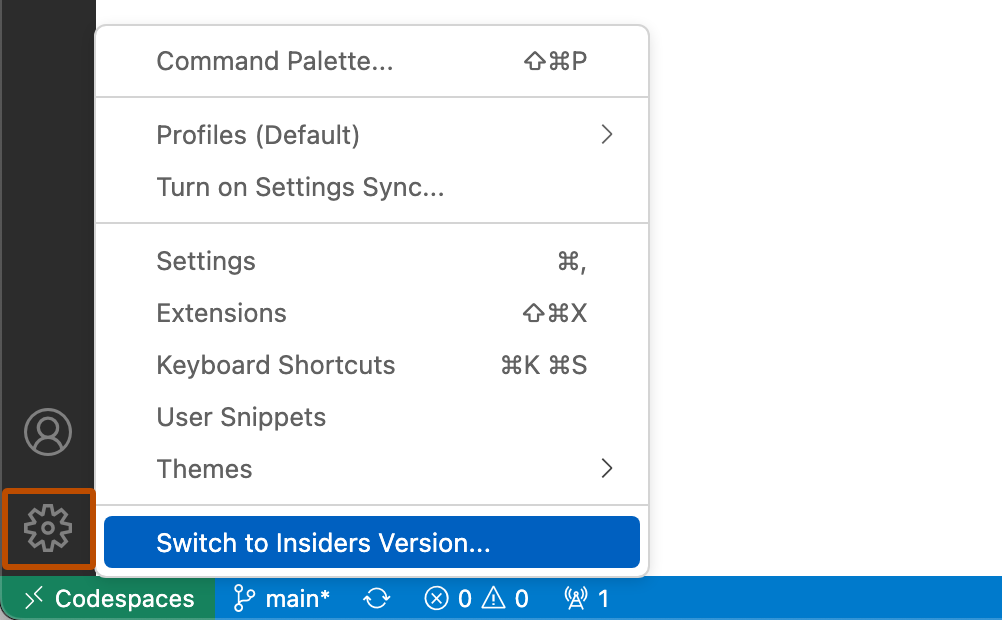
In bottom left of your Codespaces window, select
From the list, select «Switch to Insiders Version».
Once selected, Codespaces will continue to open in Insiders Version.
Help us make these docs great!
All GitHub docs are open source. See something that’s wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
How to add a new project to Github using VS Code
All the tutorials i’ve seen till now shows to first create a repository on github, copy the link go to vscode and git clone it and from that on, you can do commits and pushes.
EDIT 2020 :
You can now do it right inside vscode! just follow these steps:
1- Open your new project folder with vscode
2- click on the source conrol menu on the sidebar 
3- Click on publish to github
4- From there just login and follow the instructions and you’re good to go.
@Debu’s answer details every step, so you can jump to there
16 Answers 16
Trending sort
Trending sort is based off of the default sorting method — by highest score — but it boosts votes that have happened recently, helping to surface more up-to-date answers.
It falls back to sorting by highest score if no posts are trending.
Switch to Trending sort
Here are the detailed steps needed to achieve this.
The existing commands can be simply run via the CLI terminal of VS-CODE. It is understood that Git is installed in the system, configured with desired username and email Id.
1) Navigate to the local project directory and create a local git repository:
2) Once that is successful, click on the ‘Source Control’ icon on the left navbar in VS-Code.One should be able to see files ready to be commit-ed. Press on ‘Commit’ button, provide comments, stage the changes and commit the files. Alternatively you can run from CLI
3) Now you need to visit your GitHub account and create a new Repository. Exclude creating ‘README.md’, ‘.gitIgnore’ files. Also do not add any License to the repo. Sometimes these settings cause issue while pushing in.
4) Copy the link to this newly created GitHub Repository.
5) Come back to the terminal in VS-CODE and type these commands in succession:
Note: If it is the first time the local git account is trying to connect to GitHub, you may be required to enter credentials to GitHub in a separate window.
6) You can see the success message in the Terminal. You can also verify by refreshing the GitHub repo online.
Visual studio code github
Copy raw contents


Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code combines the simplicity of a code editor with what developers need for their core edit-build-debug cycle. It provides comprehensive code editing, navigation, and understanding support along with lightweight debugging, a rich extensibility model, and lightweight integration with existing tools.
Visual Studio Code is updated monthly with new features and bug fixes. You can download it for Windows, macOS, and Linux on Visual Studio Code’s website. To get the latest releases every day, install the Insiders build.
There are many ways in which you can participate in this project, for example:
If you are interested in fixing issues and contributing directly to the code base, please see the document How to Contribute, which covers the following:
See our wiki for a description of each of these channels and information on some other available community-driven channels.
Many of the core components and extensions to VS Code live in their own repositories on GitHub. For example, the node debug adapter and the mono debug adapter repositories are separate from each other. For a complete list, please visit the Related Projects page on our wiki.
Docker / the Codespace should have at least 4 Cores and 6 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended) to run full build. See the development container README for more information.
Code of Conduct
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
GitHub Codespaces
Environments
An environment is the «backend» half of GitHub Codespaces. It’s where all of the compute associated with software development happens: compiling, debugging, restoring, etc. When you need to work on a new project, pick up a new task, or review a PR, you can simply spin up a Cloud-hosted environment, and GitHub Codespaces takes care of configuring it correctly. It automatically configures everything you need to work on your project: the source code, runtime, compiler, debugger, editor, custom dotfile configurations, relevant editor extensions and more.
Customization
GitHub Codespaces are fully customizable on a per project basis. This is accomplished by including a devcontainer.json file in the project’s repository, similar to VS Code Remote Container development.
Example customizations include:
See the Configuring Codespaces documentation for codespace-specific devcontainer.json settings.
Dotfile per user configuration
You can specify a GitHub repo containing your dotfiles, a target location for the files, as well as install commands when creating a codespace.
See the Personalizing Codespaces documentation to learn how to add your dotfile configurations to a codespace.
Getting started
There are getting started topics for both GitHub Codespaces clients. These will fast-track you through signing in to GitHub Codespaces, creating your first codespace, and connecting to it with your preferred client:
Extension authors
The VS Code extension API hides most of the implementation details of running remotely so many extensions will just work in GitHub Codespaces environments without any modification. However, we recommend that you test your extension in a codespace to be sure that all of its functionality works as expected. See the article on Supporting Remote Development and GitHub Codespaces for details.
Browser-based editor
You also have a free, lightweight Visual Studio Code experience entirely in the browser. The web-based editor lets you browse source code repositories from GitHub safely and quickly and make lightweight code changes. You can open any repository, fork, or pull request in the editor, which has many of the features of VS Code, including search and syntax highlighting. If you want to run or debug your code, you can switch to the cloud-hosted environment or the VS Code desktop.
Limitation: You may not be able to use the web-based editor if you are running your browser with Incognito mode or have ad blockers enabled.
Note: This editor is currently in Technical Preview. You can try it out today and provide feedback at https://github.co/browser-editor-feedback.
Known limitations and adaptations
While working with Codespaces and specifically VS Code in the web, there are certain limitations to keep in mind. Some of these limitations have workarounds or adaptations in place to provide a consistent development experience.
For several issues (especially keybindings or those listed with a workaround for the desktop), you can install and use a Codespace as a progressive web application (PWA).
Some extensions behave differently in the web
Common questions
Why is an extension not installable in the browser
There are a small number of extensions that have built-in assumptions or need to run on the desktop. Examples are when an extension accesses files from the VS Code installation on the desktop or when an extension depends on an executable that must run in a desktop environment. When you try to install such an extension in the browser, you will be informed that the extension is not available.
Notice such an extension can still be used when connecting to a Codespace from VS Code running on the desktop.
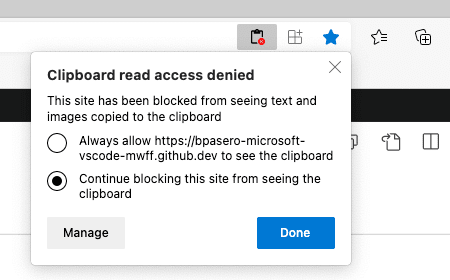
How do I allow VS Code to access my clipboard for reading?
In certain cases, VS Code might ask you for permission to access the clipboard when reading from it. You should be able to grant access to the clipboard from your browser either through settings (search for «site permissions») or by looking for this option in the address bar on the right:
Once you have granted VS Code access to the clipboard, you can retry the operation.
How do I allow VS Code to always open new tabs and windows?
Sometimes browsers will, as a security precaution, block VS Code from opening new tabs or windows. If this happens, VS Code will detect the blocking action and explicitly prompt the user. However, you can allow VS Code to always open new windows and tabs by opening the site settings via the context menu in the browser navigation bar and by allowing to Pop-up Windows.
How do I allow VS Code in a browser to access local files and folders?
Opening local files and folders in VS Code from a browser requires the browser to support the File System Access API. As of today both Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome offer this level of support. If you want to access local files and folders when using VS Code in a browser, please consider to switch to one of these two browsers.
Questions or feedback
If you have questions, you can consult the GitHub Codespaces Troubleshooting guide. If you’d like to provide feedback, you can enter issues in the GitHub Codespaces Discussions.
GitHub Pull Requests and Issues
GitHub
Review and manage your GitHub pull requests and issues directly in VS Code
This extension allows you to review and manage GitHub pull requests and issues in Visual Studio Code. The support includes:
Getting Started
It’s easy to get started with GitHub Pull Requests for Visual Studio Code. Simply follow these steps to get started.
Configuring the extension
There are several settings that can be used to configure the extension.
As mentioned above, githubPullRequests.remotes is used to specify what remotes the extension should try to fetch pull requests from.
To customize the pull request tree, you can use the githubPullRequests.queries setting. This setting is a list of labels and search queries which populate the categories of the tree. By default, these queries are «Waiting For My Review», «Assigned To Me», and «Created By Me». An example of adding a «Mentioned Me» category is to change the setting to the following:
To view additional settings for the extension, you can open VS Code settings and search for «github pull requests».
Issues
This extension is still in development, so please refer to our issue tracker for known issues, and please contribute with additional information if you encounter an issue yourself.
Questions? Authentication? GitHub Enterprise?
See our wiki for our FAQ.
Contributing
If you’re interested in contributing, or want to explore the source code of this extension yourself, see our contributing guide, which includes:
Using Version Control in VS Code
Visual Studio Code has integrated source control management (SCM) and includes Git support out-of-the-box. Many other source control providers are available through extensions on the VS Code Marketplace.
Tip: Click on an extension tile to read the description and reviews in the Marketplace.
SCM Providers
VS Code has support for handling multiple Source Control providers simultaneously. For example, you can open multiple Git repositories alongside your Azure DevOps Server local workspace and seamlessly work across your projects. To turn on the Source Control Providers view, select the overflow menu in the Source Control view ( ⌃⇧G (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+G ) ), hover over Views, and make sure that Source Control Repositories is marked with a check. The Source Control Providers view shows the detected providers and repositories, and you can scope the display of your changes by selecting a specific provider.
SCM Provider extensions
If you would like to install another SCM provider, you can search on the scm providers extension category in the Extensions view ( ⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X ) ). Start typing ‘@ca’ and you will see suggestions for extension categories like debuggers and linters. Select @category:»scm providers» to see available SCM providers.
Git support
VS Code ships with a Git source control manager (SCM) extension. Most of the source control UI and work flows are common across other SCM extensions, so reading about the general Git support in VS Code will help you understand how to use another provider.
Note: If you are new to Git, the git-scm website is a good place to start, with a popular online book, Getting Started videos and cheat sheets. The VS Code documentation assumes you are already familiar with Git.
👉 When you commit, be aware that if your username and/or email is not set in your Git configuration, Git will fall back to using information from your local machine. You can find the details in Git commit information.
The Source Control icon in the Activity Bar on the left will always indicate an overview of how many changes you currently have in your repository. Selecting the icon will show you the details of your current repository changes: CHANGES, STAGED CHANGES and MERGE CHANGES.
Clicking each item will show you in detail the textual changes within each file. Note that for unstaged changes, the editor on the right still lets you edit the file: feel free to use it!
You can also find indicators of the status of your repository in the bottom-left corner of VS Code: the current branch, dirty indicators, and the number of incoming and outgoing commits of the current branch. You can checkout any branch in your repository by clicking that status indicator and selecting the Git reference from the list.
Tip: You can open VS Code in a sub-directory of a Git repository. VS Code’s Git services will still work as usual, showing all changes within the repository, but file changes outside of the scoped directory are shaded with a tool tip indicating they are located outside the current workspace.
Commit
Staging (git add) and unstaging (git reset) can be done via contextual actions in the files or by drag-and-drop.
You can type a commit message above the changes and press Ctrl+Enter (macOS: ⌘+Enter ) to commit them. If there are any staged changes, only those changes will be committed. Otherwise, you’ll get a prompt asking you to select what changes you’d like to commit and get the option to change your commit settings.
Tip: If you commit your change to the wrong branch, undo your commit using the Git: Undo Last Commit command in the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ).
Cloning a repository
If you haven’t opened a folder yet, the Source Control view will give you the options to Open Folder from your local machine or Clone Repository.
If you select Clone Repository, you will be asked for the URL of the remote repository (for example on GitHub) and the parent directory under which to put the local repository.
For a GitHub repository, you would find the URL from the GitHub Code dialog.
You would then paste that URL into the Git: Clone prompt.
You’ll also see the option to Clone from GitHub. Once you authenticate with your GitHub account in VS Code, you’ll be able to search through repositories by name, and select any repo to clone it. You can also start the flow to clone a Git repository with the Git: Clone command in the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ). To see a step-by-step walkthrough, check out our Clone repos from VS Code video.
Note: If you’d like to work on a repository without cloning the contents to your local machine, you can install the GitHub Repositories extension to browse and edit directly on GitHub. You can learn more in the GitHub Repositories extension section.
Branches and Tags
You can create and checkout branches directly within VS code through the Git: Create Branch and Git: Checkout to commands in the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ).
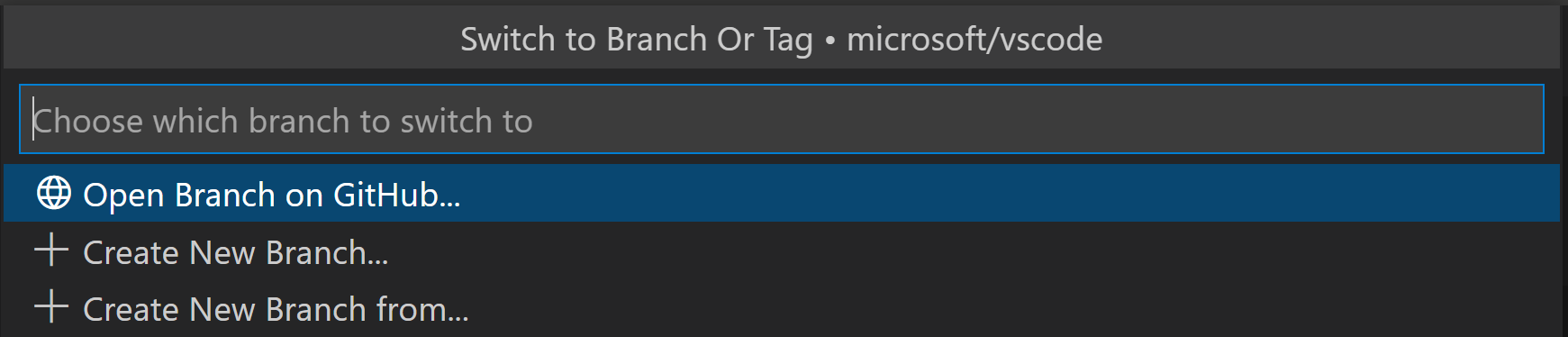
If you run Git: Checkout to, you will see a dropdown list containing all of the branches or tags in the current repository. It will also give you the option to create a new branch if you decide that’s a better option, or checkout a branch in detached mode.
Remotes
VS Code is able to periodically fetch changes from your remotes. This enables VS Code to show how many changes your local repository is ahead or behind the remote. Starting with VS Code 1.19, this feature is disabled by default and you can use the git.autofetch setting to enable it.
Tip: You should set up a credential helper to avoid getting asked for credentials every time VS Code talks to your Git remotes. If you don’t do this, you may want to consider disabling automatic fetching via the git.autofetch setting to reduce the number of prompts you get.
Git Status Bar actions
There is a Synchronize Changes action in the Status Bar, next to the branch indicator, when the current checked out branch has an upstream branch configured. Synchronize Changes will pull remote changes down to your local repository and then push local commits to the upstream branch.
If there is no upstream branch configured and the Git repository has remotes set up, the Publish action is enabled. This will let you publish the current branch to a remote.
Gutter indicators
If you open a folder that is a Git repository and begin making changes, VS Code will add useful annotations to the gutter and to the overview ruler.
Merge conflicts
Merge conflicts are recognized by VS Code. Differences are highlighted and there are inline actions to accept either one or both changes. Once the conflicts are resolved, stage the conflicting file so you can commit those changes.
Viewing diffs
Our Git tooling supports viewing of diffs within VS Code.
Tip: You can diff any two files by first right clicking on a file in the Explorer or OPEN EDITORS list and selecting Select for Compare and then right-click on the second file to compare with and select Compare with ‘file_name_you_chose’. Alternatively from the keyboard hit ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) and select File: Compare Active File With and you will be presented with a list of recent files.
Diff editor review pane
There is a review pane in the Diff editor that presents changes in a unified patch format. You can navigate between changes with Go to Next Difference ( F7 ) and Go to Previous Difference ( ⇧F7 (Windows, Linux Shift+F7 ) ). Lines can be navigated with arrow keys and pressing Enter will jump back in the Diff editor and the selected line.
Note: This experience is especially helpful for screen reader users.
Timeline view
The Timeline view, accessible at the bottom of the File Explorer by default, is a unified view for visualizing time-series events (for example, Git commits) for a file.
VS Code’s built-in Git support provides the Git commit history of the specified file. Selecting a commit will open a diff view of the changes introduced by that commit. When you right-click on a commit, you’ll get options to Copy Commit ID and Copy Commit Message.
Visual Studio Code supports more Git history workflows through extensions available on the VS Code Marketplace.
Tip: Click on an extension tile to read the description and reviews in the Marketplace.
Git output window
You can always peek under the hood to see the Git commands we are using. This is helpful if something strange is happening or if you are just curious. 🙂
To open the Git output window, run View > Output and select Git from the dropdown list.
Initialize a repository
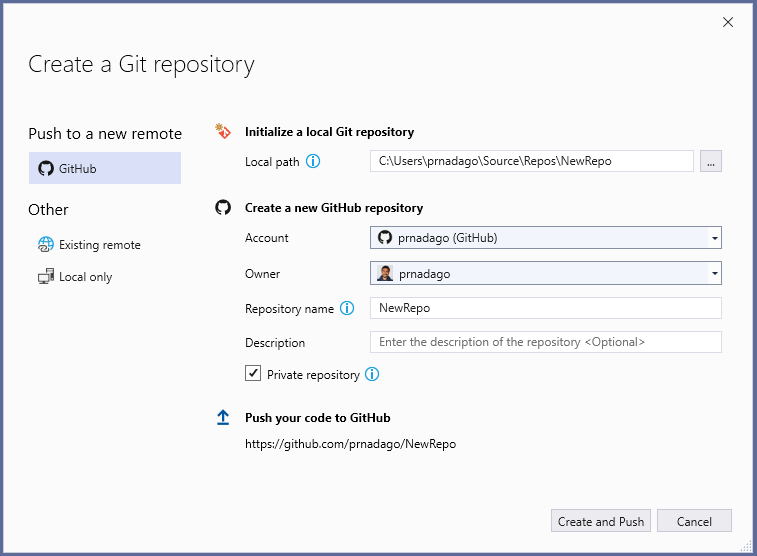
If your workspace is on your local machine, you can enable Git source control by creating a Git repository with the Initialize Repository command. When VS Code doesn’t detect an existing Git repository, the Source Control view will give you the options to Initialize Repository or Publish to GitHub.
You can also run the Git: Initialize Repository and Publish to GitHub commands from the Command Palette ( ⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P ) ). Running Initialize Repository will create the necessary Git repository metadata files and show your workspace files as untracked changes ready to be staged. Publish to GitHub will directly publish your workspace folder to a GitHub repository, allowing you to choose between a private and public repositories. Check out our publishing repos video for more information about publishing to GitHub.
VS Code as Git editor
Here are the steps to do so:
VS Code as Git diff tool
Add the following to your Git configurations to use VS Code as the diff tool:
To summarize, here are some examples of where you can use VS Code as the editor:
Working with pull requests
Visual Studio Code also supports pull request workflows through the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension available on the VS Code Marketplace. Pull request extensions let you review, comment, and verify source code contributions directly within VS Code.
Next steps
Common questions
To push, pull, and sync you need to have a Git origin set up. You can get the required URL from the repository host. Once you have that URL, you need to add it to the Git settings by running a couple of command-line actions. For example:
My team is using Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) instead of Git. What should I do?
Use the Azure Repos extension and this will light up TFVC support.
Why do the Pull, Push and Sync actions never finish?
This usually means there is no credential management configured in Git and you’re not getting credential prompts for some reason.
You can always set up a credential helper in order to pull and push from a remote server without having VS Code prompt for your credentials each time.
How can I sign in to Git with my Azure DevOps organization that requires multi-factor authentication?
Git Credential Manager (GCM) is the recommended Git credential helper for Windows, macOS, and Linux. If you’re running Git for Windows, GCM has already been installed and configured for you. If you’re running on macOS or Linux, the GCM README has setup instructions.
I have GitHub Desktop installed on my computer but VS Code ignores it
VS Code only supports the official Git distribution for its Git integration.
I keep getting Git authentication dialogs whenever VS Code is running
VS Code automatically fetches changes from the server in order to present you with a summary of incoming changes. The Git authentication dialog is independent from VS Code itself and is a part of your current Git credential helper.
One way to avoid these prompts is to set up a credential helper that remembers your credentials.
Can I use SSH Git authentication with VS Code?
Yes, though VS Code works most easily with SSH keys without a passphrase. If you have an SSH key with a passphrase, you’ll need to launch VS Code from a Git Bash prompt to inherit its SSH environment.
GitHub Repositories
GitHub
This is the pre-release edition of GitHub Repositories for early feedback and testing. It works best with VS Code Insiders.
GitHub Repositories
The GitHub Repositories extension lets you quickly browse, search, edit, and commit to any remote GitHub repository directly from within Visual Studio Code.
Why do you need GitHub Repositories?
As developers, we often clone Git repos locally just to browse them or make small edits. We may want to look at the source code of a library we use, experiment with new tools, or just feel the desire to learn something new.
However, cloning repos takes time and maintenance, as your local copy can quickly become out of date if you don’t pull changes regularly. Plus, if you don’t know the codebase you’re cloning, there may be security risks involved too!
The GitHub Repositories extension in VS Code gives you a fast, convenient, and safe way to open, browse, and edit repos quickly.
Here are some great situations in which you may choose to use GitHub Repositories to work on a codebase:
While GitHub Repositories is a great solution for many scenarios today, it does have certain limitations as you’ll see below, so it’s not (yet?) a cure-all. As such, there are still many situations where you may still want to clone a repository and get the full power of VS Code and all its extensions.
Getting started
You can quickly and easily open a GitHub repository either by searching for Remote Repositories: Open Remote Repository. from the Command Palette (press F1 ), or by choosing Open Remote Repository. from the remote indicator (the green button in the lower left corner of the status bar).
If you haven’t logged into GitHub from VS Code before, you’ll be prompted to authenticate with your GitHub account.
You can then search for a repo or pull request. In the gif below, we search for and select the VS Code repo on GitHub, VS Code reloads, and the repo’s contents loads similarly as if we cloned it locally:
Features
This extension provides the following support for GitHub repositories:
Continue Working On.
When working with GitHub repositories, you have several options to continue working in a more powerful environment.
Limitations
When you work in a traditional git workflow (i.e. git clone ), files are saved to your computer’s local file system. But when working with GitHub Repositories, the code doesn’t live on your local computer: it’s still just on GitHub. You work with the code through a virtual file system, which is an abstraction that simulates having local files while getting the content from somewhere else; GitHub in this case. When you open a workspace on a virtual file system, it’s known as a virtual workspace.
There are certain limitations while working with virtual workspaces:
You can learn more about virtual file systems, workspaces, and how to implement them for extensions in the virtual workspaces guide.
As we continue development of GitHub Repositories, expect the feature set to grow and the limitations to shrink!
Updates and release notes
While an optional install, this extension releases along with VS Code. The VS Code release notes will include a summary of changes.
You can also install the pre-release version of this extension for early feedback and testing. The pre-release version of this extension works best in VS Code Insiders.
Questions, feedback, contributing
Have a question or feedback?
Or connect with the community.
Telemetry
The GitHub Repositories extension collects telemetry data to help us build a better experience working remotely from VS Code. The extension respects the telemetry.enableTelemetry setting which you can learn more about in the Visual Studio Code FAQ.
License
By downloading and using the GitHub Repositories extension and its related components, you agree to the product license terms and privacy statement.
Visual studio code github
Using Version Control in VS Code
Visual Studio Code has integrated source control management (SCM) and includes Git support out-of-the-box. Many other source control providers are available through extensions on the VS Code Marketplace.
Tip: Click on an extension tile to read the description and reviews in the Marketplace.
VS Code has support for handling multiple Source Control providers simultaneously. For example, you can open multiple Git repositories alongside your Azure DevOps Server local workspace and seamlessly work across your projects. To turn on the Source Control Providers view, select the overflow menu in the Source Control view ( kb(workbench.view.scm) ), hover over Views, and make sure that Source Control Repositories is marked with a check. The Source Control Providers view shows the detected providers and repositories, and you can scope the display of your changes by selecting a specific provider.
SCM Provider extensions
If you would like to install another SCM provider, you can search on the scm providers extension category in the Extensions view ( kb(workbench.view.extensions) ). Start typing ‘@ca’ and you will see suggestions for extension categories like debuggers and linters. Select @category:»scm providers» to see available SCM providers.
VS Code ships with a Git source control manager (SCM) extension. Most of the source control UI and work flows are common across other SCM extensions, so reading about the general Git support in VS Code will help you understand how to use another provider.
Note: If you are new to Git, the git-scm website is a good place to start, with a popular online book, Getting Started videos and cheat sheets. The VS Code documentation assumes you are already familiar with Git.
👉 When you commit, be aware that if your username and/or email is not set in your Git configuration, Git will fall back to using information from your local machine. You can find the details in Git commit information.
The Source Control icon in the Activity Bar on the left will always indicate an overview of how many changes you currently have in your repository. Selecting the icon will show you the details of your current repository changes: CHANGES, STAGED CHANGES and MERGE CHANGES.
Clicking each item will show you in detail the textual changes within each file. Note that for unstaged changes, the editor on the right still lets you edit the file: feel free to use it!
You can also find indicators of the status of your repository in the bottom-left corner of VS Code: the current branch, dirty indicators, and the number of incoming and outgoing commits of the current branch. You can checkout any branch in your repository by clicking that status indicator and selecting the Git reference from the list.
Tip: You can open VS Code in a sub-directory of a Git repository. VS Code’s Git services will still work as usual, showing all changes within the repository, but file changes outside of the scoped directory are shaded with a tool tip indicating they are located outside the current workspace.
Staging (git add) and unstaging (git reset) can be done via contextual actions in the files or by drag-and-drop.
You can type a commit message above the changes and press kbstyle(Ctrl+Enter) (macOS: kbstyle(⌘+Enter) ) to commit them. If there are any staged changes, only those changes will be committed. Otherwise, you’ll get a prompt asking you to select what changes you’d like to commit and get the option to change your commit settings.
Tip: If you commit your change to the wrong branch, undo your commit using the Git: Undo Last Commit command in the Command Palette ( kb(workbench.action.showCommands) ).
Cloning a repository
If you haven’t opened a folder yet, the Source Control view will give you the options to Open Folder from your local machine or Clone Repository.
If you select Clone Repository, you will be asked for the URL of the remote repository (for example on GitHub) and the parent directory under which to put the local repository.
For a GitHub repository, you would find the URL from the GitHub Code dialog.
You would then paste that URL into the Git: Clone prompt.
You’ll also see the option to Clone from GitHub. Once you authenticate with your GitHub account in VS Code, you’ll be able to search through repositories by name, and select any repo to clone it. You can also start the flow to clone a Git repository with the Git: Clone command in the Command Palette ( kb(workbench.action.showCommands) ). To see a step-by-step walkthrough, check out our Clone repos from VS Code video.
Note : If you’d like to work on a repository without cloning the contents to your local machine, you can install the GitHub Repositories extension to browse and edit directly on GitHub. You can learn more in the GitHub Repositories extension section.
Branches and Tags
You can create and checkout branches directly within VS code through the Git: Create Branch and Git: Checkout to commands in the Command Palette ( kb(workbench.action.showCommands) ).
If you run Git: Checkout to, you will see a dropdown list containing all of the branches or tags in the current repository. It will also give you the option to create a new branch if you decide that’s a better option, or checkout a branch in detached mode.
VS Code is able to periodically fetch changes from your remotes. This enables VS Code to show how many changes your local repository is ahead or behind the remote. Starting with VS Code 1.19, this feature is disabled by default and you can use the git.autofetch setting to enable it.
Tip: You should set up a credential helper to avoid getting asked for credentials every time VS Code talks to your Git remotes. If you don’t do this, you may want to consider disabling automatic fetching via the git.autofetch setting to reduce the number of prompts you get.
Git Status Bar actions
There is a Synchronize Changes action in the Status Bar, next to the branch indicator, when the current checked out branch has an upstream branch configured. Synchronize Changes will pull remote changes down to your local repository and then push local commits to the upstream branch.
If there is no upstream branch configured and the Git repository has remotes set up, the Publish action is enabled. This will let you publish the current branch to a remote.
If you open a folder that is a Git repository and begin making changes, VS Code will add useful annotations to the gutter and to the overview ruler.
Merge conflicts are recognized by VS Code. Differences are highlighted and there are inline actions to accept either one or both changes. Once the conflicts are resolved, stage the conflicting file so you can commit those changes.
Our Git tooling supports viewing of diffs within VS Code.
Tip: You can diff any two files by first right clicking on a file in the Explorer or OPEN EDITORS list and selecting Select for Compare and then right-click on the second file to compare with and select Compare with ‘file_name_you_chose’. Alternatively from the keyboard hit kb(workbench.action.showCommands) and select File: Compare Active File With and you will be presented with a list of recent files.
Diff editor review pane
There is a review pane in the Diff editor that presents changes in a unified patch format. You can navigate between changes with Go to Next Difference ( kb(editor.action.diffReview.next) ) and Go to Previous Difference ( kb(editor.action.diffReview.prev) ). Lines can be navigated with arrow keys and pressing kbstyle(Enter) will jump back in the Diff editor and the selected line.
Note: This experience is especially helpful for screen reader users.
The Timeline view, accessible at the bottom of the File Explorer by default, is a unified view for visualizing time-series events (for example, Git commits) for a file.
VS Code’s built-in Git support provides the Git commit history of the specified file. Selecting a commit will open a diff view of the changes introduced by that commit. When you right-click on a commit, you’ll get options to Copy Commit ID and Copy Commit Message.
Visual Studio Code supports more Git history workflows through extensions available on the VS Code Marketplace.
Tip: Click on an extension tile to read the description and reviews in the Marketplace.
Git output window
You can always peek under the hood to see the Git commands we are using. This is helpful if something strange is happening or if you are just curious. 🙂
To open the Git output window, run View > Output and select Git from the dropdown list.
Initialize a repository
If your workspace is on your local machine, you can enable Git source control by creating a Git repository with the Initialize Repository command. When VS Code doesn’t detect an existing Git repository, the Source Control view will give you the options to Initialize Repository or Publish to GitHub.
You can also run the Git: Initialize Repository and Publish to GitHub commands from the Command Palette ( kb(workbench.action.showCommands) ). Running Initialize Repository will create the necessary Git repository metadata files and show your workspace files as untracked changes ready to be staged. Publish to GitHub will directly publish your workspace folder to a GitHub repository, allowing you to choose between a private and public repositories. Check out our publishing repos video for more information about publishing to GitHub.
VS Code as Git editor
Here are the steps to do so:
VS Code as Git diff tool
Add the following to your Git configurations to use VS Code as the diff tool:
To summarize, here are some examples of where you can use VS Code as the editor:
Working with pull requests
Visual Studio Code also supports pull request workflows through the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension available on the VS Code Marketplace. Pull request extensions let you review, comment, and verify source code contributions directly within VS Code.
To push, pull, and sync you need to have a Git origin set up. You can get the required URL from the repository host. Once you have that URL, you need to add it to the Git settings by running a couple of command-line actions. For example:
My team is using Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) instead of Git. What should I do?
Use the Azure Repos extension and this will light up TFVC support.
Why do the Pull, Push and Sync actions never finish?
This usually means there is no credential management configured in Git and you’re not getting credential prompts for some reason.
You can always set up a credential helper in order to pull and push from a remote server without having VS Code prompt for your credentials each time.
How can I sign in to Git with my Azure DevOps organization that requires multi-factor authentication?
Git Credential Manager (GCM) is the recommended Git credential helper for Windows, macOS, and Linux. If you’re running Git for Windows, GCM has already been installed and configured for you. If you’re running on macOS or Linux, the GCM README has setup instructions.
I have GitHub Desktop installed on my computer but VS Code ignores it
VS Code only supports the official Git distribution for its Git integration.
I keep getting Git authentication dialogs whenever VS Code is running
VS Code automatically fetches changes from the server in order to present you with a summary of incoming changes. The Git authentication dialog is independent from VS Code itself and is a part of your current Git credential helper.
One way to avoid these prompts is to set up a credential helper that remembers your credentials.
Can I use SSH Git authentication with VS Code?
Yes, though VS Code works most easily with SSH keys without a passphrase. If you have an SSH key with a passphrase, you’ll need to launch VS Code from a Git Bash prompt to inherit its SSH environment.
Visual studio code github
Start Visual Studio Code.
Select File > Open Folder (File > Open. on macOS) from the main menu.
In the Open Folder dialog, create a HelloWorld folder and select it. Then click Select Folder (Open on macOS).
In the Do you trust the authors of the files in this folder? dialog, select Yes, I trust the authors.
Open the Terminal in Visual Studio Code by selecting View > Terminal from the main menu.
The Terminal opens with the command prompt in the HelloWorld folder.
In the Terminal, enter the following command:
The project template creates a simple application that displays «Hello World» in the console window by calling the xref:System.Console.WriteLine(System.String)?displayProperty=nameWithType method in Program.cs.
Replace the contents of Program.cs with the following code:
The first time you edit a .cs file, Visual Studio Code prompts you to add the missing assets to build and debug your app. Select Yes, and Visual Studio Code creates a .vscode folder with launch.json and tasks.json files.
[!NOTE] If you don’t get the prompt, or if you accidentally dismiss it without selecting Yes, do the following steps to create launch.json and tasks.json:
In the latest version of C#, a new feature named top-level statements lets you omit the Program class and the Main method. Most existing C# programs don’t use top-level statements, so this tutorial doesn’t use this new feature. But it’s available in C# 10, and whether you use it in your programs is a matter of style preference.
Run the following command in the Terminal:
The program displays «Hello World!» and ends.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
xref:System.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are \n in C# and vbCrLf in Visual Basic.
Save your changes.
[!IMPORTANT] In Visual Studio Code, you have to explicitly save changes. Unlike Visual Studio, file changes are not automatically saved when you build and run an app.
Run the program again:
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
. image type=»content» source=»media/debugging-with-visual-studio-code/run-modified-program.png» alt-text=»Terminal window with modified program output».
Press any key to exit the program.
Start Visual Studio Code.
Select File > Open Folder (File > Open. on macOS) from the main menu.
In the Open Folder dialog, create a HelloWorld folder and click Select Folder (Open on macOS).
Open the Terminal in Visual Studio Code by selecting View > Terminal from the main menu.
The Terminal opens with the command prompt in the HelloWorld folder.
In the Terminal, enter the following command:
The template creates a simple «Hello World» application. It calls the xref:System.Console.WriteLine(System.String)?displayProperty=nameWithType method to display «. no-loc text=»Hello World!». » in the console window.
Main is the application entry point, the method that’s called automatically by the runtime when it launches the application. Any command-line arguments supplied when the application is launched are available in the args array.
Run the following command in the Terminal:
The program displays «Hello World!» and ends.
Enhance the app
Enhance the application to prompt the user for their name and display it along with the date and time.
Open Program.cs by clicking on it.
The first time you open a C# file in Visual Studio Code, OmniSharp loads in the editor.
Select Yes when Visual Studio Code prompts you to add the missing assets to build and debug your app.
xref:System.Environment.NewLine is a platform-independent and language-independent way to represent a line break. Alternatives are \n in C# and vbCrLf in Visual Basic.
Save your changes.
[!IMPORTANT] In Visual Studio Code, you have to explicitly save changes. Unlike Visual Studio, file changes are not automatically saved when you build and run an app.
Run the program again:
Respond to the prompt by entering a name and pressing the Enter key.
. image type=»content» source=»media/debugging-with-visual-studio-code/run-modified-program.png» alt-text=»Terminal window with modified program output».
Press any key to exit the program.
github/VisualStudio
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
GitHub Extension for Visual Studio
The GitHub Extension for Visual Studio provides GitHub integration in Visual Studio 2015 and newer. Most of the extension UI lives in the Team Explorer pane, which is available from the View menu.
Official builds of this extension are available at the Visual Studio Marketplace.

Visit the documentation for details on how to use the features in the GitHub Extension for Visual Studio.
The built VSIX will work with Visual Studio 2015 or newer
Clone the repository and its submodules.
To be able to use the GitHub API, you’ll need to:
Visual Studio Build
Build GitHubVS.sln using Visual Studio 2019.
Logs can be viewed at the following location:
If you have issues building with failures similar to:
«The type or namespace name does not exist. «
«Unable to find project. Check that the project reference is valid and that the project file exists.»*
Close Visual Studio and run the following command to update submodules and clean your environment.
Visit the Contributor Guidelines for details on how to contribute as well as the Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct for details on how to participate.
microsoft/vscode-pull-request-github
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Review and manage your GitHub pull requests and issues directly in VS Code
This extension allows you to review and manage GitHub pull requests and issues in Visual Studio Code. The support includes:
It’s easy to get started with GitHub Pull Requests for Visual Studio Code. Simply follow these steps to get started.
Configuring the extension
There are several settings that can be used to configure the extension.
As mentioned above, githubPullRequests.remotes is used to specify what remotes the extension should try to fetch pull requests from.
To customize the pull request tree, you can use the githubPullRequests.queries setting. This setting is a list of labels and search queries which populate the categories of the tree. By default, these queries are «Waiting For My Review», «Assigned To Me», and «Created By Me». An example of adding a «Mentioned Me» category is to change the setting to the following:
To view additional settings for the extension, you can open VS Code settings and search for «github pull requests».
This extension is still in development, so please refer to our issue tracker for known issues, and please contribute with additional information if you encounter an issue yourself.
Questions? Authentication? GitHub Enterprise?
See our wiki for our FAQ.
If you’re interested in contributing, or want to explore the source code of this extension yourself, see our contributing guide, which includes:
About
GitHub Pull Requests for Visual Studio Code
microsoft/vscode-docs
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Visual Studio Code Documentation
You’ve found the Visual Studio Code documentation GitHub repository, which contains the content for the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Topics submitted here will be published to the Visual Studio Code portal.
If you are looking for the VS Code product GitHub repository, you can find it here.
Visual Studio Code
If you landed here looking for other information about VS Code, head over to our website for additional information.
If you want to give documentation feedback, please use the feedback control located at the bottom of each documentation page.
To enter documentation bugs, please create a new GitHub issue. Please check if there is an existing issue first.
If you think the issue is with the VS Code product itself, please enter issues in the VS Code product repo here.
To contribute new topics/information or make changes to existing documentation, please read the Contributing Guideline.
The two suggested workflows are:
Cloning without binary files
You might want to clone the repo without the 1.6GB images. Here are the steps:
The history of this repo before we adopted LFS can be found at microsoft/vscode-docs-archive.
Steps for how to publish documentation changes can be found here in the (private) repository of the VS Code website.
Visual studio code github
Authenticate your GitHub.com or GitHub enterprise account to create a repository, and push your first commits to GitHub, all through Visual Studio.
Clone and code from within the IDE
Browse your GitHub repositories, and clone your repo down to your local machine to start committing and pushing.
Create and push new repos
Take local code and push it to a new repository on GitHub in one step. Visual Studio handles the local and remote repository creation. You can even choose to make the repo completely private.
Branching, staging, and committing
Create and switch between branches from the status bar. View your changes, stage the files you want to commit, and make commits with the Git Changes tool window.
Merge and Rebase
Merge or rebase branches after completing features directly from within Visual Studio. You can also choose to merge or rebase when pulling, or prune branches when fetching.
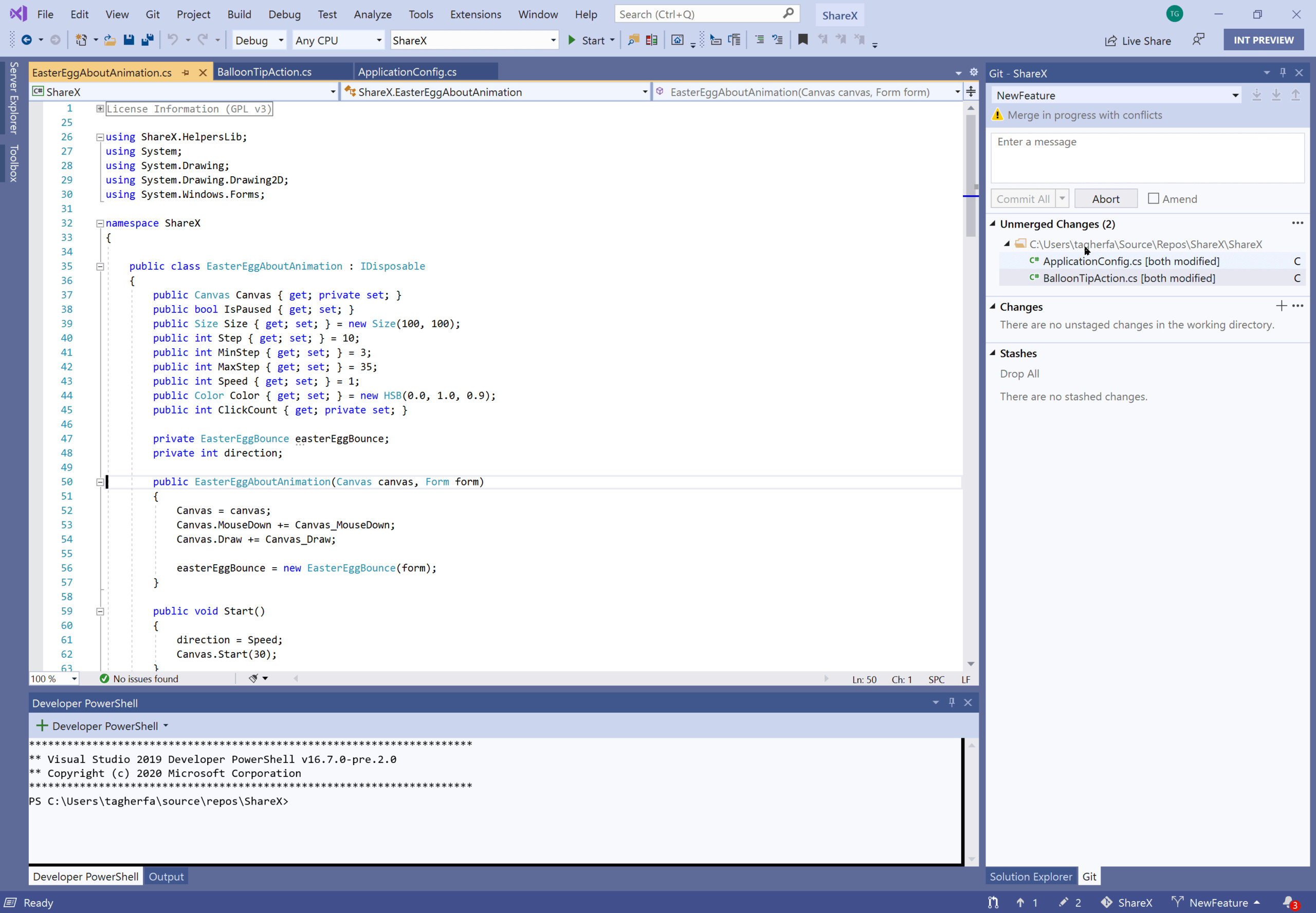
Resolve merge conflicts
Visual Studio will recognize merge conflicts right when they occur, and show you the unmerged changes in the Git Changes window. The built-in merge editor takes you through each conflicting change, allowing you to take either the incoming or current side, and shows the result when you accept the merge.
Browse your repository history
Use the Git Repository window to get a full picture of your branches and their history. Select individual commits to see details and file diffs. Some people prefer a to see their diff’s side-by-side and some prefer an inline view. Get both in Visual Studio. This setting persists when it’s changed so you can set it and forget it.
How Visual Studio makes version control easy with Git
Have you ever wished you could go back to a previously working version of your code? Do you find yourself manually storing copies of your code in different locations as a backup? Well, version control is the answer.
Git is the most widely used modern version control system. With Git, you can track the code changes you make over time and you can revert to specific versions. So whether you’re a professional developer or if you’re learning how to code, Visual Studio’s Git experience can be very useful to you.
To learn about using Git and GitHub in Visual Studio, sign up for the Git learning series.
Start with Git & GitHub in Visual Studio
Version control with Visual Studio is easy with Git. We meet you where you are. You can work remotely with the Git provider of your choice, such as GitHub or Azure DevOps. Or, you can work locally with no provider at all.
To get started using Git with Visual Studio:
If you have a Git repo hosted on a Git provider like GitHub, clone the repository to your local machine.
Otherwise, easily create a new Git repository and add your code. If you don’t have a Git provider yet, we recommend you start with GitHub since the Git experience in Visual Studio is optimized for this provider. GitHub offers free and secured cloud code storage where you can store your code and access it from any device, anywhere.
Not only can you add both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise accounts to your keychain, but you can also leverage them just as you do with Microsoft accounts. If you don’t have a GitHub account, follow these steps to create a GitHub account to use with Visual Studio now.
If you’re new to Git, the https://git-scm.com/ website is a good place to start.
View files in Solution Explorer
Intuitive inner-loop workflow
For your day-to-day Git workflow, Visual Studio provides a seamless way to interact with Git while coding without having you switch away from your code.
You are empowered to multi-task and experiment with your code through branches. If you or your team works on multiple features at the same time, or if you’d like to explore ideas without affecting your working code, branching is very helpful. The recommended Git workflow uses a new branch for every feature or fix that you work on. Learn how to create a branch from Visual Studio.
Once you create a new branch and switch to it, you can start working by changing existing files or by adding new ones and then committing your work to the repository. To learn more about making a commit in Visual Studio and to better understand file states in Git, refer to the Make a commit page.
Git is a distributed version control system, meaning that all the changes made so far are local only changes. To contribute these changes to a remote repository, you must push those local commit(s) to a remote.
If you are working in a team or if you are using different machines, you will also need to continually fetch and pull new changes on the remote repository. To learn more about managing Git network operations in Visual Studio, refer to the Fetch, pull, push, and sync page.
Repository management & collaboration
However, there are times when it makes more sense to focus on your Git repository. For example, you might need to get a good picture of what your team has been working on, or copy a commit from a different branch, or just clean-up your outgoing commits. Visual Studio includes powerful repository browsing and collaboration features that eliminate the need to use other tools.
To help you focus on your Git repository, Visual Studio has a Git Repository window, which is a consolidated view of all the details in your repository, including local and remote branches and commit history. You can access this window directly from either Git or View on the menu bar or from the status bar.
Browse and manage Git repositories
To learn more about how you can use the Git Repository window in Visual Studio to browse and manage your Git repository, refer to the following pages:
Handle merge conflicts
Conflicts can occur during a merge if two developers modify the same lines in a file and Git doesn’t automatically know which one is correct. Git halts the merge and informs you that you are in a conflicted state. Learn more in the Resolve merge conflicts page.
Personalize your Git settings
To personalize your Git settings at a repository level as well as at a global level:
Enhanced experience & feedback
We continue to add new features to enhance the Git experience. For more info about recent features and a feedback survey, see the Multi-repo support in Visual Studio blog post. If you have a suggestion, let us know! We appreciate the opportunity to engage with you in the Developer Community.
To try more recent/preview updates to the Git experience available, download and install from the Visual Studio 2022 Preview page. Read our Visual Studio 2022 release notes for details on each release.
Git is now the default version control experience in Visual Studio 2019. Since version 16.6, we’ve worked on building out the feature set and iterating on it based on your feedback. In version 16.8, it became the default version control experience for everyone.
We continue to build out and iterate on the Git feature set in Visual Studio 2022, too. To learn more about a recent feature update, see the Multi-repo support in Visual Studio blog post.
Learn more about Git
Git is the most widely used modern version control system, so whether you’re a professional developer or if you’re learning how to code, Git can be very useful to you. If you’re new to Git, the https://git-scm.com/ website is a good place to start. There, you’ll find cheat sheets, a popular online book, and Git Basics videos.
Start with Git in Visual Studio 2019
We’ll walk you through how to use the new Git experience in Visual Studio, but if you’d like to take a quick tour first, check out the following video:
Video length: 5.27 minutes
There are three ways to start using Git with Visual Studio to be more productive:
Starting with Visual Studio 2019 version 16.8, we include a fully integrated GitHub account experience. You can now add both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise accounts to your keychain. You can add and leverage them just as you do with Microsoft accounts, which means that you’ll have an easier time accessing your GitHub resources across Visual Studio. For more information, see the Work with GitHub accounts in Visual Studio page.
If you don’t have a GitHub account, you can start by following the steps outlined in the Create a GitHub account to use with Visual Studio page.
Create a new Git repository in Visual Studio 2019
If your code is not associated with Git, you can start by creating a new Git repository. To do so, select Git > Create Git Repository from the menu bar. Then, in the Create a Git repository dialog box, enter your information.
The Create a Git repository dialog box makes it easy to push your new repository to GitHub. By default, your new repository is private, which means that you are the only one who can access it. If you uncheck the box, your repository will be public, which means that anyone on GitHub can view it.
Whether your repository is public or private, it’s best to have a remote backup of your code stored securely on GitHub even if you are not working with a team. This also makes your code available to you no matter what computer you’re using.
You can choose to create a local-only Git repository by using the Local only option. Or, you can link your local project with an existing empty remote repository on Azure DevOps or any other Git provider by using the Existing Remote option.
Clone an existing Git repository in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio includes a straightforward clone experience. If you know the URL of the repository that you would like to clone, you can paste the URL in the Repository location section and then choose the disk location you would like Visual Studio to clone to.
If you don’t know the repository URL, Visual Studio makes it easy to browse to and then clone your existing GitHub or Azure DevOps repository.
Open an existing local repository in Visual Studio 2019
After you’ve cloned a repository or created one, Visual Studio detects the Git repository and adds it to your list of Local Repositories in the Git menu.
From here, you can quickly access and switch between your Git repositories.
View files in Solution Explorer in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio adjusts its View based on which file you load in Solution Explorer:
You can toggle between the currently open View and the list of Views by using the Switch Views button in the Solution Explorer toolbar.
For more information, see the View files in Solution Explorer section of the Open a project from a repo tutorial.
Git Changes window in Visual Studio 2019
Git tracks file changes in your repo as you work, and separates the files in your repo into three categories. These changes are equivalent to what you would see when you enter the git status command in the command line:
As you do your work, Visual Studio keeps track of the file changes to your project in the Changes section of the Git Changes window.
When you are ready to stage changes, click the + (plus) button on each file you want to stage, or right-click a file and then select Stage. You can also stage all your modified files with one click by using the stage all + (plus) button at the top of the Changes section.
Visual Studio also makes it easy to commit and sync with one click by using the Commit All and Push and Commit All and Sync shortcuts. When you double-click any file in the Changes and the Staged changes sections, you can see a line-by-line comparison with the unmodified version of the file.
You can associate an Azure DevOps work item with a commit by using the «#» character if you are connected to the Azure DevOps repository. You can connect your Azure DevOps repository through Team Explorer > Manage Connections.
Select an existing branch in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio displays the current branch in the selector at the top of the Git Changes window.
The current branch is also available in the status bar on the bottom-right corner of the Visual Studio IDE.
From both locations, you can switch between existing branches.
Create a new branch in Visual Studio 2019
Creating a new branch is as simple as entering the branch name and basing it off an existing branch.
Git Repository window in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio has a new Git Repository window, which is a consolidated view of all the details in your repository, including all of the branches, remotes, and commit histories. You can access this window directly from either Git or View on the menu bar or from the status bar.
Manage branches in Visual Studio 2019
When you select Manage Branches from the Git menu, you’ll see the branches tree-view in the Git Repository window. From the left pane, you can use the right-click context menu to checkout branches, create new branches, merge, rebase, cherry-pick, and more. When you click the branch, you can see a preview of its commit history in the right pane.
Incoming and outgoing commits in Visual Studio 2019
When you fetch a branch, the Git Changes window has an indicator under the branch drop-down, which displays the number of unpulled commits from the remote branch. This indicator also shows you the number of unpushed local commits.
The indicator also functions as a link to take you to the commit history of that branch in the Git Repository window. The top of the history now displays the details of these incoming and outgoing commits. From here, you can also decide to Pull or Push the commits.
Commit Details in Visual Studio 2019
When you double-click a Commit, Visual Studio opens its details in a separate tool window. From here you can revert the commit, reset the commit, amend the commit message, or create a tag on the commit. When you click a changed file in the commit, Visual Studio opens the side-by-side Diff view of the commit and its parent.
Handle merge conflicts in Visual Studio 2019
Conflicts can occur during a merge if two developers modify the same lines in a file and Git doesn’t automatically know which is correct. Git halts the merge and informs you that you are in a conflicted state.
Visual Studio makes it easy to identify and resolve a merge conflict. First, the Git Repository window shows a gold info bar at the top of the window.
The Git Changes window also displays a вЂMerge is in progress with conflicts’ message, with the unmerged files in their separate section below it.
But if you have neither of these windows open, and instead you go to the file that has merge conflicts, you won’t have to search for the following text:
Instead, Visual Studio displays a gold info bar on the top of the page that indicates that the opened file has conflicts. Then, you can click the link to open the Merge Editor.
The Merge Editor in Visual Studio 2019
The Merge Editor in Visual Studio is a three-way merge tool that displays the incoming changes, your current changes, and the result of the merge. You can use the tool bar at the top level of the Merge Editor to navigate between conflicts and auto-merged differences in the file.
You can also use the toggles to show/hide differences, show/hide word differences, and customize the layout. There are checkboxes on the top of each side that you can use to take all the changes from one side or the other. But to take individual changes, you can click the checkboxes to the left of the conflicting lines on either side. Finally, when you finish resolving the conflicts, you can select the Accept Merge button in the Merge Editor. You then write a commit message and commit the changes to complete the resolution.
Personalize your Git settings in Visual Studio 2019
To personalize and customize your Git settings at a repository level as well as at a global level, go to either Git > Settings on the menu bar, or to Tools > Options > Source Control on the menu bar. Then, choose the options you want.
How to use the full Team Explorer experience in Visual Studio 2019
The new Git experience is the default version control system in Visual Studio 2019 from version 16.8 onwards. However, if you want to turn it off, you can. Go to Tools > Options > Environment > Preview Features and then toggle the New Git user experience checkbox, which will switch you back to Team Explorer for Git.
How Visual Studio makes version control easy with Git
Have you ever wished you could go back to a previously working version of your code? Do you find yourself manually storing copies of your code in different locations as a backup? Well, version control is the answer.
Git is the most widely used modern version control system. With Git, you can track the code changes you make over time and you can revert to specific versions. So whether you’re a professional developer or if you’re learning how to code, Visual Studio’s Git experience can be very useful to you.
To learn about using Git and GitHub in Visual Studio, sign up for the Git learning series.
Start with Git & GitHub in Visual Studio
Version control with Visual Studio is easy with Git. We meet you where you are. You can work remotely with the Git provider of your choice, such as GitHub or Azure DevOps. Or, you can work locally with no provider at all.
To get started using Git with Visual Studio:
If you have a Git repo hosted on a Git provider like GitHub, clone the repository to your local machine.
Otherwise, easily create a new Git repository and add your code. If you don’t have a Git provider yet, we recommend you start with GitHub since the Git experience in Visual Studio is optimized for this provider. GitHub offers free and secured cloud code storage where you can store your code and access it from any device, anywhere.
Not only can you add both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise accounts to your keychain, but you can also leverage them just as you do with Microsoft accounts. If you don’t have a GitHub account, follow these steps to create a GitHub account to use with Visual Studio now.
If you’re new to Git, the https://git-scm.com/ website is a good place to start.
View files in Solution Explorer
Intuitive inner-loop workflow
For your day-to-day Git workflow, Visual Studio provides a seamless way to interact with Git while coding without having you switch away from your code.
You are empowered to multi-task and experiment with your code through branches. If you or your team works on multiple features at the same time, or if you’d like to explore ideas without affecting your working code, branching is very helpful. The recommended Git workflow uses a new branch for every feature or fix that you work on. Learn how to create a branch from Visual Studio.
Once you create a new branch and switch to it, you can start working by changing existing files or by adding new ones and then committing your work to the repository. To learn more about making a commit in Visual Studio and to better understand file states in Git, refer to the Make a commit page.
Git is a distributed version control system, meaning that all the changes made so far are local only changes. To contribute these changes to a remote repository, you must push those local commit(s) to a remote.
If you are working in a team or if you are using different machines, you will also need to continually fetch and pull new changes on the remote repository. To learn more about managing Git network operations in Visual Studio, refer to the Fetch, pull, push, and sync page.
Repository management & collaboration
However, there are times when it makes more sense to focus on your Git repository. For example, you might need to get a good picture of what your team has been working on, or copy a commit from a different branch, or just clean-up your outgoing commits. Visual Studio includes powerful repository browsing and collaboration features that eliminate the need to use other tools.
To help you focus on your Git repository, Visual Studio has a Git Repository window, which is a consolidated view of all the details in your repository, including local and remote branches and commit history. You can access this window directly from either Git or View on the menu bar or from the status bar.
Browse and manage Git repositories
To learn more about how you can use the Git Repository window in Visual Studio to browse and manage your Git repository, refer to the following pages:
Handle merge conflicts
Conflicts can occur during a merge if two developers modify the same lines in a file and Git doesn’t automatically know which one is correct. Git halts the merge and informs you that you are in a conflicted state. Learn more in the Resolve merge conflicts page.
Personalize your Git settings
To personalize your Git settings at a repository level as well as at a global level:
Enhanced experience & feedback
We continue to add new features to enhance the Git experience. For more info about recent features and a feedback survey, see the Multi-repo support in Visual Studio blog post. If you have a suggestion, let us know! We appreciate the opportunity to engage with you in the Developer Community.
To try more recent/preview updates to the Git experience available, download and install from the Visual Studio 2022 Preview page. Read our Visual Studio 2022 release notes for details on each release.
Git is now the default version control experience in Visual Studio 2019. Since version 16.6, we’ve worked on building out the feature set and iterating on it based on your feedback. In version 16.8, it became the default version control experience for everyone.
We continue to build out and iterate on the Git feature set in Visual Studio 2022, too. To learn more about a recent feature update, see the Multi-repo support in Visual Studio blog post.
Learn more about Git
Git is the most widely used modern version control system, so whether you’re a professional developer or if you’re learning how to code, Git can be very useful to you. If you’re new to Git, the https://git-scm.com/ website is a good place to start. There, you’ll find cheat sheets, a popular online book, and Git Basics videos.
Start with Git in Visual Studio 2019
We’ll walk you through how to use the new Git experience in Visual Studio, but if you’d like to take a quick tour first, check out the following video:
Video length: 5.27 minutes
There are three ways to start using Git with Visual Studio to be more productive:
Starting with Visual Studio 2019 version 16.8, we include a fully integrated GitHub account experience. You can now add both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise accounts to your keychain. You can add and leverage them just as you do with Microsoft accounts, which means that you’ll have an easier time accessing your GitHub resources across Visual Studio. For more information, see the Work with GitHub accounts in Visual Studio page.
If you don’t have a GitHub account, you can start by following the steps outlined in the Create a GitHub account to use with Visual Studio page.
Create a new Git repository in Visual Studio 2019
If your code is not associated with Git, you can start by creating a new Git repository. To do so, select Git > Create Git Repository from the menu bar. Then, in the Create a Git repository dialog box, enter your information.
The Create a Git repository dialog box makes it easy to push your new repository to GitHub. By default, your new repository is private, which means that you are the only one who can access it. If you uncheck the box, your repository will be public, which means that anyone on GitHub can view it.
Whether your repository is public or private, it’s best to have a remote backup of your code stored securely on GitHub even if you are not working with a team. This also makes your code available to you no matter what computer you’re using.
You can choose to create a local-only Git repository by using the Local only option. Or, you can link your local project with an existing empty remote repository on Azure DevOps or any other Git provider by using the Existing Remote option.
Clone an existing Git repository in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio includes a straightforward clone experience. If you know the URL of the repository that you would like to clone, you can paste the URL in the Repository location section and then choose the disk location you would like Visual Studio to clone to.
If you don’t know the repository URL, Visual Studio makes it easy to browse to and then clone your existing GitHub or Azure DevOps repository.
Open an existing local repository in Visual Studio 2019
After you’ve cloned a repository or created one, Visual Studio detects the Git repository and adds it to your list of Local Repositories in the Git menu.
From here, you can quickly access and switch between your Git repositories.
View files in Solution Explorer in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio adjusts its View based on which file you load in Solution Explorer:
You can toggle between the currently open View and the list of Views by using the Switch Views button in the Solution Explorer toolbar.
For more information, see the View files in Solution Explorer section of the Open a project from a repo tutorial.
Git Changes window in Visual Studio 2019
Git tracks file changes in your repo as you work, and separates the files in your repo into three categories. These changes are equivalent to what you would see when you enter the git status command in the command line:
As you do your work, Visual Studio keeps track of the file changes to your project in the Changes section of the Git Changes window.
When you are ready to stage changes, click the + (plus) button on each file you want to stage, or right-click a file and then select Stage. You can also stage all your modified files with one click by using the stage all + (plus) button at the top of the Changes section.
Visual Studio also makes it easy to commit and sync with one click by using the Commit All and Push and Commit All and Sync shortcuts. When you double-click any file in the Changes and the Staged changes sections, you can see a line-by-line comparison with the unmodified version of the file.
You can associate an Azure DevOps work item with a commit by using the «#» character if you are connected to the Azure DevOps repository. You can connect your Azure DevOps repository through Team Explorer > Manage Connections.
Select an existing branch in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio displays the current branch in the selector at the top of the Git Changes window.
The current branch is also available in the status bar on the bottom-right corner of the Visual Studio IDE.
From both locations, you can switch between existing branches.
Create a new branch in Visual Studio 2019
Creating a new branch is as simple as entering the branch name and basing it off an existing branch.
Git Repository window in Visual Studio 2019
Visual Studio has a new Git Repository window, which is a consolidated view of all the details in your repository, including all of the branches, remotes, and commit histories. You can access this window directly from either Git or View on the menu bar or from the status bar.
Manage branches in Visual Studio 2019
When you select Manage Branches from the Git menu, you’ll see the branches tree-view in the Git Repository window. From the left pane, you can use the right-click context menu to checkout branches, create new branches, merge, rebase, cherry-pick, and more. When you click the branch, you can see a preview of its commit history in the right pane.
Incoming and outgoing commits in Visual Studio 2019
When you fetch a branch, the Git Changes window has an indicator under the branch drop-down, which displays the number of unpulled commits from the remote branch. This indicator also shows you the number of unpushed local commits.
The indicator also functions as a link to take you to the commit history of that branch in the Git Repository window. The top of the history now displays the details of these incoming and outgoing commits. From here, you can also decide to Pull or Push the commits.
Commit Details in Visual Studio 2019
When you double-click a Commit, Visual Studio opens its details in a separate tool window. From here you can revert the commit, reset the commit, amend the commit message, or create a tag on the commit. When you click a changed file in the commit, Visual Studio opens the side-by-side Diff view of the commit and its parent.
Handle merge conflicts in Visual Studio 2019
Conflicts can occur during a merge if two developers modify the same lines in a file and Git doesn’t automatically know which is correct. Git halts the merge and informs you that you are in a conflicted state.
Visual Studio makes it easy to identify and resolve a merge conflict. First, the Git Repository window shows a gold info bar at the top of the window.
The Git Changes window also displays a вЂMerge is in progress with conflicts’ message, with the unmerged files in their separate section below it.
But if you have neither of these windows open, and instead you go to the file that has merge conflicts, you won’t have to search for the following text:
Instead, Visual Studio displays a gold info bar on the top of the page that indicates that the opened file has conflicts. Then, you can click the link to open the Merge Editor.
The Merge Editor in Visual Studio 2019
The Merge Editor in Visual Studio is a three-way merge tool that displays the incoming changes, your current changes, and the result of the merge. You can use the tool bar at the top level of the Merge Editor to navigate between conflicts and auto-merged differences in the file.
You can also use the toggles to show/hide differences, show/hide word differences, and customize the layout. There are checkboxes on the top of each side that you can use to take all the changes from one side or the other. But to take individual changes, you can click the checkboxes to the left of the conflicting lines on either side. Finally, when you finish resolving the conflicts, you can select the Accept Merge button in the Merge Editor. You then write a commit message and commit the changes to complete the resolution.
Personalize your Git settings in Visual Studio 2019
To personalize and customize your Git settings at a repository level as well as at a global level, go to either Git > Settings on the menu bar, or to Tools > Options > Source Control on the menu bar. Then, choose the options you want.
How to use the full Team Explorer experience in Visual Studio 2019
The new Git experience is the default version control system in Visual Studio 2019 from version 16.8 onwards. However, if you want to turn it off, you can. Go to Tools > Options > Environment > Preview Features and then toggle the New Git user experience checkbox, which will switch you back to Team Explorer for Git.
Visual studio code github
Install Docker Desktop or Docker for Linux on your local machine. (See docs for additional details.)
Important: Docker needs at least 4 Cores and 8 GB of RAM to run a full build. If you are on macOS, or are using the old Hyper-V engine for Windows, update these values for Docker Desktop by right-clicking on the Docker status bar item and going to Preferences/Settings > Resources > Advanced.
Note: The Resource Monitor extension is included in the container so you can keep an eye on CPU/Memory in the status bar.
Tip: While you can use your local source tree instead, operations like yarn install can be slow on macOS or when using the Hyper-V engine on Windows. We recommend the «clone repository in container» approach instead since it uses «named volume» rather than the local filesystem.
After the container is running, open a web browser and go to http://localhost:6080, or use a VNC Viewer to connect to localhost:5901 and enter vscode as the password.
Anything you start in VS Code, or the integrated terminal, will appear here.
Next: Try it out!
From the microsoft/vscode GitHub repository, click on the Code dropdown, select Open with Codespaces, and then click on New codespace. If prompted, select the Standard machine size (which is also the default).
Note: You will not see these options within GitHub if you are not in the Codespaces beta.
After the codespace is up and running in your browser, press Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P or F1 and select Ports: Focus on Ports View.
You should see VNC web client (6080) under in the list of ports. Select the line and click on the globe icon to open it in a browser tab.
In the new tab, you should see noVNC. Click Connect and enter vscode as the password.
Anything you start in VS Code, or the integrated terminal, will appear here.
Next: Try it out!
Using VS Code with GitHub Codespaces
You may see improved VNC responsiveness when accessing a codespace from VS Code client since you can use a VNC Viewer. Here’s how to do it.
After you have connected to the codespace, you can use a VNC Viewer to connect to localhost:5901 and enter vscode as the password.
Tip: You may also need change your VNC client’s Picture Quality setting to High to get a full color desktop.
Anything you start in VS Code, or the integrated terminal, will appear here.
Next: Try it out!
This container uses the Fluxbox window manager to keep things lean. Right-click on the desktop to see menu options. It works with GNOME and GTK applications, so other tools can be installed if needed.
In your local VS Code client, open a terminal ( Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + ` ) and type the following commands:
After the build is complete, open a web browser or a VNC Viewer to connect to the desktop environment as described in the quick start and enter vscode as the password.
Next, let’s try debugging.
Go to your local VS Code client, and use the Run / Debug view to launch the VS Code configuration. (Typically the default, so you can likely just press F5 ).
Note: If launching times out, you can increase the value of timeout in the «VS Code», «Attach Main Process», «Attach Extension Host», and «Attach to Shared Process» configurations in launch.json. However, running scripts/code.sh first will set up Electron which will usually solve timeout issues.
Visual studio code github
Project Management
Contributing
Documentation
Clone this wiki locally
Welcome to the Visual Studio Code Wiki. These pages are primarily intended for those who wish to contribute to the VS Code project by submitting bug reports, suggesting new features, building extensions, commenting on new ideas, or even by submitting pull requests.
Please refer to the sidebar (on the right) for details on Project Management, Contributing to VS Code, and Documentation.
If you are looking for more information on using VS Code, please visit our the Visual Studio Code portal and follow us on Twitter!
Want to contribute to this Wiki?
Footer
© 2022 GitHub, Inc.
You can’t perform that action at this time.
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Visual studio code github
Using React in Visual Studio Code
React is a popular JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building user interfaces. The Visual Studio Code editor supports React.js IntelliSense and code navigation out of the box.
Welcome to React
We’ll be using the create-react-app generator for this tutorial. To use the generator as well as run the React application server, you’ll need Node.js JavaScript runtime and npm (Node.js package manager) installed. npm is included with Node.js which you can download and install from Node.js downloads.
You can now create a new React application by typing:
where my-app is the name of the folder for your application. This may take a few minutes to create the React application and install its dependencies.
Let’s quickly run our React application by navigating to the new folder and typing npm start to start the web server and open the application in a browser:
You should see the React logo and a link to «Learn React» on http://localhost:3000 in your browser. We’ll leave the web server running while we look at the application with VS Code.
In the File Explorer, one file you’ll see is the application README.md Markdown file. This has lots of great information about the application and React in general. A nice way to review the README is by using the VS Code Markdown Preview. You can open the preview in either the current editor group (Markdown: Open Preview kb(markdown.showPreview) ) or in a new editor group to the side (Markdown: Open Preview to the Side kb(markdown.showPreviewToSide) ). You’ll get nice formatting, hyperlink navigation to headers, and syntax highlighting in code blocks.
Syntax highlighting and bracket matching
Now expand the src folder and select the index.js file. You’ll notice that VS Code has syntax highlighting for the various source code elements and, if you put the cursor on a parenthesis, the matching bracket is also selected.
If you select a method, you’ll also get parameter help:
Go to Definition, Peek definition
Press kbstyle(Escape) to close the Peek window.
Once you save the index.js file, the running instance of the server will update the web page and you’ll see «Hello World!» when you refresh your browser.
Tip: VS Code supports Auto Save, which by default saves your files after a delay. Check the Auto Save option in the File menu to turn on Auto Save or directly configure the files.autoSave user setting.
To debug the client side React code, we’ll use the built-in JavaScript debugger.
Set a breakpoint
Configure the debugger
Ensure that your development server is running ( npm start ). Then press kb(workbench.action.debug.start) or the green arrow to launch the debugger and open a new browser instance. The source code where the breakpoint is set runs on startup before the debugger was attached, so we won’t hit the breakpoint until we refresh the web page. Refresh the page and you should hit your breakpoint.
For more information about the debugger and its available options, check out our documentation on browser debugging.
Live editing and debugging
If you are using webpack together with your React app, you can have a more efficient workflow by taking advantage of webpack’s HMR mechanism which enables you to have live editing and debugging directly from VS Code. You can learn more in this Live edit and debug your React apps directly from VS Code blog post and the webpack Hot Module Replacement documentation.
Linters analyze your source code and can warn you about potential problems before you run your application. The JavaScript language services included with VS Code has syntax error checking support by default, which you can see in action in the Problems panel (View > Problems kb(workbench.actions.view.problems) ).
Try making a small error in your React source code and you’ll see a red squiggle and an error in the Problems panel.
Linters can provide more sophisticated analysis, enforcing coding conventions and detecting anti-patterns. A popular JavaScript linter is ESLint. ESLint, when combined with the ESLint VS Code extension, provides a great in-product linting experience.
First, install the ESLint command-line tool:
Then install the ESLint extension by going to the Extensions view and typing ‘eslint’.
ESLint will now analyze open files and shows a warning in index.js about ‘App’ being defined but never used.
Let’s add an error rule for extra semi-colons:
Now when you mistakenly have multiple semicolons on a line, you’ll see an error (red squiggle) in the editor and error entry in the Problems panel.
Popular Starter Kits
In this tutorial, we used the create-react-app generator to create a simple React application. There are lots of great samples and starter kits available to help build your first React application.
VS Code React Sample
This is a sample React application, which creates a simple TODO application and includes the source code for a Node.js Express server. It also shows how to use the Babel ES6 transpiler and then use webpack to bundle the site assets.
If you’re curious about TypeScript and React, you can also create a TypeScript version of the create-react-app application by specifying that you want to use the TypeScript template:
Angular is another popular web framework. If you’d like to see an example of Angular working with VS Code, check out the Debugging with Angular CLI recipe. It will walk you through creating an Angular application and configuring the launch.json file for the JavaScript debugger.
Can I get IntelliSense within declarative JSX?
Visual studio code github
Project Management
Contributing
Documentation
Clone this wiki locally
Welcome to the Visual Studio Code Wiki. These pages are primarily intended for those who wish to contribute to the VS Code project by submitting bug reports, suggesting new features, building extensions, commenting on new ideas, or even by submitting pull requests.
Please refer to the sidebar (on the right) for details on Project Management, Contributing to VS Code, and Documentation.
If you are looking for more information on using VS Code, please visit our the Visual Studio Code portal and follow us on Twitter!
Want to contribute to this Wiki?
Footer
© 2022 GitHub, Inc.
You can’t perform that action at this time.
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
microsoft/vscode-python
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
This branch is 62 commits ahead of DonJayamanne:main.
Open a pull request to contribute your changes upstream.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Python extension for Visual Studio Code
A Visual Studio Code extension with rich support for the Python language (for all actively supported versions of the language: >=3.7), including features such as IntelliSense (Pylance), linting, debugging, code navigation, code formatting, refactoring, variable explorer, test explorer, and more!
The Python extension does offer some support when running on vscode.dev (which includes github.dev). This includes partial IntelliSense for open files in the editor.
The Python extension will automatically install the Pylance and Jupyter extensions to give you the best experience when working with Python files and Jupyter notebooks. However, Pylance is an optional dependency, meaning the Python extension will remain fully functional if it fails to be installed. You can also uninstall it at the expense of some features if you’re using a different language server.
Extensions installed through the marketplace are subject to the Marketplace Terms of Use.
Set up your environment
Select your Python interpreter by clicking on the status bar
Configure the debugger through the Debug Activity Bar
Configure tests by running the Configure Tests command
Jupyter Notebook quick start
The Python extension and the Jupyter extension work together to give you a great Notebook experience in VS Code.
Open or create a Jupyter Notebook file (.ipynb) and start coding in our Notebook Editor!
For more information you can:
Open the Command Palette (Command+Shift+P on macOS and Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows/Linux) and type in one of the following commands:
Learn more about the rich features of the Python extension:
IntelliSense: Edit your code with auto-completion, code navigation, syntax checking and more
Linting: Get additional code analysis with Pylint, Flake8 and more
Code formatting: Format your code with black, autopep or yapf
Debugging: Debug your Python scripts, web apps, remote or multi-threaded processes
Testing: Run and debug tests through the Test Explorer with unittest or pytest.
Jupyter Notebooks: Create and edit Jupyter Notebooks, add and run code cells, render plots, visualize variables through the variable explorer, visualize dataframes with the data viewer, and more
Environments: Automatically activate and switch between virtualenv, venv, pipenv, conda and pyenv environments
Refactoring: Restructure your Python code with variable extraction, method extraction and import sorting
Questions, issues, feature requests, and contributions
Visual studio code github
Project Management
Contributing
Documentation
Clone this wiki locally
Welcome to the Visual Studio Code Wiki. These pages are primarily intended for those who wish to contribute to the VS Code project by submitting bug reports, suggesting new features, building extensions, commenting on new ideas, or even by submitting pull requests.
Please refer to the sidebar (on the right) for details on Project Management, Contributing to VS Code, and Documentation.
If you are looking for more information on using VS Code, please visit our the Visual Studio Code portal and follow us on Twitter!
Want to contribute to this Wiki?
Footer
© 2022 GitHub, Inc.
You can’t perform that action at this time.
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Getting started with GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code
In this article
Learn how to install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code, and start seeing suggestions as you write comments and code.
GitHub Copilot is available to GitHub customers with a personal account on GitHub.com. GitHub Copilot is free to use for verified students and maintainers of popular open source projects. If you are not a student or maintainer of a popular open source project, you can try GitHub Copilot for free with a one-time 60 day trial. After the free trial, you will need a paid subscription for continued use. For more information, see «About billing for GitHub Copilot.»
About GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code
GitHub Copilot provides autocomplete-style suggestions from an AI pair programmer as you code. For more information, see «About GitHub Copilot».
If you use Visual Studio Code, you can view and incorporate suggestions from GitHub Copilot directly within the editor. This guide demonstrates how to use GitHub Copilot within Visual Studio Code for macOS, Windows, or Linux.
To use GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code, you must have Visual Studio Code installed. For more information, see the Visual Studio Code download page.
Installing the Visual Studio Code extension
To use GitHub Copilot, you must first install the Visual Studio Code extension.
Seeing your first suggestion
GitHub Copilot provides suggestions for numerous languages and a wide variety of frameworks, but works especially well for Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Ruby, Go, C# and C++. The following samples are in JavaScript, but other languages will work similarly.
Seeing alternative suggestions
For any given input, GitHub Copilot may offer multiple suggestions. You can select which suggestion to use, or reject all suggestions.
In Visual Studio Code, create a new JavaScript (*.js) file.
In the JavaScript file, type the following function header. GitHub Copilot will show you a suggestion.
Optionally, you can see alternative suggestions, if any are available.
| OS | See next suggestion | See previous suggestion |
|---|---|---|
| macOS | Option (⌥) or Alt + ] | Option (⌥) or Alt + [ |
| Windows | Alt + ] | Alt + [ |
| Linux | Alt + ] | Alt + [ |
Alternatively, you can hover over the suggestion to see the GitHub Copilot command palette for choosing suggestions.
Seeing multiple suggestions in a new tab
You may not want any of the initial suggestions GitHub Copilot offers. You can use a keyboard shortcut to prompt GitHub Copilot to show you multiple suggestions in a new tab.
Generating code suggestions from comments
You can describe something you want to do using natural language within a comment, and GitHub Copilot will suggest the code to accomplish your goal.
Using a framework
You can also use GitHub Copilot to generate suggestions for APIs and frameworks. The following example uses GitHub Copilot to create a simple Express server that returns the current time.
Enabling or disabling GitHub Copilot
You can enable or disable GitHub Copilot from within Visual Studio Code. The GitHub Copilot status icon in the bottom panel of the Visual Studio Code window indicates whether GitHub Copilot is enabled or disabled. When enabled, the background color of the icon will match the color of the status bar. When disabled, the background color of the icon will contrast with the color of the status bar.
If you are disabling GitHub Copilot, you will be asked whether you want to disable suggestions globally, or for the language of the file you are currently editing.
Work with GitHub accounts in Visual Studio
If you have a public GitHub or GitHub Enterprise account, you can add it to your Visual Studio keychain. After you add your account, you’ll be able to take advantage of the platform integration by accessing and creating GitHub repositories, right from Visual Studio.
Adding public GitHub accounts
You can add your public GitHub account if you’re already signed into Visual Studio with a Microsoft account, work account, or school account.
From the All Accounts submenu, select the plus sign to add an account, and select GitHub.
You’ll be redirected to the browser, where you can sign in with your GitHub credentials. After you sign in, you’ll get a success window in the browser, and you can return to Visual Studio.
You’ll have both accounts present in your All Accounts submenu.
Adding GitHub Enterprise Managed User (EMU) accounts
You can add your GitHub EMU account if you’re already signed into Visual Studio with a Microsoft account, work account, or school account.
From the All Accounts submenu, select the + or the Add dropdown to add an account, and then select GitHub.
You’ll be redirected to the browser, where you can sign in with your GitHub EMU credentials.
Ensure you enter your GitHub EMU account credentials (the username has an underscore followed by the company name) on this page.
After you sign in, you’ll get a success window in the browser, and you can return to Visual Studio.
Adding GitHub enterprise accounts
By default, Visual Studio only has public GitHub accounts enabled.
To enable GitHub enterprise accounts, go to Tools > Options and search for the Accounts options.
Then, check the box to Include GitHub Enterprise Server accounts. The next time you go to your Account Settings and try to add a GitHub account, you’ll see options for both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise.
After you enter your GitHub Enterprise server address, select Sign in with your browser. There, you can sign in using your GitHub Enterprise credentials.
microsoft/vscode
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md


Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code combines the simplicity of a code editor with what developers need for their core edit-build-debug cycle. It provides comprehensive code editing, navigation, and understanding support along with lightweight debugging, a rich extensibility model, and lightweight integration with existing tools.
Visual Studio Code is updated monthly with new features and bug fixes. You can download it for Windows, macOS, and Linux on Visual Studio Code’s website. To get the latest releases every day, install the Insiders build.
There are many ways in which you can participate in this project, for example:
If you are interested in fixing issues and contributing directly to the code base, please see the document How to Contribute, which covers the following:
See our wiki for a description of each of these channels and information on some other available community-driven channels.
Many of the core components and extensions to VS Code live in their own repositories on GitHub. For example, the node debug adapter and the mono debug adapter repositories are separate from each other. For a complete list, please visit the Related Projects page on our wiki.
Docker / the Codespace should have at least 4 Cores and 6 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended) to run full build. See the development container README for more information.
Code of Conduct
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
microsoft/vscode-remote-release
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Visual Studio Code Remote Development
 | Visual Studio Code Remote Development Open any folder in a container, on a remote machine, or in WSL and take advantage of VS Code’s full feature set. Learn more!  |
This repository is for providing feedback on the Visual Studio Remote Development extension pack and its related extensions. You can use the repository to report issues or submit feature requests on any of these extensions:
You may also use this repo to provide feedback on the Visual Studio Code Server.
If you are running into an issue with another extension you’d like to use with the Remote Development extensions, please raise an issue in the extension’s repository. You can reference our summary of tips for remote related issues and our extension guide to help the extension author get started.
Issues related to dev container definitions can be reported in the vscode-dev-containers repository. You may use the dev container spec repository to file and review issues to shape the direction of development containers and the dev container CLI.
Running into trouble? Wondering what you can do? These articles can help.
VS Code Remote Development extension «stable» releases are tied directly to VS Code releases. Release highlights can be found in VS Code release notes which will include a link to detailed extension release notes.
The extensions are developed using the same development process and schedule as VS Code itself. You can see what is planned for the current development iteration in a pinned planning issue in this repository. This issue will include a link to the broader VS Code plan. As with VS Code itself, the extensions will update during a development iteration with changes that are only available in VS Code Insiders Edition.
You can use this repository to:
If you have a question, connect with the community using any of these social platforms:
See our CONTRIBUTING guide for more details.
By downloading and using the Visual Studio Remote Development extension pack and its related extensions, you agree to the product license terms and privacy statement.
License for this repository:
Copyright © Microsoft Corporation All rights reserved.
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License (International): https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
About
Visual Studio Code Remote Development: Open any folder in WSL, in a Docker container, or on a remote machine using SSH and take advantage of VS Code’s full feature set.
microsoft/vscode-mssql
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md

mssql for Visual Studio Code
Welcome to mssql for Visual Studio Code! An extension for developing Microsoft SQL Server, Azure SQL Database and SQL Data Warehouse everywhere with a rich set of functionalities, including:
See the mssql extension tutorial for the step by step guide.
See the SQL developer tutorial to develop an app with C#, Java, Node.js, PHP, Python and R with SQL Server databases.
Supported Operating Systems
Currently this extension supports the following operatings systems:
Support for this extension is provided on our GitHub Issue Tracker. You can submit a bug report, a feature suggestion or participate in [discussions].
Contributing to the Extension
See the developer documentation for details on how to contribute to this extension.
Code of Conduct
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
The Microsoft Enterprise and Developer Privacy Statement describes the privacy statement of this software.
This extension is licensed under the MIT License. Please see the third-party notices file for additional copyright notices and license terms applicable to portions of the software.
microsoft/vscode-docs
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Visual Studio Code Documentation
You’ve found the Visual Studio Code documentation GitHub repository, which contains the content for the Visual Studio Code documentation.
Topics submitted here will be published to the Visual Studio Code portal.
If you are looking for the VS Code product GitHub repository, you can find it here.
Visual Studio Code
If you landed here looking for other information about VS Code, head over to our website for additional information.
If you want to give documentation feedback, please use the feedback control located at the bottom of each documentation page.
To enter documentation bugs, please create a new GitHub issue. Please check if there is an existing issue first.
If you think the issue is with the VS Code product itself, please enter issues in the VS Code product repo here.
To contribute new topics/information or make changes to existing documentation, please read the Contributing Guideline.
The two suggested workflows are:
Cloning without binary files
You might want to clone the repo without the 1.6GB images. Here are the steps:
The history of this repo before we adopted LFS can be found at microsoft/vscode-docs-archive.
Steps for how to publish documentation changes can be found here in the (private) repository of the VS Code website.
Work with GitHub accounts in Visual Studio
If you have a public GitHub or GitHub Enterprise account, you can add it to your Visual Studio keychain. After you add your account, you’ll be able to take advantage of the platform integration by accessing and creating GitHub repositories, right from Visual Studio.
Adding public GitHub accounts
You can add your public GitHub account if you’re already signed into Visual Studio with a Microsoft account, work account, or school account.
From the All Accounts submenu, select the plus sign to add an account, and select GitHub.
You’ll be redirected to the browser, where you can sign in with your GitHub credentials. After you sign in, you’ll get a success window in the browser, and you can return to Visual Studio.
You’ll have both accounts present in your All Accounts submenu.
Adding GitHub Enterprise Managed User (EMU) accounts
You can add your GitHub EMU account if you’re already signed into Visual Studio with a Microsoft account, work account, or school account.
From the All Accounts submenu, select the + or the Add dropdown to add an account, and then select GitHub.
You’ll be redirected to the browser, where you can sign in with your GitHub EMU credentials.
Ensure you enter your GitHub EMU account credentials (the username has an underscore followed by the company name) on this page.
After you sign in, you’ll get a success window in the browser, and you can return to Visual Studio.
Adding GitHub enterprise accounts
By default, Visual Studio only has public GitHub accounts enabled.
To enable GitHub enterprise accounts, go to Tools > Options and search for the Accounts options.
Then, check the box to Include GitHub Enterprise Server accounts. The next time you go to your Account Settings and try to add a GitHub account, you’ll see options for both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise.
After you enter your GitHub Enterprise server address, select Sign in with your browser. There, you can sign in using your GitHub Enterprise credentials.
Git, GitHub и Visual Studio. В помощь новичкам
О чем:
В ней будет коротко рассмотрено что это за вещи, зачем нужны, и простой способ работы – из среды Visual Studio. То есть Bash или GitHub клиент использоваться не будут.
Внимание:
На Хабре уже есть похожая статья – [вот она]. В своей публикации я дополню слова Алексея и расскажу метод проще.
Для кого:
Статья направлена в помощь людям которые не работали с Git, GitHub, и хотят освоить в общих чертах как можно быстрее и без сложностей начать работу с ними.
О тексте:
Старался писать проще и с большим количеством скриншотов и пояснений. Ведь лучше, когда они есть чем, когда их нет и о чем-то приходится догадываться.
Итак, немного теории чтоб понять, что делать дальше:
Инструкция:
После, с GitHub копируем ссылку:
Дополнительно:
Чтоб GitHub верно отображал русские комментарии (если есть) при просмотре кода через сайт нужно сделать следующее:
Cоветую всё-таки изучить Git Bash.
Я старался писать как можно понятнее, если что-то не так, то поправьте в комментариях!
На этом все. Спасибо за внимание!
microsoft/vscode-python
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
This branch is 62 commits ahead of DonJayamanne:main.
Open a pull request to contribute your changes upstream.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Python extension for Visual Studio Code
A Visual Studio Code extension with rich support for the Python language (for all actively supported versions of the language: >=3.7), including features such as IntelliSense (Pylance), linting, debugging, code navigation, code formatting, refactoring, variable explorer, test explorer, and more!
The Python extension does offer some support when running on vscode.dev (which includes github.dev). This includes partial IntelliSense for open files in the editor.
The Python extension will automatically install the Pylance and Jupyter extensions to give you the best experience when working with Python files and Jupyter notebooks. However, Pylance is an optional dependency, meaning the Python extension will remain fully functional if it fails to be installed. You can also uninstall it at the expense of some features if you’re using a different language server.
Extensions installed through the marketplace are subject to the Marketplace Terms of Use.
Set up your environment
Select your Python interpreter by clicking on the status bar
Configure the debugger through the Debug Activity Bar
Configure tests by running the Configure Tests command
Jupyter Notebook quick start
The Python extension and the Jupyter extension work together to give you a great Notebook experience in VS Code.
Open or create a Jupyter Notebook file (.ipynb) and start coding in our Notebook Editor!
For more information you can:
Open the Command Palette (Command+Shift+P on macOS and Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows/Linux) and type in one of the following commands:
Learn more about the rich features of the Python extension:
IntelliSense: Edit your code with auto-completion, code navigation, syntax checking and more
Linting: Get additional code analysis with Pylint, Flake8 and more
Code formatting: Format your code with black, autopep or yapf
Debugging: Debug your Python scripts, web apps, remote or multi-threaded processes
Testing: Run and debug tests through the Test Explorer with unittest or pytest.
Jupyter Notebooks: Create and edit Jupyter Notebooks, add and run code cells, render plots, visualize variables through the variable explorer, visualize dataframes with the data viewer, and more
Environments: Automatically activate and switch between virtualenv, venv, pipenv, conda and pyenv environments
Refactoring: Restructure your Python code with variable extraction, method extraction and import sorting
Questions, issues, feature requests, and contributions
Упрощение управления версиями в Visual Studio с помощью Git
Вам когда-нибудь хотелось, чтобы можно было вернуться к ранее работающей версии кода? Вы вручную храните резервные копии кода в разных местах? Здесь вам поможет управление версиями.
Git — это самая широко используемая система управления версиями в современном мире. С помощью Git вы можете отслеживать изменения, вносимые в код с течением времени, и выполнять откат к определенным версиям. Возможности Git в Visual Studio могут принести большую пользу и новичкам, и профессиональным разработчикам.
Чтобы узнать об использовании Git и GitHub в Visual Studio, зарегистрируйтесь для прохождения серии курсов Git Learning Series.
Начало работы с Git GitHub & в Visual Studio
С помощью Git можно легко управлять версиями в Visual Studio. Работайте так, как вам удобно: удаленно через выбранного поставщика Git, такого как GitHub или Azure DevOps, или локально без каких-либо поставщиков.
Чтобы начать работу с Git в Visual Studio, сделайте следующее:
Если у вас есть Git-репозиторий, размещенный у поставщика, например в GitHub, клонируйте репозиторий на свой локальный компьютер.
Либо вы можете легко создать репозиторий Git и добавить свой код. Если у вас еще нет поставщика Git, рекомендуем начать с GitHub, так как именно под этого поставщика оптимизирован интерфейс Git в Visual Studio. GitHub предоставляет бесплатное и защищенное облачное хранилище кода, в котором вы можете хранить код и обращаться к нему с любого устройства и в любом месте.
Вы можете добавить учетные записи GitHub и GitHub Enterprise в свою цепочку ключей и использовать их так же, как учетные записи Майкрософт. Если у вас нет учетной записи GitHub, воспользуйтесь инструкциями, чтобы создать учетную запись GitHub для использования с Visual Studio прямо сейчас.
Если вы новичок в Git, вы можете начать с сайта https://git-scm.com/.
Просмотр файлов в обозревателе решений
Интуитивный повседневный рабочий процесс
Для повседневного рабочего процесса Git Visual Studio предоставляет простой способ взаимодействия с Git при написании кода без необходимости покидать свой код.
Вы можете выполнять несколько задач и экспериментировать с кодом с помощью ветвей. Если вы или ваша команда работаете с несколькими компонентами одновременно или хотите опробовать какие-то идеи, не затрагивая рабочий код, ветвление оказывается очень полезным. Рекомендуемый рабочий процесс Git использует новую ветвь для каждого компонента или исправления, над которым вы работаете. Узнайте, как создать ветвь из Visual Studio.
После создания новой ветви и переключения на нее можно начать работу, изменив существующие файлы или добавив новые, а затем зафиксировав свою работу в репозитории. Чтобы узнать больше о фиксации в Visual Studio и состоянии файлов в Git см. страницу Фиксация кода.
Git — это распределенная система управления версиями, то есть все изменения, которые мы уже внесли, существуют только локально. Чтобы внести эти изменения в удаленный репозиторий, необходимо отправить локальные фиксации на удаленный узел.
Если вы работаете в команде или используете разные компьютеры, вам также потребуется постоянно получать новые изменения из удаленного репозитория. Дополнительные сведения об управлении сетевыми операциями Git в Visual Studio см. на странице Получение, вытягивание, отправка и синхронизация.
Совместная работа с репозиториями &
Однако бывают случаи, когда лучше сосредоточиться на репозитории Git. Например, вы хотите понять, над чем работает команда, скопировать фиксацию из другой ветви или просто очистить исходящие фиксации. Visual Studio включает мощные функции для просмотра репозиториев и совместной работы, благодаря которым использовать другие средства не требуется.
Чтобы вы могли сосредоточиться на репозитории Git, в Visual Studio есть окно Репозиторий Git, в котором представлены все сведения о репозитории, включая локальные и удаленные ветви и журналы фиксации. Открыть это окно можно из меню GIT или Вид либо непосредственно из строки состояния.
Просмотр репозиториев Git и управление ими
Дополнительные сведения об использовании окна репозитория Git в Visual Studio для просмотра репозитория Git и управления им см. на следующих страницах:
Разрешение конфликтов слияния
Во время слияния могут возникать конфликты, если два разработчика изменяют одни и те же строки в файле и Git неизвестно, какой вариант правильный. В этом случае GIT прерывает слияние и сообщает о конфликтном состоянии. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье о разрешении конфликтов слияния.
Настройка параметров GIT
Чтобы настроить параметры Git на уровне репозитория, а также на глобальном уровне, выполните приведенные ниже действия.
Отзывы о расширенном интерфейсе &
Мы продолжаем добавлять новые функции для расширения возможностей Git. Дополнительные сведения о недавно появившихся функциях, а также опрос, в котором можно поделиться отзывом, доступны в записи блога Multi-repo support in Visual Studio (Поддержка множества репозиториев в Visual Studio). Если у вас есть предложение, отправьте его нам. Мы будем рады вашему участию в работе над решением на портале Сообщества разработчиков.
Чтобы попробовать более новые обновления функций Git и обновления из выпуска предварительной версии, скачайте и установите его со страницы Visual Studio 2022 Preview. Сведения о каждом выпуске см. в Заметках о выпуске Visual Studio 2022.
Теперь Git является интерфейсом системы управления версиями по умолчанию в Visual Studio 2019. Начиная с версии 16.6 мы работаем над созданием набора функций на основе ваших отзывов. В версии 16.8 Git стал интерфейсом управления версиями по умолчанию для всех.
Мы продолжаем расширять набор возможностей Git в Visual Studio 2022. Дополнительные сведения о последнем обновлении компонентов см. в записи блога Поддержка нескольких репозиториев в Visual Studio.
Дополнительные сведения о Git
Git — это наиболее широко используемая современная система управления версиями, которая может быть полезна как профессиональным разработчикам, так и только начинающим изучать программирование. Если вы новичок в Git, вы можете начать с сайта https://git-scm.com/. Там вы найдете памятки, популярную электронную книгу и видеоматериалы по основам Git.
Начало работы с Git в Visual Studio 2019
Мы подробно расскажем вам о том, как использовать новый интерфейс Git в Visual Studio. Однако если вы хотите сначала ознакомиться с кратким обзором, посмотрите следующее видео:
Длительность видео: 05:27 мин.
Существует три способа начать использование Git в Visual Studio для повышения производительности:
Начиная с версии 16.8 Visual Studio 2019 включает полностью интегрированный интерфейс для работы с учетными записями GitHub. Теперь вы можете добавить в цепочку ключей учетные записи GitHub и GitHub Enterprise. Вы сможете добавлять и использовать их так же, как и учетные записи Майкрософт. Это позволит упростить доступ к ресурсам GitHub в Visual Studio. Дополнительные сведения см. на странице Работа с учетными записями GitHub в Visual Studio.
Если у вас нет учетной записи GitHub, можно начать с выполнения действий, описанных в разделе Создание учетной записи GitHub для использования с Visual Studio.
Создание нового репозитория Git в Visual Studio 2019
Если ваш код не связан с GIT, можно начать с создания нового репозитория GIT. Для этого в строке меню выберите GIT>Создать репозиторий GIT. Затем в диалоговом окне Создание репозитория GIT введите свои данные.
С помощью диалогового окна Создание репозитория GIT можно легко отправить новый репозиторий в GitHub. По умолчанию новый репозиторий является частным. Это означает, что доступ к нему есть только у вас. Если снять соответствующий флажок, репозиторий будет общедоступным. Это означает, что любой пользователь в GitHub сможет его просмотреть.
Независимо от того, является ли репозиторий общедоступным или частным, лучше создать удаленную резервную копию кода, которая будет безопасно храниться в GitHub, даже если вы работаете сами по себе. Это также позволит вам получать доступ к коду с любого компьютера.
Вы можете создать исключительно локальный репозиторий GIT, выбрав параметр Только локальный. Вы также можете связать локальный проект с любым существующим пустым удаленным репозиторием, размещенным в Azure DevOps или у любого другого поставщика Git, с помощью параметра Существующий удаленный репозиторий.
Клонирование существующего репозитория Git в Visual Studio 2019
В Visual Studio процесс клонирования прост. Если вы знаете URL-адрес репозитория, который нужно клонировать, можно вставить его в разделе Расположение репозитория, а затем выбрать место на диске, в которое будет клонирован репозиторий.
Если вы не знаете URL-адрес репозитория, в Visual Studio можно легко перейти к существующему репозиторию GitHub или Azure DevOps и выбрать его.
Открытие существующего локального репозитория в Visual Studio 2019
После клонирования или создания репозитория GIT Visual Studio обнаружит его и добавит в список Локальные репозитории в меню GIT.
В нем можно быстро открывать репозитории GIT и переключаться между ними.
Просмотр файлов в Обозревателе решений в Visual Studio 2019
При клонировании репозитория или открытии локального репозитория Visual Studio переключается в этот контекст GIT, сохраняя и закрывая все ранее открытые решения и проекты. Обозреватель решений загружает папку в корне репозитория Git и проверяет дерево каталогов на наличие просматриваемых файлов. К ним относятся такие файлы, как CMakeLists.txt или файлы с расширением SLN.
Visual Studio настраивает представление в зависимости от файла, загруженного в обозреватель решений:
Переключаться между текущим представлением и списком представлений можно с помощью кнопки Переключить представления на панели инструментов обозревателя решений.
Окно «Изменения Git» в Visual Studio 2019
GIT отслеживает изменения файлов в репозитории в процессе работы и разделяет файлы на три категории. Это те же изменения, которые отображаются при вводе команды git status в командной строке.
В процессе работы Visual Studio отслеживает изменения в файлах проекта в разделе Изменения окна Изменения GIT.
Когда вы будете готовы подготовить изменения, нажмите кнопку + (плюс) для каждого из файлов, которые необходимо подготовить, или щелкните файл правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт Промежуточно сохранить. Можно также подготовить все измененные файлы одним щелчком мыши, используя кнопку «Промежуточно сохранить все» ( + ) в верхней части раздела Изменения.
Visual Studio также позволяет выполнить фиксацию и синхронизацию одним щелчком мыши с помощью ярлыков Зафиксировать все и отправить и Зафиксировать все и синхронизировать. Если дважды щелкнуть любой файл в разделе Изменения или Подготовленные изменения, то можно построчно сравнить измененную версию файла с неизмененной.
Если вы подключены к репозиторию Azure DevOps, вы можете связать рабочий элемент Azure DevOps с фиксацией, используя символ #. Чтобы подключить репозиторий Azure DevOps, выберите Team Explorer>Управление подключениями.
Выбор существующей ветви в Visual Studio 2019
В Visual Studio текущая ветвь отображается в селекторе в верхней части окна Изменения GIT.
Текущая ветвь также доступна в строке состояния в правом нижнем углу интегрированной среды разработки Visual Studio.
В обоих местах можно переключаться между имеющимися ветвями.
Создание новой ветви в Visual Studio 2019
Чтобы создать ветвь, достаточно ввести ее имя и указать существующую ветвь, на основе которой будет создана данная.
Окно репозитория Git в Visual Studio 2019
В Visual Studio имеется новое окно Репозиторий GIT, в котором представлены все сведения о репозитории, включая все ветви, удаленные репозитории и журналы фиксации. Открыть это окно можно из меню GIT или Вид либо непосредственно из строки состояния.
Управления ветвями в Visual Studio 2019
При выборе в меню GIT пункта Управление ветвями отображается древовидное представление ветвей в окне Репозиторий GIT. В левой области можно использовать контекстное меню для извлечения, создания, объединения ветвей, перемещения изменений из одной ветви в другую, отбора изменений и других действий. Щелкнув ветвь, можно просмотреть ее журнал фиксаций в правой области.
Входящие и исходящие фиксации в Visual Studio 2019
При принесении ветви в окне Изменения GIT под раскрывающемся списком ветвей отображается индикатор, который показывает количество фиксаций, которые не были вытянуты из удаленной ветви. Он также показывает число локальных фиксаций, которые не были отправлены.
Индикатор также является ссылкой, по которой можно перейти к журналу фиксаций этой ветви в окне Репозиторий GIT. В начале журнала теперь отображаются сведения об этих входящих и исходящих фиксациях. Здесь можно также вытянуть или отправить фиксации.
Сведения о фиксации в Visual Studio 2019
Если дважды щелкнуть фиксацию, в Visual Studio откроются сведения о ней в отдельном окне инструментов. Здесь можно отменить фиксацию, сбросить ее, исправить сообщение о фиксации или создать тег для нее. Если щелкнуть измененный файл в фиксации, в Visual Studio откроется инструмент сравнения, в котором рядом друг с другом показаны фиксация и ее предок.
Обработка конфликтов слияния в Visual Studio 2019
Во время слияния могут возникать конфликты, если два разработчика изменяют одни и те же строки в файле и GIT неизвестно, какой вариант правильный. В этом случае GIT прерывает слияние и сообщает о конфликтном состоянии.
В Visual Studio можно легко выявлять и устранять конфликты слияния. Во-первых, в верхней части окна Репозиторий GIT имеется золотистая информационная панель.
В окне Изменения GIT также выводится сообщение Слияние выполняется с конфликтами, под которым в отдельном разделе указываются файлы, слияние которых не было выполнено.
Но если ни одно из этих окон не открыто и вы переходите к файлу с конфликтами слияния, вам не придется искать следующий текст:
Вместо этого в верхней части страницы в Visual Studio отображается золотистая информационная панель с сообщением о наличии конфликтов в открытом файле. Щелкните ссылку, чтобы открыть редактор слияния.
Редактор слияния в Visual Studio 2019
Редактор слияния в Visual Studio позволяет выполнять трехстороннее сравнение: в нем приводятся входящие изменения, текущие изменения и результат слияния. С помощью панели инструментов вверху редактора слияния можно переходить между конфликтами и просматривать результаты автоматического слияния в файле.
Можно также использовать переключатели для отображения и скрытия различий, отображения и скрытия различий в словах и настройки макета. Вверху с каждой стороны есть флажки, с помощью которых можно перенести все изменения с одной стороны на другую. Чтобы перенести отдельные изменения, можно установить флажки слева от конфликтующих строк с любой стороны. Завершив разрешение конфликтов, нажмите в редакторе слияния кнопку Принять слияние. После этого нужно ввести сообщение о фиксации и зафиксировать изменения, чтобы завершить процесс разрешения.
Персонализация параметров Git в Visual Studio 2019
Чтобы настроить параметры GIT на уровне репозитория, а также на глобальном уровне, выберите в строке меню пункты GIT>Параметры или Сервис>Параметры>Управление исходным кодом. Затем выберите нужные параметры.
Использование всех возможностей Team Explorer в Visual Studio 2019
Новый интерфейс GIT — это система контроля версий по умолчанию в Visual Studio 2019 начиная с версии 16.8. Однако при желании этот интерфейс можно отключить. Чтобы вернуться в Team Explorer для Git, выберите Средства>Параметры>Среда>Функции предварительной версии и снимите флажок Новый пользовательский интерфейс Git.
Visual studio code github
Git is a distributed version control system. Git repositories can live locally (such as on a developer’s machine). Each developer has a copy of the source repository on their dev machine. Developers can commit each set of changes on their dev machine and perform version control operations such as history and compare without a network connection.
In this lab, you will learn how to clone an existing Git repository from GitHub. In addition, you will learn about Git branching and merging support. You will use Visual Studio Code, but the same processes apply for using any Git-compatible client with GitHub.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio Code with the C# extension installed.
Exercise 1: Configuring the lab environment
Task 1: Configuring Visual Studio Code
Open Visual Studio Code. In this task, you will configure a Git credential helper to securely store the Git credentials used to communicate with GitHub. If you have already configured a credential helper and Git identity, you can skip to the next task.
Execute the command below to configure a credential helper.
The commands below will configure your user name and email for Git commits. Replace the parameters with your preferred user name and email and execute them.
Task 2: Forking an existing repository
In a browser tab, navigate to the GitHub project at https://github.com/Microsoft/PartsUnlimitedE2E.
Click Fork. This will copy the entire repository into the account you specify so that you can work on it without impacting the original repo.
Task 3: Cloning an existing repository
Your GitHub browser tab should now be open to your forked version of the repo.
Getting a local copy of a Git repo is called “cloning”. Every mainstream development tool supports this and will be able to connect to GitHub to pull down the latest source to work with. From the Clone or download dropdown, click the Copy to clipboard button.
Open an instance of Visual Studio Code.
Press Ctrl+Shift+P to show the Command Palette. The Command Palette provides an easy and convenient way to access a wide variety of tasks, including those provided by 3rd party extensions.
Execute the Git: Clone command. It may help to type “Git” to bring it to the shortlist.
Paste in the URL to your repo and press Enter.
Select a local path to clone the repo to.
When prompted, log in to your GitHub account.
Once the cloning has completed, click Open. You can ignore any warnings raised about opening the projects. The solution may not be in a buildable state, but that’s okay since we’re going to focus on working with Git and building the project itself is not necessary.
Exercise 2: Saving work with commits
When you make changes to your files, Git will record the changes in the local repository. You can select the changes that you want to commit by staging the changes. Commits are always made against your local Git repository, so you don’t have to worry about the commit being perfect or ready to share with others. You can make more commits as you continue to work, and push the changes to others when they are ready to be shared.
What’s in a commit?
Git commits consists of the following:
The file(s) changed in the commit. Git keeps the contents of all file changes in your repo in the commits. This keeps it fast and allows intelligent merging.
A reference to the parent commit(s). Git manages your code history using these references.
A message describing a commit. You give this message to Git when you create the commit. It’s a good idea to keep this message descriptive, but to the point.
Task 1: Committing changes
From the Explorer tab, open /PartsUnlimited-aspnet45/src/PartsUnlimitedWebsite/Models/CartItem.cs.
Add a comment to the file. It doesn’t really matter what the comment is since the goal is just to make a change. Press Ctrl+S to save the file.
Select the Source Control tab to see the one change to the solution.
Enter a commit message of “My commit” and press Ctrl+Enter to commit it locally.
If asked whether you would like to automatically stage your changes and commit them directly, click Always. We will discuss staging later in the lab.
Click the Synchronize Changes button to synchronize your changes with the server. Confirm the sync if prompted.
If prompted, log in to your GitHub account.
Task 2: Staging changes
Staging changes allows you to selectively add certain files to a commit while passing over the changes made in other files.
Return to Visual Studio Code.
Update the open CartItem.cs class by editing the comment you made earlier and saving the file.
Open Category.cs as well.
Add a new comment to Category.cs so there will be two files with changes. Save the file.
From the Source Control tab, click the Stage Changes button for CartItem.cs.
This will prepare CartItem.cs for committing without Category.cs.
Enter a comment of “Added comments”. From the More Actions dropdown, select Commit Staged.
Click the Synchronize Changes button to synchronize the committed changes with the server. Note that since only the staged changes were committed, the other changes are still pending locally.
Exercise 3: Reviewing history
Git uses the parent reference information stored in each commit to manage a full history of your development. You can easily review this commit history to find out when file changes were made and determine differences between versions of your code using the terminal or from one of the many Visual Studio Code extensions available. You can also review changes using the GitHub portal.
Git’s use of the Branches and Merges feature works through pull requests, so the commit history of your development doesn’t necessarily form a straight, chronological line. When you use history to compare versions, think in terms of file changes between two commits instead of file changes between two points in time. A recent change to a file in the master branch may have come from a commit created two weeks ago in a feature branch but was only merged yesterday.
Task 1: Comparing files
In the Source Control tab, select Category.cs.
A comparison view is opened to enable you to easily locate the changes you’ve made. In this case, it’s just the one comment.
Return to the GitHub browser tab.
Task 3: Reviewing commits
Switch to the GitHub browser tab. You can review the latest commits on GitHub under the Commits tab.
The recent commits should be right at the top. Click the most recent one.
This view enables you to review the changes applied by this commit. Click View file.
Click History to track the commits made to this file over time.
Click the Browse repository at this point in the history button for the second commit. This was the first commit pushed from this lab.
You can now review the state of the repo at the time this commit was pushed. The dropdown at the top provides a convenient way to switch between branches as well.
Exercise 4: Working with branches
You can manage the work in your GitHub repo from the Branches tab. You can also customize the view to track the branches you care most about so you can stay on top of changes made by your team.
Committing changes to a branch will not affect other branches, and you can share branches with others without having to merge the changes into the main project. You can also create new branches to isolate changes for a feature or a bug fix from your master branch and other work. Since the branches are lightweight, switching between branches is quick and easy. Git does not create multiple copies of your source when working with branches, but rather uses the history information stored in commits to recreate the files on a branch when you start working on it. Your Git workflow should create and use branches for managing features and bugfixes. The rest of the Git workflow, such as sharing code and reviewing code with pull requests, all work through branches. Isolating work in branches makes it very simple to change what you are working on by simply changing your current branch.
Task 1: Creating a new branch in your local repository
Return to Visual Studio Code.
Click the master branch from the bottom left.
Select Create new branch.
Enter the name “dev” for the new branch and press Enter.
If prompted, select master as the reference branch.
You are now working on that branch.
Task 2: Working with branches
Git keeps track of which branch you are working on and makes sure that when you checkout a branch your files match the most recent commit on the branch. Branches let you work with multiple versions of the source code in the same local Git repository at the same time. You can use Visual Studio Code to publish, check out, and delete branches.
Click the Publish changes button next to the branch.
From the GitHub browser tab, select the Branches tab.
You should see the newly pushed dev branch. Click the Delete this branch button to delete it.
Return to Visual Studio Code.
Click the dev branch.
Note that there are two dev branches listed. The local (dev) branch is there because it’s not deleted when the server branch is deleted. The server (origin/dev) is there because it hasn’t been pruned. Select the master branch to check it out.
Press Ctrl+Shift+P to open the Command Palette.
Start typing “Git: Delete” and select Git: Delete Branch when it becomes visible.
There is only one local branch to delete, so select it.
Click the master branch.
Note that the local dev branch is gone, but the remote origin/dev is still showing.
Press Ctrl+Shift+P to open the Command Palette.
Start typing “Git: Fetch” and select Git: Fetch (Prune) when it becomes visible. This command will update the origin branches in the local snapshot and delete those that are no longer there.
Note that if you don’t see the Git logs in the output console, you may need to select Git as the source.
Click the master branch.
The origin/dev branch should no longer be in the list.
Exercise 5: Managing branches from GitHub
In addition to all the functionality available in Visual Studio Code, you can also manage your repo branches from the GitHub portal.
Task 1: Creating a new branch
Switch to the GitHub browser tab.
Return to the Code tab root.
From the branches dropdown, enter a branch name of “release”. Click Create branch: release. This will create a new branch and switch to it.
You can confirm that the newly created release branch is selected.
Return to Visual Studio Code.
Press Ctrl+Shift+P to open the Command Palette.
Start typing “Git: Fetch” and select Git: Fetch when it becomes visible. This command will update the origin branches in the local snapshot.
Click the master branch.
Select origin/release. This will create a new local branch called “release” and check it out.
Task 2: Deleting a branch
Return to the GitHub browser tab and navigate to the Branches tab.
Click the Delete button for the release branch.
However, maybe we should keep it around for a little longer. Click Restore to undo the delete.
Task 3: Tagging a release
While it may not seem like much, the product team has decided that this version of the site is exactly what’s needed for v1.1. In order to mark it as such, return to the Code tab and select Releases.
Click Create a new release.
Enter tag and release names of “v1.1” and a Description of “Great release!”. Click Publish release.
You have now tagged the project at this release. You could tag commits for a variety of reasons, and GitHub offers the flexibility to edit and delete them, as well as manage their permissions.
Select the Tags option to review tags by name.
Exercise 6: Managing repositories
You can create Git repos in team projects to manage your project’s source code. Each Git repo has its own set of permissions and branches to isolate itself from other work in your project.
Task 1: Creating a new repo
From the New dropdown, select New repository.
Set the Repository name to “New Repo”. Note that you also have the option to create a file named README.md. This would be the default markdown file that is rendered when someone navigates to the repo root in a browser. Additionally, you can preconfigure the repo with a .gitignore file. This file specifies which files, based on naming pattern and/or path, to ignore from source control. There are multiple templates available that include the common patterns and paths to ignore based on the project type you are creating. Click Create repository.
That’s it. Your repo is ready. You now have the ability to clone it with Visual Studio or your tools of choice.
Task 2: Renaming and deleting Git repos
Sometimes you’ll have a need to rename or delete a repo, which is just as easy. Navigate to Settings.
You can update the name of the repository here.
From the Danger Zone section of the settings view, click Delete this repository.
Enter the full repo name and click the option to delete the repository.
GitHub Pull Requests in Visual Studio Code
September 10, 2018 Kenneth Auchenberg, @auchenberg
Like many other open-source projects, the Visual Studio Code community collaborates through pull requests to land fixes and new features. Starting this past spring, our team has been working to bring you a new integrated pull request experience so that you can collaborate, comment, review, and validate GitHub pull requests directly from within Visual Studio Code.
Today, we are announcing the public preview of GitHub Pull Requests for Visual Studio Code, closing a gap in the workflow that we and millions of engineers experience every day: The ability to review source code where it was written – inside the editor.
Review and manage Pull Requests
The new GitHub Pull Requests extension is designed to help you review and manage pull requests (PR) from within Visual Studio Code, including:
Collaboration with GitHub
As part of our broader efforts to bring pull requests into Visual Studio Code in the past year, we reached out to numerous partners. After learning that the GitHub Editor team was already thinking along these lines, we began to work together in April to create a new pull request experience in Visual Studio Code. We developed a new extension to create and review pull requests integrated directly into Visual Studio Code through a set of new Visual Studio Code extension APIs.
A more natural PR experience
Today when reviewing source code, many of us are forced to leave our editors to use a simplified web interface or third party review tool that presents changes in a different editor. This makes it easy to get a visual overview of the changes, but most of the time you don’t have full context of where the changes were made and how they affect surrounding source code. Being outside of your normal coding environment also means that you don’t have your favorite keyboard shortcuts, themes, and customizations. More importantly, it means that you don’t have an environment with the power to navigate the source code and validate that the changes you are reviewing actually work as expected.
The new pull request extension changes this with a new Pull Requests explorer inside the Source Control view in Visual Studio Code, where you can browse and interact with pull requests.
New open extension APIs
Our new pull requests experience is powered by a set of extension APIs that allow Visual Studio Code extension authors to create extensions that manage pull requests and their related metadata. This open extension model means that pull request providers work just like our existing source control providers and anyone can write an extension for Visual Studio Code that provides in-editor commenting and capabilities to review source code hosted on their platform. You can read more about the new APIs in our August 2018 release notes.
If you are interested, you can read more about how we are introducing new APIs, and the details for our extension API process here.
Going forward
We are excited about bringing pull requests into Visual Studio Code, as we believe it will simplify the way you review source code. Our GitHub extension is just the first example of integrating source control platform providers for code reviews in Visual Studio Code.
Please try out the public preview of GitHub Pull Requests for Visual Studio Code, and as always, we are eager to hear your feedback, so don’t hesitate in reaching to us on GitHub or @code on Twitter.
One more thing, today we are also releasing Azure DevOps, and the new Azure Pipelines extension on the GitHub Marketplace. For more information, visit https://aka.ms/azurecicd.
and on behalf of the Visual Studio Code team:
Remote Repositories
June 10, 2021 by Brigit Murtaugh, @BrigitMurtaugh, Eric Amodio, @eamodio
Note: The Remote Repositories extension has been renamed to GitHub Repositories since this blog post was published.
We’re excited to present the new Remote Repositories extension for Visual Studio Code! This is a new experience that we’ve been building in partnership with our friends at GitHub to enable working with source code repositories quickly and safely inside VS Code.
A quicker way to open source code repositories
In VS Code, we’ve offered integrated support for Git from the very beginning, and we’ve been supporting many other source control management (SCM) providers through extensions. This has allowed developers to clone and work with repositories directly within VS Code.
However, a large part of what developers do every day involves reading other people’s code: reviewing pull requests, browsing open-source repositories, experimenting with new technologies or projects, inspecting upstream dependencies to debug applications, etc. What all of these have in common is that as a first step, you usually clone the repository locally and then open the code in your favorite code editor (which we hope is VS Code!). Yet, cloning a repository takes time, may lead you to review an outdated version of the repo if you forget to pull, and can sometimes be a security risk if you’re unfamiliar with the code.
The new Remote Repositories extension, published by GitHub, makes the experience of opening source code repositories in VS Code instant and safe. With this, you can quickly browse, search, edit, and commit to any remote GitHub repository (and soon, Azure Repos) directly from within VS Code, no clone necessary!
You can work on as many repos as you like without having to save any source code on your machine. Remote Repositories saves you time and local disk space and empowers you to stay entirely within VS Code for all your source control tasks.
In this blog post, we’ll explore just how easy it is to get started with Remote Repositories, what you can do after opening your first remote repo, technical details supporting this virtual environment, and how you can provide us with feedback today.
Open your first remote repo in VS Code
Let’s open a remote repo in VS Code. First, make sure you have installed the Remote Repositories extension.
Currently, Remote Repositories supports GitHub repos, with support for Azure Repos coming soon. In this blog post, we’ll start by opening the VS Code repository (microsoft/vscode).
After installing the Remote Repositories extension, we get instant access to its Open Remote Repository command by clicking on the remote indicator in the lower left of VS Code (along with commands from any other Remote Development extensions you have installed):
If you haven’t logged into GitHub from VS Code before, you’ll be prompted to authenticate your GitHub account. Once logged in, search for a repo or PR, select the one you want, and you’ll be ready to go.
In the short video below, we search for and select the VS Code repo, VS Code reloads, and the repo’s contents loads as if we cloned it locally:
You’re able to explore and contribute to the repo without ever having to leave VS Code. You feel like you’re working on local code, using the familiar VS Code interface, and can use features like the VS Code Explorer, search, timeline view, quick open, and of course source control.
You’re now connected to what’s known as a virtual workspace (more information on virtual workspaces below); the remote indicator reads «GitHub.» When you hover over the remote indicator, you are notified that some features are not available while in a virtual workspace:
A virtual workspace is a special setup, and some features, like extensions, are disabled or have limited functionality. You can easily find out which extensions are disabled by clicking on the Some features link shown when hovering over the remote indicator.
Clicking the link shows which extensions are disabled and which ones have limited functionality. The limited functionality can be seen when hovering over the extension.
If you would like to manually enable an extension in a virtual workspace, you can use the extensions.supportVirtualWorkspaces setting in your user settings.json file.
Keep in mind that an extension might not be implemented to handle a virtual workspace without access to the local file system, and so the extension might not work as expected.
You opened a repo, what’s next?
With your repo open, Remote Repositories makes it easy to contribute to your project.
Simplified Git workflow that keeps your project up to date
Remote Repositories helps you stay on the latest version of your repos every time, without any complex Git commands.
Any time you open a new repo, you open the latest version. And whenever Remote Repositories detects there are new changes from GitHub, it will list how many commits you need to pull down in the Status bar:
and highlights the modified files in the Explorer:
When you commit changes, they’ll automatically show up on GitHub – you don’t need to push your changes or publish any new branches you create.
Create or check out pull requests
Remote Repositories works well with the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension, which allows you to review and manage pull requests and issues from GitHub directly in VS Code. Use the two extensions in parallel to quickly check out PRs and work on issues without ever having to clone code locally or leave VS Code.
You can make a change to your code, create a new branch and a pull request (PR) based on that change, and then check out the PR, all in a few clicks.
You can learn more about the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension in our Working with GitHub article.
Keep changes isolated to branches
You may need to switch between branches as you complete your work. In a typical environment, this can get tricky when you need to decide which changes to stash or commit.
Let’s explore how to push changes to a branch.
In the Status bar, select your current branch to open the list of branches, for example «main»:
Select + Create New Branch. and type a name for your branch:
You can then switch to that new branch:
The new branch will not include any changes from your previous branch.
Limitations
There are certain limitations while working with Remote Repositories:
We are just getting started on this journey, so expect the feature set to grow and the limitations to shrink as we continue development.
Continue working in a more powerful environment
Using Remote Repositories, VS Code operates in an environment where not all features are available because there is no physical file system. This is great to quickly get started browsing a repository, but what about when you’re ready to do some more «advanced» work, such as:
To move to more advanced workflows, Remote Repositories provides a way for you to «upgrade» your environment and continue your work there, picking up from wherever you currently are.
You’ll be presented with three options:
Now that we’ve explored how to use Remote Repositories in VS Code, we’d like to describe some of the technical details powering the experience, and how you can ensure your extension will work in a Remote Repository session.
Virtual file systems and workspaces
The core concepts powering this remote work are virtual file systems and virtual workspaces.
As an end user, all you need to know is which repo or PR you want to work on – VS Code will take care of the virtual file system and manage your workspace for you. As an extension developer, you’ll want to adopt the virtual file system API to ensure your extension behaves as expected.
How virtual file systems work
When you work in a traditional git workflow, you «git clone» a repo, and a copy is saved to your computer’s local file system. But when working with Remote Repositories, the code doesn’t live on your local computer; it’s still just on GitHub.
You work with the code through a virtual file system, which is an abstraction away from files that exist physically on disk. Virtual file systems can serve content from code hosts like GitHub, from cloud storage, or from databases and seamlessly provide these as files to the user in VS Code.
When you open a workspace on a virtual file system, it’s known as a virtual workspace. While working in a virtual workspace, you still get access to VS Code features, including extensions.
Ensuring your extension works in a virtual workspace
For extensions to behave properly, they must support a virtual file system.
When an extension has no code but is a pure color theme, keybinding, snippets, or grammar extension, then it can run in a virtual workspace and no adoption is necessary.
Extensions that run actual code, meaning it defines a main entry point, require inspection and possibly adoption.
The API support for virtual file systems is through the FileSystemProvider interface. A file system provider is registered for a new URI scheme (for example, vscode-vfs ), and resources on that file system will be represented by URIs using that schema ( vscode-vfs://github/microsoft/vscode/package.json ).
You can learn more about virtual file systems, workspaces, and how to implement them for extensions in the virtual workspaces extension authors guide.
Feedback & further reading
We are very excited for you to try out Remote Repositories and can’t wait for your feedback.
Please install the Remote Repositories extension. You can file any issues or feature requests or Tweet us your thoughts @code.
You can also check out our new YouTube video about how to use the Remote Repositories extension.
If you’re an extension author, check out the Virtual Workspace Support for Extension Authors guide and share any questions or feedback in our tracking issue. You can also join the Extension Authors community Slack group.
Brigit Murtaugh, VS Code Program Manager @BrigitMurtaugh
Eric Amodio, VS Code Principal Software Engineer @eamodio
Клонирование и использование репозитория GitHub в Visual Studio Code
Сведения о клонировании общедоступного репозитория из GitHub на локальный компьютер с помощью Visual Studio Code.
Клонирование репозитория
Чтобы приступить к работе, скачайте пример проекта, как описано ниже.
Если появится запрос на ввод URL-адреса репозитория, выберите параметр клонирования из GitHub и нажмите клавишу ВВОД.
Если поступает запрос на вход в GitHub, завершите процедуру входа.
Введите azure-samples/js-e2e-express-server в поле URL-адрес репозитория.
Выберите (или создайте) локальный каталог, в который нужно клонировать проект.
Когда появится уведомление с вопросом, нужно ли открыть клонированный репозиторий, выберите вариант Открыть.
Откройте интегрированный терминал из терминала —> новый терминал.
Клонируйте репозиторий с помощью следующей команды Git:
Измените терминал на новый подкаталог:
Затем откройте Visual Studio Code:
Инициализация нового репозитория
Если у вас еще нет репозитория GitHub, но вы хотите запустить проект локально, инициализируйте папку с помощью Git.
Создание ветви для изменений
Введите имя для новой ветви. Имя ветви будет отображатся в строке состояния.
Выберите имя ветви в строке состояния. Откроется палитра команд.
Строка состояния обычно находится в нижней части Visual Studio code.
Выберите в палитре команд элемент Создание ветви.
Введите имя для новой ветви.
Введите имя для новой ветви. Имя ветви будет отображатся в строке состояния.
Откройте интегрированный терминал из терминала —> новый терминал.
Создайте новую ветвь с именем MY-BRANCH с помощью следующей команды Git:
Фиксация изменений в локальной среде
После внесения изменений в ветвь зафиксируйте изменения.
Отправка локальной ветви в GitHub
В строке состояния Visual Studio Code выберите значок отправки справа от имени ветви.
Выберите имя удаленного расположения во всплывающем окне. Если вы имеете только одно удаленное расположение, вам не будет предложено выбрать имя такого расположения.
Щелкните значок «Система управления версиями» на панели действий.
Выберите имя удаленного расположения во всплывающем окне. Если вы имеете только одно удаленное расположение, вам не будет предложено выбрать имя такого расположения.
Просмотр выходных данных Git
Вы можете просмотреть команды Git, выполняемые при использовании расширения системы управления версиями. Это помогает выполнить отладку при сбое команды.
Щелкните значок «Система управления версиями» на панели действий.
Щелкните многоточие (. ) и выберите элемент Показать выходные данные Git.
средства Visual Studio Code для работы с Git и GitHub
При работе в Visual Studio Code с репозиторием необходимо использовать отдельные средства.
Visual studio code github
Develop code in Visual Studio without projects or solutions
You can open code from nearly any type of directory-based project into Visual Studio without the need for a solution or project file. This means you can, for example, clone a repo on GitHub, open it directly into Visual Studio, and begin developing, without having to create a solution or project. If needed, you can specify custom build tasks and launch parameters through simple JSON files.
After you open your code files in Visual Studio, Solution Explorer displays all the files in the folder. You can click on any file to begin editing it. In the background, Visual Studio starts indexing the files to enable IntelliSense, navigation, and refactoring features. As you edit, create, move, or delete files, Visual Studio tracks the changes automatically and continuously updates its IntelliSense index. Code will appear with syntax colorization and, in many cases, include basic IntelliSense statement completion.
[!NOTE] If you’re looking for information that’s specific to VS Code, visit the Getting started with Visual Studio Code page.
You can open code into Visual Studio in the following ways:
On the Visual Studio menu bar, choose File > Open > Folder, and then browse to the code location.
On the context (right-click) menu of a folder containing code, choose the Open in Visual Studio command.
Choose the Open Folder link on the start window.
If you are a keyboard user, press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+O in Visual Studio.
Open code from a cloned GitHub repo.
To open code from a cloned GitHub repo
The following example shows how to clone a GitHub repo and then open its code in Visual Studio. To follow this procedure, you must have a GitHub account and Git for Windows installed on your system. See Create a GitHub account to use with Visual Studio and Git for Windows for more information.
Go to the repo you want to clone on GitHub.
Choose the Clone or Download button and then choose the Copy to Clipboard button in the dropdown menu to copy the secure URL for the GitHub repo.
Use Git in Visual Studio
As of Visual Studio 2019 version 16.8, we introduced a new, streamlined Git interface that you can use to interact with your files on GitHub. To learn more, visit the Visual Studio version control docs.
Use Team Explorer in Visual Studio
You can still use Team Explorer in Visual Studio 2022 and in Visual Studio 2019 version 16.8 and later. However, you might find it easier to use the new Git experience. For more information, see How Visual Studio makes version control easy with Git.
In Visual Studio, choose the Team Explorer tab to open Team Explorer. If you don’t see the tab, open it from View > Team Explorer.
In Team Explorer, under the Local Git Repositories section, choose the Clone command and then paste the URL of the GitHub page into the text box.
Choose the Clone button to clone the project’s files to a local Git repository. Depending on the size of the repo, this process could take several minutes.
After the repo has been cloned to your system, in Team Explorer, choose the Open command on the context (right-click) menu of the newly cloned repo.
Choose the Show Folder View command to view the files in Solution Explorer.
You can now browse folders and files in the cloned repo, and view and search the code in the Visual Studio code editor, complete with syntax colorization and other features.
Run and debug your code
You can debug your code in Visual Studio without a project or solution! To debug some languages, you may need to specify a valid startup file in the codebase, such as a script, executable, or project. The drop-down list box next to the Start button on the toolbar lists all of the startup items that Visual Studio detects, as well as items you specifically designate. Visual Studio runs this code first when you debug your code.
Configuring your code to run in Visual Studio differs depending on what kind of code it is, and what the build tools are.
Codebases that use MSBuild
MSBuild-based codebases can have multiple build configurations that appear in the Start button’s drop-down list. Select the file that you want to use as the startup item, and then choose the Start button to begin debugging.
[!NOTE] For C# and Visual Basic codebases, you must have the .NET desktop development workload installed. For C++ codebases, you must have the Desktop development with C++ workload installed.
Codebases that use custom build tools
If your codebase uses custom build tools, then you must tell Visual Studio how to build your code using build tasks that are defined in a .json file. For more information, see Customize build and debug tasks.
Codebases that contain Python or JavaScript code
If your codebase contains Python or JavaScript code, you don’t have to configure any .json files, but you do have to install the corresponding workload. You must also configure the startup script:
Install the Node.js development or Python development workload by choosing Tools > Get Tools and Features, or by closing Visual Studio and running the Visual Studio Installer.
In Solution Explorer, on the right-click or context menu of a JavaScript or Python file, choose the Set as Startup Item command.
Choose the Start button to begin debugging.
Codebases that contain C++ code
For information about opening C++ code without solutions or projects in Visual Studio, see Open Folder projects for C++.
Codebases that contain a Visual Studio project
If your code folder contains a Visual Studio project, you can designate the project as the startup item.
The Start button’s text changes to reflect that the project is the startup item.
github/vscode-codeql
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
CodeQL for Visual Studio Code
This project is an extension for Visual Studio Code that adds rich language support for CodeQL. It’s used to find problems in code bases using CodeQL. It’s written primarily in TypeScript.
The extension is released. You can download it from the Visual Studio Marketplace.
To see what has changed in the last few versions of the extension, see the Changelog.
Project goals and scope
This project will track new feature development in CodeQL and, whenever appropriate, bring that functionality to the Visual Studio Code experience.
This project welcomes contributions. See CONTRIBUTING.md for details on how to build, install, and contribute.
The CodeQL extension for Visual Studio Code is licensed under the MIT License. The version of CodeQL used by the CodeQL extension is subject to the CodeQL Research Terms & Conditions.
When using the GitHub logos, be sure to follow the GitHub logo guidelines.
About
An extension for Visual Studio Code that adds rich language support for CodeQL
Supporting Remote Development and GitHub Codespaces
Visual Studio Code Remote Development allows you to transparently interact with source code and runtime environments sitting on other machines (whether virtual or physical). GitHub Codespaces is a service that expands these capabilities with managed cloud-hosted environments that are accessible from both VS Code and a browser-based editor.
To ensure performance, Remote Development and GitHub Codespaces both transparently run certain VS Code extensions remotely. However, this can have subtle impacts on how extensions need to work. While many extensions will work without any modifications, you may need to make changes so that your extension works properly in all environments, although these changes are often fairly minor.
This article summarizes what extension authors need to know about Remote Development and Codespaces including the extension architecture, how to debug your extension in remote workspaces or Codespaces, and recommendations on what to do if your extension does not work properly.
Architecture and extension kinds
In order to make working with Remote Development or Codespaces as transparent as possible to users, VS Code distinguishes two kinds of extensions:
UI Extensions: These extensions contribute to the VS Code user interface and are always run on the user’s local machine. UI Extensions cannot directly access files in the remote workspace, or run scripts/tools installed in that workspace or on the machine. Example UI Extensions include: themes, snippets, language grammars, and keymaps.
Workspace Extensions: These extensions are run on the same machine as where the workspace is located. When in a local workspace, Workspace Extensions run on the local machine. When in a remote workspace or when using Codespaces, Workspace Extensions run on the remote machine / environment. Workspace Extensions can access files in the workspace to provide rich, multi-file language services, debugger support, or perform complex operations on multiple files in the workspace (either directly or by invoking scripts/tools). While Workspace Extensions do not focus on modifying the UI, they can contribute explorers, views, and other UI elements as well.
When a user installs an extension, VS Code automatically installs it to the correct location based on its kind. If an extension can run as either kind, VS Code will attempt to choose the optimal one for the situation. UI Extensions are run in VS Code’s local Extension Host, while Workspace Extensions are run in a Remote Extension Host that sits in a small VS Code Server. To ensure the latest VS Code client features are available, the server needs to match the VS Code client version exactly. Therefore, the server is automatically installed (or updated) by the Remote Development or GitHub Codespaces extensions when you open a folder in a container, on a remote SSH host, using Codespaces, or in the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). (VS Code also automatically manages starting and stopping the server, so users aren’t aware of its presence.)
The VS Code APIs are designed to automatically run on the correct machine (either local or remote) when called from both UI or Workspace Extensions. However, if your extension uses APIs not provided by VS Code — such using Node APIs or running shell scripts — it may not work properly when run remotely. We recommend that you test that all features of your extension work properly in both local and remote workspaces.
Debugging Extensions
While you can install a development version of your extension in a remote environment for testing, if you encounter issues, you will likely want to debug your extension directly in a remote environment. In this section, we will cover how to edit, launch, and debug your extension in GitHub Codespaces, a local container, an SSH host, or in WSL.
Typically, your best starting point for testing is to use a remote environment that restricts port access (for example Codespaces, a container, or remote SSH hosts with a restrictive firewall) since extensions that work in these environments tend to work in less restrictive ones like WSL.
Debugging with GitHub Codespaces
Debugging your extension in GitHub Codespaces preview can be a great starting point since you can use both VS Code and the Codespaces browser-based editor for testing and troubleshooting. You can also use a custom development container if preferred.
Follow these steps:
Navigate to the repository that contains your extension on GitHub and open it in a codespace to work with it in a browser-based editor. You can also open the codespace in VS Code if you prefer.
While the default image for GitHub Codespaces should have all the needed prerequisites for most extensions, you can install any other required dependencies (for example, using yarn install or sudo apt-get ) in a new VS Code terminal window ( ⌃⇧` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+` ) ).
Finally, press F5 or use the Run and Debug view to launch the extension inside in the codespace.
Note: You will not be able to open the extension source code folder in the window that appears, but you can open a sub-folder or somewhere else in the codespace.
The extension development host window that appears will include your extension running in a codespace with the debugger attached to it.
Debugging in a custom development container
Follow these steps:
Select Remote-Containers: Add Development Container Configuration Files. or Codespaces: Add Development Container Configuration Files. from the Command Palette ( F1 ), and pick Node.js & TypeScript (or Node.js if you are not using TypeScript) to add the needed container configuration files.
Run Remote-Containers: Reopen Folder in Container or Codespaces: Add Development Container Configuration Files.. and in a moment, VS Code will set up the container and connect. You will now be able to develop your source code from inside the container just as you would in the local case.
Finally, press F5 or use the Run and Debug view to launch the extension inside this same container and attach the debugger.
Note: You will not be able to open the extension source code folder in the window that appears, but you can open a sub-folder or somewhere else in the container.
The extension development host window that appears will include your extension running in the container you defined in step 2 with the debugger attached to it.
Debugging using SSH
Once connected, either use File > Open. / Open Folder. to select the remote folder with your extension source code in it or select Git: Clone from the Command Palette ( F1 ) to clone it and open it on the remote host.
Install any required dependencies that might be missing (for example using yarn install or apt-get ) in a new VS Code terminal window ( ⌃⇧` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+` ) ).
Finally, press F5 or use the Run and Debug view to launch the extension inside on the remote host and attach the debugger.
Note: You will not be able to open the extension source code folder in the window that appears, but you can open a sub-folder or somewhere else on the SSH host.
The extension development host window that appears will include your extension running on the SSH host with the debugger attached to it.
Debugging using WSL
Follow these steps:
In the new window that appears, either use File > Open. / Open Folder. to select the remote folder with your extension source code in it or select Git: Clone from the Command Palette ( F1 ) to clone it and open it in WSL.
Tip: You can select the /mnt/c folder to access any cloned source code you have on the Windows side.
Install any required dependencies that might be missing (for example using apt-get ) in a new VS Code terminal window ( ⌃⇧` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+` ) ). You will at least want to run yarn install or npm install to ensure Linux versions of native Node.js dependencies are available.
Finally, press F5 or use the Run and Debug view to launch the extension and attach the debugger as you would locally.
Note: You will not be able to open the extension source code folder in the window that appears, but you can open a sub-folder or somewhere else in WSL.
The extension development host window that appears will include your extension running in WSL with the debugger attached to it.
Installing a development version of your extension
Anytime VS Code automatically installs an extension on an SSH host, inside a container or WSL, or through GitHub Codespaces, the Marketplace version is used (and not the version already installed on your local machine).
While this makes sense in most situations, you may want to use (or share) an unpublished version of your extension for testing without having to set up a debugging environment. To install an unpublished version of your extension, you can package the extension as a VSIX and manually install it into a VS Code window that is already connected to a running remote environment.
Follow these steps:
Tip: Once installed, you can use the Developer: Show Running Extensions command to see whether VS Code is running the extension locally or remotely.
Handling dependencies with remote extensions
Extensions can take dependencies on other extensions for APIs. For example:
Extension dependencies work fine when all the extensions are running locally and share the same extension host.
This may seem an unnecessarily strict constraint on the providing extension, but an extension that uses «api»: «none» only gives up the ability to return APIs from its activate method. Consumer extensions that execute on other extension hosts can still take a dependency on them and will be activated.
Common problems
VS Code’s APIs are designed to automatically run in the right location regardless of where your extension happens to be located. With this in mind, there are a few APIs that will help you avoid unexpected behaviors.
Incorrect execution location
If your extension is not functioning as expected, it may be running in the wrong location. Most commonly, this shows up as an extension running remotely when you expect it to only be run locally. You can use the Developer: Show Running Extensions command from the Command Palette ( F1 ) to see where an extension is running.
If the Developer: Show Running Extensions command shows that a UI extension is incorrectly being treated as a workspace extension or vice versa, try setting the extensionKind property in your extension’s package.json as described in the Extension Kinds section.
You can quickly test the effect of changing an extension’s kind with the remote.extensionKind setting. This setting is a map of extension IDs to extension kinds. For example, if you want to force the Azure Databases extension to be a UI extension (instead of its Workspace default) and the Debugger for Edge to be a workspace extension (instead of its UI default), you would set:
Using remote.extensionKind allows you to quickly test published versions of extensions without having to modify their package.json and rebuild them.
Persisting extension data or state
However, if your extension relies on current VS Code pathing conventions (for example
/.vscode ) or the presence of certain OS folders (for example
/.config/Code on Linux) to persist data, you may run into problems. Fortunately, it should be simple to update your extension and avoid these challenges.
If you are persisting simple key-value pairs, you can store workspace specific or global state information using vscode.ExtensionContext.workspaceState or vscode.ExtensionContext.globalState respectively. If your data is more complicated than key-value pairs, the globalStoragePath and storagePath properties provide «safe» paths that you can use to read/write global workspace-specific information in a file.
To use the APIs:
Sync user global state between machines
There is an example of using setKeysforSync in the Extension Capabilities topic.
Persisting secrets
Visual Studio Code does not provide a secret persistence mechanism itself, but many extension authors have opted to use the keytar node module for this purpose. For this reason, VS Code includes keytar and will automatically and transparently run it locally if referenced in a Workspace Extension. That way you can always take advantage of the local OS keychain / keyring / cert store and avoid the problems mentioned above.
Using the clipboard
Historically, extension authors have used Node.js modules such as clipboardy to interact with the clipboard. Unfortunately, if you use these modules in a Workspace Extension, they will use the remote clipboard instead of the user’s local one. The VS Code clipboard API solves this problem. It is always run locally, regardless of the type of extension that calls it.
To use the VS Code clipboard API in an extension:
Opening something in a local browser or application
Spawning a process or using a module like opn to launch a browser or other application for particular URI can work well for local scenarios, but Workspace Extensions run remotely, which can cause the application to launch on the wrong side. VS Code Remote Development partially shims the opn node module to allow existing extensions to function. You can call the module with a URI and VS Code will cause the default application for the URI to appear on the client side. However, this is not a complete implementation, as options are not supported and a child_process object is not returned.
Instead of relying on a third-party node module, we recommend that extensions take advantage of the vscode.env.openExternal method to launch the default registered application on your local operating system for given URI. Even better, vscode.env.openExternal does automatic localhost port forwarding! You can use it to point to a local web server on a remote machine or codespace and serve up content even if that port is blocked externally.
Note: Currently the forwarding mechanism in the Codespaces browser-based editor only supports http and https requests. However, you can interact with any TCP connection when connecting to a codespace from VS Code.
To use the vscode.env.openExternal API:
Forwarding localhost
While the localhost forwarding mechanism in vscode.env.openExternal is useful, there may also be situations where you want to forward something without actually launching a new browser window or application. This is where the vscode.env.asExternalUri API comes in.
Note: Currently the forwarding mechanism in the Codespaces browser-based editor only supports http and https requests. However, you can interact with any TCP connection when connecting to a codespace from VS Code.
To use the vscode.env.asExternalUri API:
It is important to note that the URI that is passed back by the API may not reference localhost at all, so you should use it in its entirety. This is particularly important for the Codespaces browser-based editor, where localhost cannot be used.
Callbacks and URI handlers
The vscode.window.registerUriHandler API allows your extension to register a custom URI that, if opened in a browser, will fire a callback function in your extension. A common use case for registering a URI handler is when implementing a service sign in with an OAuth 2.0 authentication provider (for example, Azure AD). However, it can be used for any scenario where you want an external application or the browser to send information to your extension.
The Remote Development and Codespaces extensions in VS Code will transparently handle passing the URI to your extension regardless of where it is actually running (local or remote). However, vscode:// URIs will not work with the Codespaces browser-based editor since opening these URIs in something like a browser would attempt to pass them to the local VS Code client rather than the browser-based editor. Fortunately, this can be easily remedied by using the vscode.env.asExternalUri API.
Let’s use a combination of vscode.window.registerUriHandler and vscode.env.asExternalUri to wire up an example OAuth authentication callback:
When running this sample in VS Code, it wires up a vscode:// or vscode-insiders:// URI that can be used as a callback for an authentication provider. When running in the Codespaces browser-based editor, it wires up a https://*.github.dev URI without any code changes or special conditions.
While OAuth is outside the scope of this document, note that if you adapted this sample to a real authentication provider, you may need to build a proxy service in front of the provider. This is because not all providers allow vscode:// callback URIs and others do not allow wildcard host names for callbacks over HTTPS. We also recommend using an OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code with PKCE flow wherever possible (e.g. Azure AD supports PKCE) to improve the security of the callback.
Varying behaviors when running remotely or in the Codespaces browser editor
Next, you can use the three APIs as follows:
Communicating between extensions using commands
Some extensions return APIs as a part of their activation that are intended for use by other extensions (via vscode.extension.getExtension(extensionName).exports ). While these will work if all extensions involved are on the same side (either all UI Extensions or all Workspace Extensions), these will not work between UI and Workspace Extensions.
Fortunately, VS Code automatically routes any executed commands to the correct extension regardless of its location. You can freely invoke any command (including those provided by other extensions) without worrying about impacts.
If you have a set of extensions that need to interact with one another, exposing functionality using a private command can help you avoid unexpected impacts. However, any objects you pass in as parameters will be «stringified» ( JSON.stringify ) before being transmitted, so the object cannot have cyclic references and will end up as a «plain old JavaScript object» on the other side.
See the command API guide for details on working with commands.
Using the Webview API
Like the clipboard API, the Webview API is always run on the user’s local machine or in the browser, even when used from a Workspace Extension. This means that many webview-based extensions should just work, even when used in remote workspaces or Codespaces. However, there are some considerations to be aware of so that your webview extension works properly when run remotely.
Always use asWebviewUri
You should use the asWebviewUri API to manage extension resources. Using this API instead of hard coding vscode-resource:// URIs is required to ensure the Codespaces browser-based editor works with your extension. See the Webview API guide for details, but here is a quick example.
You can use the API in your content as follows:
Use the message passing API for dynamic webview content
The VS Code webview includes a message passing API that allows you to dynamically update your webview content without the use of a local web server. Even if your extension is running some local web services that you want to interact with to update webview content, you can do this from the extension itself rather than directly from your HTML content.
This is an important pattern for Remote Development and GitHub Codespaces to ensure your webview code works in both VS Code and the Codespaces browser-based editor.
Why message passing instead of a localhost web server?
The alternate pattern is to serve up web content in an iframe or have webview content directly interact with a localhost server. Unfortunately, by default, localhost inside a webview will resolve to a developer’s local machine. This means that for a remotely running workspace extension, the webviews it creates would not be able to access local servers spawned by the extension. Even if you use the IP of the machine, the ports you are connecting to will typically be blocked by default in a cloud VM or a container. Even if this worked in VS Code, it would not work in the Codespaces browser-based editor.
If possible, you should avoid doing this since it complicates your extension significantly. Message passing API can enable the same type of user experience without these types of headaches. The extension itself will be running in VS Code Server on the remote side, so it can transparently interact with any web servers your extension starts up as a result of any messages passed to it from the webview.
Workarounds for using localhost from a webview
If you can’t use the message passing API for some reason, there are two options that will work with the Remote Development and GitHub Codespaces extensions in VS Code.
VS Code 1.40 introduced the vscode.env.asExternalUri API to allow extensions to forward local http and https requests remotely in a programmatic way. You can use this same API to forward requests to localhost web servers from the webview when your extension is running in VS Code.
Use the API to get a full URI for the iframe and add it to your HTML. You will also need to enable scripts in your webview and add a CSP to your HTML content.
If you do not intend to support the Codespaces browser-based editor, you can use the portMapping option available in the webview API. (This approach will also work with Codespaces from the VS Code client, but not in the browser).
To use a port mapping, pass in a portMapping object when you create your webview:
In this example, in both the remote and local cases, any requests made to http://localhost:3000 will automatically be mapped to the dynamic port an Express.js web server is running on.
Using native Node.js modules
To solve this problem:
You can find the «modules» version VS Code uses by going to Help > Developer Tools and typing process.versions.modules in the console. However, to make sure native modules work seamlessly in different Node.js environments, you may want to compile the native modules against all possible Node.js «modules» versions and platforms you want support (Electron Node.js, official Node.js Windows/Darwin/Linux, all versions). The node-tree-sitter module is a good example of a module that does this well.
Supporting non-x86_64 hosts or Alpine Linux containers
If your extension is purely written in JavaScript/TypeScript, you may not need to do anything to add support for other processor architectures or the musl based Alpine Linux to your extension.
However, if your extension works on Debian 9+, Ubuntu 16.04+, or RHEL / CentOS 7+ remote SSH hosts, containers, or WSL, but fails on supported non-x86_64 hosts (for example ARMv7l) or Alpine Linux containers, the extension may include x86_64 glibc specific native code or runtimes that will fail on these architectures/operating systems.
For example, your extension may only include x86_64 compiled versions of native modules or runtimes. For Alpine Linux, the included native code or runtimes may not work due to fundamental differences between how libc is implemented in Alpine Linux ( musl ) and other distributions ( glibc ).
To resolve this problem:
If you are dynamically acquiring compiled code, you can add support by detecting non-x86_64 targets using process.arch and downloading versions compiled for the right architecture. If you are including binaries for all supported architectures inside your extension instead, you can use this logic to use the correct one.
For Alpine Linux, you can detect the operating system using await fs.exists(‘/etc/alpine-release’) and once again download or use the correct binaries for a musl based operating system.
If you’d prefer not to support these platforms, you can use the same logic to provide a good error message instead.
It is important to note that some third-party npm modules include native code that can cause this problem. So, in some cases you may need to work with the npm module author to add additional compilation targets.
Avoid using Electron modules
Use base Node.js modules or modules in your extension VSIX to avoid these problems. If you absolutely have to use an Electron module, be sure to have a fallback if the module is missing.
The example below will use the Electron original-fs node module if found, and fall back to the base Node.js fs module if not.
Try to avoid these situations whenever possible.
Known issues
There are a few extension problems that could be resolved with some added functionality for Workspace Extensions. The following table is a list of known issues under consideration:
Источники:
- http://vscode.github.com/
- http://zencod.ru/articles/first-step-git/
- http://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/github
- http://adamtheautomator.com/visual-studio-code-github-setup/
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode/wiki/How-to-Contribute
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/javascript/how-to/with-visual-studio-code/clone-github-repository
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/azure/developer/javascript/how-to/with-visual-studio-code/clone-github-repository
- http://powerupwebdev.medium.com/deploy-your-projects-on-github-using-visual-studio-code-and-git-5f7221b272ca
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/contribute/get-started-setup-tools
- http://docs.github.com/en/codespaces/developing-in-codespaces/using-github-codespaces-in-visual-studio-code
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/46877667/how-to-add-a-new-project-to-github-using-vs-code
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode/blob/main/README.md
- http://code.visualstudio.com/docs/remote/codespaces
- http://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=GitHub.vscode-pull-request-github
- http://code.visualstudio.com/docs/editor/versioncontrol
- http://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=GitHub.remotehub
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-docs/blob/main/docs/editor/versioncontrol.md
- http://github.com/dotnet/docs/blob/main/docs/core/tutorials/with-visual-studio-code.md
- http://github.com/github/VisualStudio
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-pull-request-github
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-docs
- http://visualstudio.microsoft.com/vs/github/
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/version-control/git-with-visual-studio?view=vs-2019
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/version-control/git-with-visual-studio?view=vs-2022
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode/blob/main/.devcontainer/README.md
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/wiki/
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-docs/blob/main/docs/nodejs/reactjs-tutorial.md
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode/wiki
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-python
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode/wiki
- http://docs.github.com/en/copilot/getting-started-with-github-copilot/getting-started-with-github-copilot-in-visual-studio-code
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/ide/work-with-github-accounts?view=vs-2022
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode?
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-remote-release
- http://github.com/microsoft/vscode-mssql
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-docs/
- http://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/ide/work-with-github-accounts?view=vs-2019
- http://habr.com/ru/sandbox/112936/
- http://github.com/Microsoft/vscode-python
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/visualstudio/version-control/git-with-visual-studio?view=vs-2019
- http://www.azuredevopslabs.com/labs/azuredevops/github/
- http://code.visualstudio.com/blogs/2018/09/10/introducing-github-pullrequests
- http://code.visualstudio.com/blogs/2021/06/10/remote-repositories
- http://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/azure/developer/javascript/how-to/with-visual-studio-code/clone-github-repository?tabs=create-repo-command-palette,initialize-repo-activity-bar,create-branch-command-palette,commit-changes-command-palette,push-command-palette
- http://github.com/MicrosoftDocs/visualstudio-docs/blob/main/docs/ide/develop-code-in-visual-studio-without-projects-or-solutions.md
- http://github.com/github/vscode-codeql
- http://code.visualstudio.com/api/advanced-topics/remote-extensions